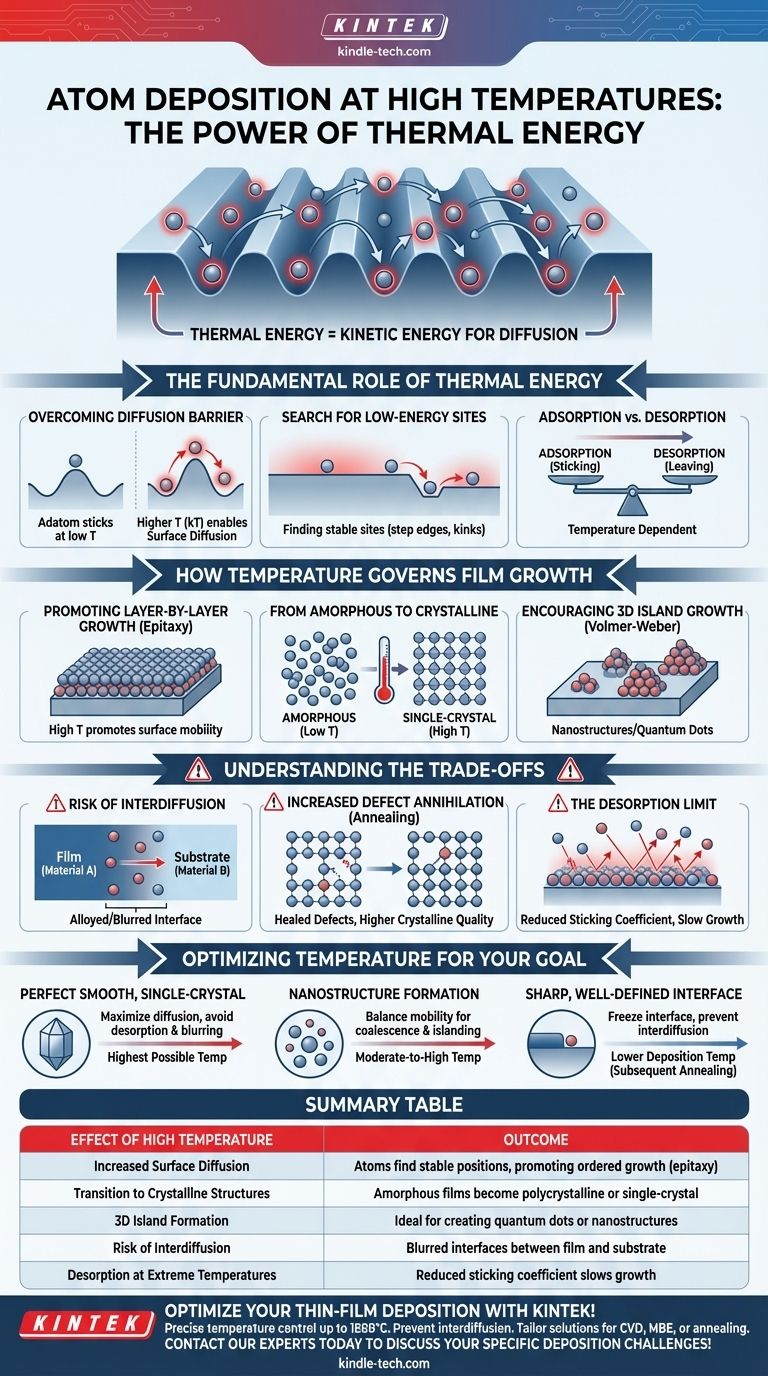
At higher temperatures, depositing atoms gain significant thermal energy, which dramatically increases their mobility on the surface. This allows them to move around, or "diffuse," overcoming energy barriers to find and settle into more stable, ordered positions. This process is fundamental to creating high-quality, crystalline thin films rather than the disordered, amorphous structures that form at low temperatures.
The core effect of higher temperature during atom deposition is to provide the kinetic energy needed for the system to approach its thermodynamic equilibrium. This allows atoms to self-organize into lower-energy, more perfect structures, but introduces trade-offs like interdiffusion and material desorption.

The Fundamental Role of Thermal Energy
The final structure of a deposited film is a competition between the rate of atom arrival and the rate at which those atoms can rearrange themselves. Temperature is the primary control for this rearrangement.
Overcoming the Diffusion Barrier
Every atom that lands on a surface, known as an adatom, faces small energy barriers to move from one lattice site to the next. At low temperatures, the adatom lacks the energy to overcome these barriers and essentially sticks where it lands.
Higher temperature provides this energy (often expressed as kT), allowing adatoms to hop from site to site in a process called surface diffusion.
