At its core, the catalytic prowess of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) stems from their unique combination of physical structure, high surface area, and tunable electronic properties. Unlike traditional bulk materials, CNTs can function in two distinct capacities: either as a metal-free catalyst themselves or as an exceptionally effective support that enhances the performance of other catalytic particles. This dual nature makes them a highly versatile platform for a wide range of chemical reactions.
The key insight is that CNTs are not just passive scaffolds. Their value lies in their active participation in the catalytic cycle, either by directly providing reaction sites or by electronically modifying the catalyst particles they support, leading to performance that often surpasses conventional materials.

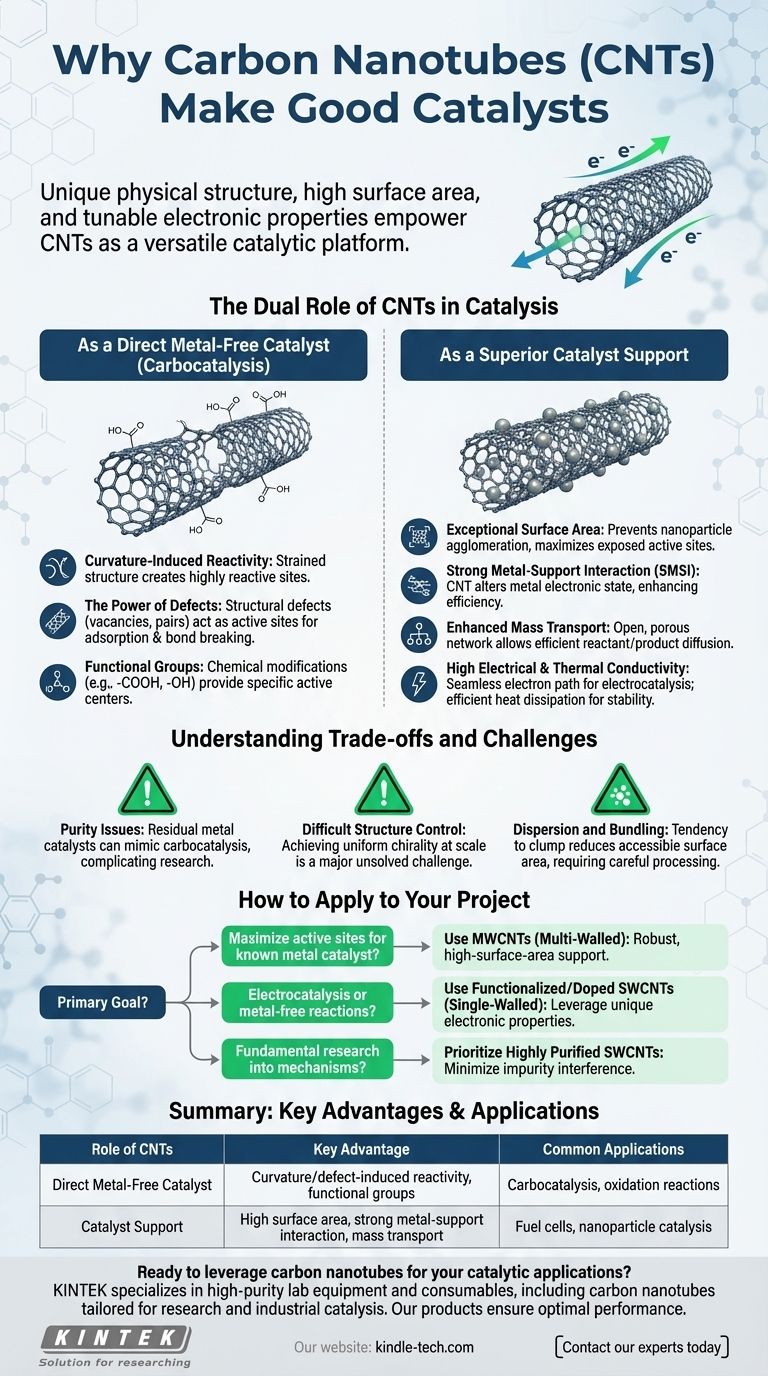
The Dual Role of CNTs in Catalysis
To understand why CNTs are effective, we must first distinguish between their two primary functions in a catalytic system. They can be the main actor or a game-changing supporting cast member.
As a Direct Metal-Free Catalyst
The notion that a pure carbon structure can catalyze reactions is known as carbocatalysis. The chemical inertness of a "perfect" graphene sheet is overcome in nanotubes.
