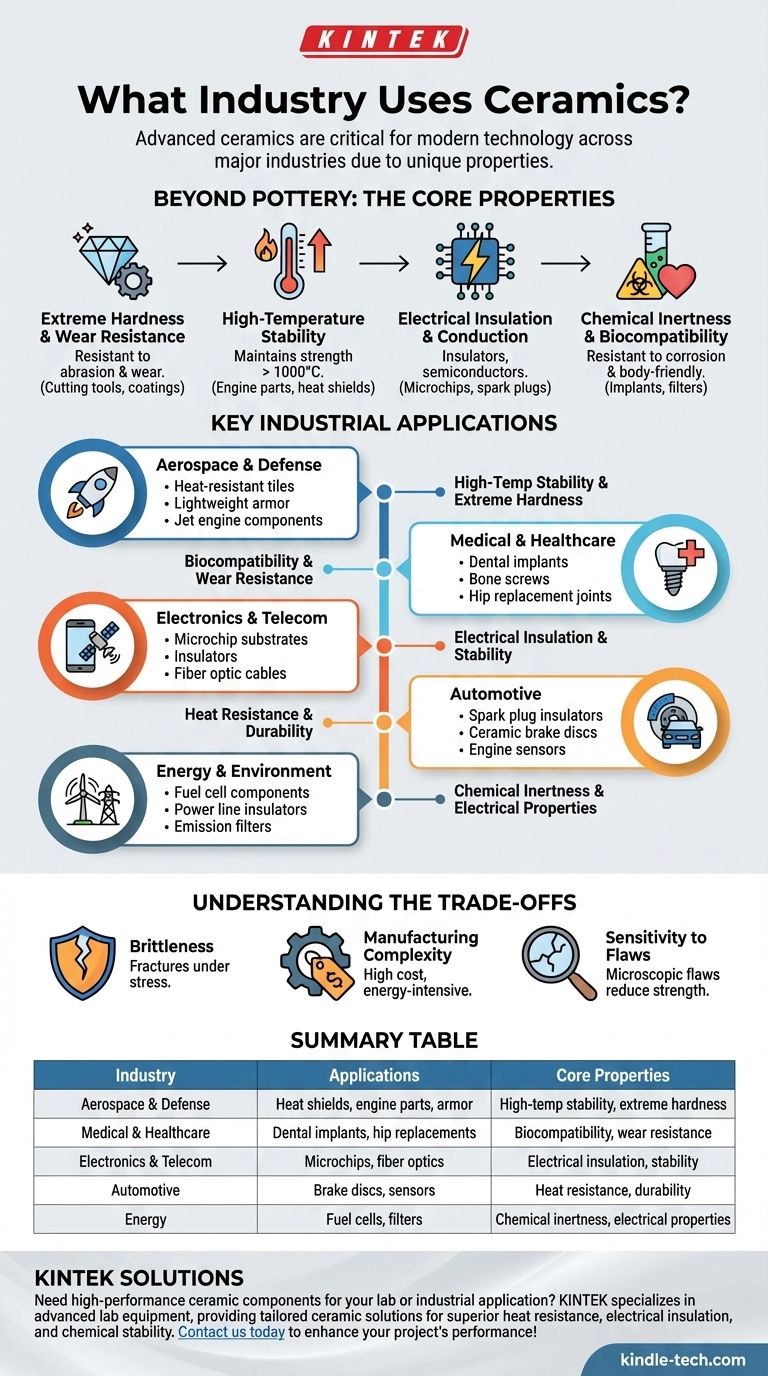
In short, virtually every major industry uses ceramics. From the aerospace and medical fields to electronics and energy, advanced ceramic materials are critical components that enable modern technology to function under extreme conditions where traditional materials like metals and plastics would fail.
The core reason for this widespread use is not a single feature, but a unique and powerful combination of properties. Advanced ceramics are chosen for their exceptional hardness, stability at high temperatures, chemical inertness, and specific electrical properties, making them irreplaceable in a vast range of demanding applications.

Beyond Pottery: The Core Properties of Advanced Ceramics
To understand where and why ceramics are used, you must first understand their fundamental characteristics. These materials are engineered to solve specific problems that other materials cannot.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramics like silicon carbide and tungsten carbide are among the hardest materials known. This property makes them exceptionally resistant to abrasion and wear.
This is why they are essential for industrial cutting tools, abrasive powders, and wear-resistant coatings on machine parts.
High-Temperature Stability
Unlike metals that soften and plastics that melt, many ceramics maintain their strength and structure at incredibly high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C (1800°F).