The Search for Low-Energy Sites
A flat, perfect surface is actually a high-energy state. The system can lower its total energy if the adatoms find more stable binding sites, such as step edges, kink sites, or joining an existing island of other adatoms.
Increased surface diffusion gives adatoms the time and mobility to explore the surface and locate these energetically favorable positions before they are buried by subsequent arriving atoms.
Adsorption vs. Desorption
There is an upper limit to this effect. If the temperature is too high, an adatom may gain enough energy not just to diffuse, but to leave the surface entirely and return to the vapor phase.
This process is called desorption. The balance between atoms sticking (adsorption) and atoms leaving (desorption) determines the film's growth rate and is highly temperature-dependent.
How Temperature Governs Film Growth
The increased mobility at higher temperatures directly influences the way the film assembles, known as the "growth mode."
Promoting Layer-by-Layer Growth
For creating atomically smooth, continuous films (epitaxial growth), the ideal mode is layer-by-layer (Frank-van der Merwe). This requires atoms to diffuse across the surface and complete one full layer before the next one begins to form.
High temperature promotes this by providing the necessary surface mobility, assuming the adatoms are more strongly attracted to the substrate than to each other.
From Amorphous to Crystalline
At very low temperatures, atoms have no mobility and the resulting film is amorphous, with a disordered atomic structure similar to glass.
As temperature increases, atoms gain enough energy to arrange themselves into ordered lattices, forming a polycrystalline (many small crystals) or even a single-crystal film. This transition is one of the most critical applications of temperature control.
Encouraging 3D Island Growth
In systems where the depositing atoms are more strongly bonded to each other than to the substrate, higher temperatures will still increase mobility. However, instead of spreading out, the adatoms will diffuse to find each other, forming distinct three-dimensional islands.
This is known as Volmer-Weber growth and is a common method for intentionally creating nanostructures or quantum dots.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using higher temperatures is not a universal solution and involves critical compromises that must be managed.
Risk of Interdiffusion
When depositing a film (Material A) onto a substrate (Material B) at high temperatures, the atoms at the interface can become mobile enough to cross it. Substrate atoms can diffuse up into the film, and film atoms can diffuse down into the substrate.
This creates an alloyed or blurred interface, which can be detrimental for devices that rely on sharp, distinct junctions, like in semiconductors and optics.
Increased Defect Annihilation
On the positive side, the increased atomic mobility at high temperatures can help "heal" the growing film. Point defects like vacancies or misaligned atoms can be resolved as the atoms have enough energy to shift into their correct lattice positions.
This process, known as annealing, leads to higher crystalline quality and fewer defects in the final film.
The Desorption Limit
As noted earlier, if the substrate temperature is too high, the sticking coefficient (the probability an arriving atom will stick to the surface) drops significantly.
This can drastically slow or even halt the film's growth, as more atoms desorb than adsorb, making the process highly inefficient.
Optimizing Temperature for Your Goal
The "correct" temperature is entirely dependent on the desired outcome for your material. You must balance the positive effects of atomic mobility against the negative consequences.
- If your primary focus is a perfectly smooth, single-crystal film: Use the highest possible temperature that allows for maximum surface diffusion without causing significant desorption or interface blurring.
- If your primary focus is the formation of distinct nanostructures: Use a moderate-to-high temperature in a system that favors island growth to give atoms the mobility they need to find each other and coalesce.
- If your primary focus is a sharp, well-defined interface: Use a lower deposition temperature to "freeze" the interface and prevent interdiffusion, even if this results in a less perfect crystal structure that may require subsequent annealing.
Ultimately, temperature is the most powerful lever for controlling the kinetics of surface processes to achieve your desired material structure.
Summary Table:
| Effect of High Temperature | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Increased Surface Diffusion | Atoms find stable positions, promoting ordered growth (epitaxy). |
| Transition to Crystalline Structures | Amorphous films become polycrystalline or single-crystal. |
| 3D Island Formation | Ideal for creating quantum dots or nanostructures. |
| Risk of Interdiffusion | Blurred interfaces between film and substrate. |
| Desorption at Extreme Temperatures | Reduced sticking coefficient slows growth. |
Optimize your thin-film deposition process with KINTEK!
Whether you're growing epitaxial layers for semiconductors or engineering nanostructures, precise temperature control is critical. KINTEK's advanced lab equipment ensures the thermal stability and uniformity needed to achieve perfect crystalline films, minimize defects, and maintain sharp interfaces.
Let our expertise in laboratory heating solutions enhance your research:
- Achieve superior film quality with precise temperature control up to 1800°C.
- Prevent interdiffusion with our uniform heating systems.
- Tailor solutions for CVD, MBE, or annealing processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific deposition challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