- Curvature-Induced Reactivity: The strain required to roll a graphene sheet into a tube alters the
sp2hybridization of the carbon atoms. This change in electronic structure creates sites with higher reactivity compared to a flat plane. - The Power of Defects: Structural defects, such as vacancies (missing atoms) or pentagon-heptagon pairs, are not flaws but are often the true active sites. These sites have a different local electron density and can readily adsorb reactant molecules and facilitate bond breaking/formation.
- Functional Groups: CNTs can be chemically modified, or "functionalized," with groups like carboxyl (-COOH) or hydroxyl (-OH). These groups act as specific, well-defined active centers for reactions like esterification or oxidation.
As a Superior Catalyst Support
More commonly, CNTs are used as a support material for metal nanoparticles (like Platinum, Palladium, or Gold). In this role, they dramatically outperform traditional supports like activated carbon or alumina.
- Exceptional Surface Area: CNTs possess an enormous surface area-to-volume ratio. This allows for a very high dispersion of metal nanoparticles, preventing them from clumping together (agglomerating) and maximizing the number of active metal sites exposed to reactants.
- Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI): There is a significant electronic interaction between the CNT and the metal particle it holds. The CNT can donate or withdraw electron density from the metal, altering its electronic state and making it a more efficient catalyst.
- Enhanced Mass Transport: The open, porous network formed by tangled CNTs allows for efficient diffusion of reactants to the catalytic sites and products away from them, preventing bottlenecks that can slow down a reaction.
- High Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: For electrocatalysis (e.g., in fuel cells), the CNT's excellent electrical conductivity provides a seamless path for electrons. Its high thermal conductivity also helps dissipate heat from highly exothermic reactions, improving catalyst stability and lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, using CNTs in catalysis is not without its difficulties. An objective assessment requires acknowledging their limitations.
The Problem of Purity
Most commercial CNTs are synthesized using metal catalysts (e.g., Iron, Cobalt, Nickel). Removing these residual metal impurities is a significant challenge. The presence of even trace amounts of metal can create catalytic activity, making it difficult to determine if the observed effect is from the CNT itself (carbocatalysis) or the hidden impurity.
Controlling Structure is Difficult
The electronic properties of a CNT are dictated by its chirality—the angle at which the graphene sheet is rolled up. This determines if the tube is metallic or semiconducting. As of today, synthesizing a batch of CNTs with a single, uniform chirality at scale is a major, largely unsolved challenge. Most applications must therefore work with a mixture of different types, leading to averaged, and sometimes inconsistent, performance.
Dispersion and Bundling
Due to strong attractive forces (van der Waals forces), CNTs tend to clump together in tight bundles. This bundling severely reduces the accessible surface area, negating one of their key advantages. Achieving a stable, uniform dispersion of CNTs in a solvent or matrix without damaging their structure is a critical but often complex processing step.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The decision to use CNTs should be driven by a clear understanding of your specific goal and the trade-offs involved.
- If your primary focus is maximizing active sites for a known metal catalyst: Use multi-walled CNTs (MWCNTs) as a robust, high-surface-area support. They are generally more affordable and easier to handle for creating highly dispersed nanoparticle systems.
- If your primary focus is electrocatalysis or exploring metal-free reactions: Use functionalized or heteroatom-doped (e.g., nitrogen-doped) single-walled CNTs (SWCNTs). This leverages their unique electronic properties and defect-driven reactivity.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research into catalytic mechanisms: Prioritize highly purified SWCNTs to minimize interference from residual metal catalysts. This is essential for isolating and proving the intrinsic catalytic activity of the carbon nanostructure itself.
By treating carbon nanotubes as a tunable catalytic platform rather than a simple inert material, you can strategically harness their properties to solve your specific chemical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Role of CNTs | Key Advantage | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Metal-Free Catalyst | Curvature/defect-induced reactivity, functional groups | Carbocatalysis, oxidation reactions |
| Catalyst Support | High surface area, strong metal-support interaction, mass transport | Fuel cells, nanoparticle catalysis |
Ready to leverage carbon nanotubes for your catalytic applications? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including carbon nanotubes tailored for research and industrial catalysis. Our products ensure optimal performance, whether you're developing metal-free catalysts or enhancing supported nanoparticle systems. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with precision materials and reliable solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods



