This thermal stability is critical for applications like furnace linings, jet engine turbine blades, and heat shields for spacecraft re-entry.
Electrical Insulation and Conduction
Most ceramics are excellent electrical insulators, meaning they do not conduct electricity. This is fundamental to their use in electronics.
They form the insulating base for microchips (substrates) and are used for spark plug insulators. However, some advanced ceramics can be engineered to be semiconductors, superconductors, or sensors.
Chemical Inertness and Biocompatibility
Ceramics are highly resistant to chemical attack from acids, bases, and other corrosive environments.
Furthermore, many are biocompatible, meaning they do not provoke an immune response in the human body. This allows them to be used for medical implants like dental crowns and hip replacements.
A Survey of Key Industrial Applications
These core properties directly translate into mission-critical applications across numerous sectors.
Aerospace and Defense
In this industry, materials must perform under the most extreme conditions. Ceramics are used for heat-resistant tiles on space shuttles, lightweight armor plating, and components within jet engines that must withstand immense heat and stress.
Medical and Healthcare
The biocompatibility and hardness of ceramics make them ideal for the human body. They are used for durable dental implants, bone screws, and the ball heads in hip replacement joints, where low friction and high wear resistance are essential.
Electronics and Telecommunications
The modern digital world is built on ceramics. They serve as insulators, substrates for circuit boards, and components in capacitors and sensors. Fiber optic cables, the backbone of the internet, are also a form of glass ceramic.
Automotive and Transportation
Ceramics are crucial for efficiency and safety. They are found in the insulators of spark plugs, high-performance ceramic brake discs that don't fade at high temperatures, and various sensors throughout the engine and exhaust systems.
Energy and Environment
In the energy sector, ceramics are used as electrical insulators for high-voltage power lines and as components in solid oxide fuel cells. Their ability to withstand corrosive environments also makes them ideal for filters in emission control systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite their remarkable strengths, ceramics are not a universal solution. Their limitations define where they cannot or should not be used.
The Challenge of Brittleness
The most significant drawback of most ceramics is their brittleness. Unlike metals, which bend or deform under stress, ceramics tend to fracture catastrophically with little to no warning.
This property requires careful engineering and design to manage stress concentrations and avoid impact loading.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Ceramics are extremely hard, which makes them very difficult to machine or shape after they have been fired.
The manufacturing processes are often energy-intensive and require precise control, leading to higher costs compared to many metals and plastics.
Sensitivity to Flaws
The strength of a ceramic component can be dramatically reduced by the presence of microscopic flaws, such as pores or cracks, introduced during manufacturing.
This necessitates rigorous quality control and non-destructive testing to ensure reliability, particularly in critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material requires understanding these trade-offs. The decision to use a ceramic is almost always driven by a performance requirement that no other material can meet.
- If your primary focus is performance at extreme temperatures or high wear: An advanced ceramic is often the only viable choice for components like engine parts, cutting tools, or furnace linings.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or specific electronic properties: Ceramics provide the stable, non-conductive base required for nearly all modern microelectronics.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and chemical resistance: Bioceramics are the industry standard for medical implants and components used in harsh chemical processing.
Ultimately, ceramics are enabling materials that push the boundaries of what is technologically possible.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Ceramic Applications | Core Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Heat shields, jet engine components, armor | High-temperature stability, extreme hardness |
| Medical & Healthcare | Dental implants, hip replacements, bone screws | Biocompatibility, wear resistance |
| Electronics & Telecom | Microchip substrates, insulators, fiber optics | Electrical insulation, stability |
| Automotive | Brake discs, spark plugs, sensors | Heat resistance, durability |
| Energy | Fuel cells, power line insulators, filters | Chemical inertness, electrical properties |
Need high-performance ceramic components for your lab or industrial application? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored ceramic solutions that offer superior heat resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical stability. Whether you're in R&D, manufacturing, or quality control, our expertise ensures you get the right materials for extreme conditions. Contact us today to discuss how our ceramic products can enhance your project's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia grinding balls recommended for sulfide solid electrolytes? Essential Tips for High Purity Milling
- What are the technical advantages of using zirconia (ZrO2) grinding balls? Enhancing Silicon Composite Anode Performance
- Why are 3mm zirconia grinding balls selected for Na3FePO4CO3 synthesis? Optimize Energy and Purity
- Why are high-purity zirconia grinding balls recommended for LATP ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and High Conductivity.
- What is the purpose of using high-hardness zirconia grinding balls? Ensure Purity & Power in Electrolyte Milling



















