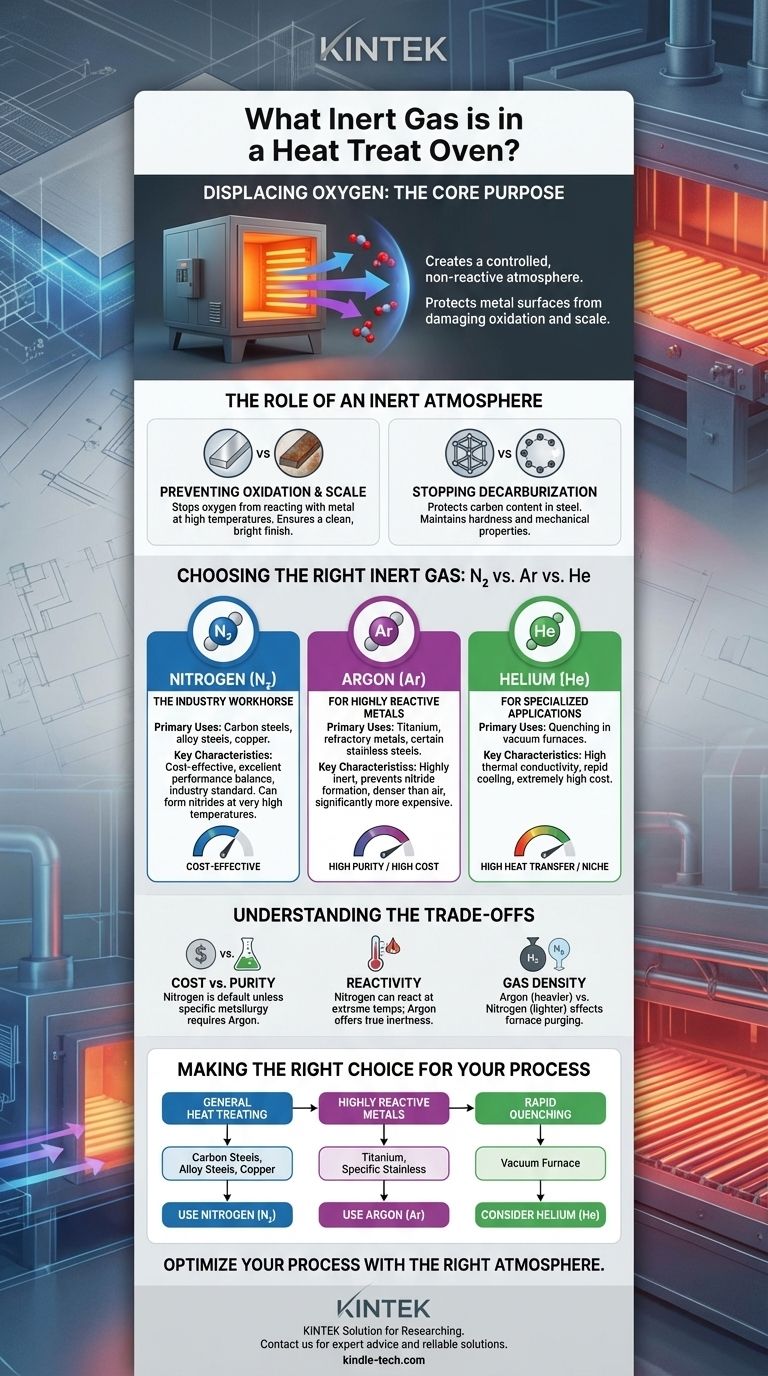
The most common inert gases used in heat treating ovens are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar). Nitrogen is the industry standard for a vast range of applications due to its cost-effectiveness, while Argon is used for more sensitive, reactive metals that require a higher degree of inertness.
The core purpose of using an inert gas is not about the gas itself, but about what it displaces: oxygen. By creating a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere, these gases protect the metal's surface from damaging chemical reactions like oxidation at high temperatures.

The Role of an Inert Atmosphere in Heat Treating
When metals are heated to the high temperatures required for processes like annealing, hardening, or brazing, they become highly susceptible to reacting with the surrounding air. An inert atmosphere is a protective shield against these reactions.
Preventing Oxidation and Scale
At elevated temperatures, oxygen readily reacts with the surface of most metals. This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a layer of brittle, flaky scale.
Using an inert gas purges the furnace of oxygen, preventing scale from forming. This results in a clean, bright finish, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning operations like sandblasting or chemical pickling.
Stopping Decarburization
For carbon steels, oxygen in the atmosphere can react with the carbon near the metal's surface. This process, decarburization, leaches carbon out of the steel.
Since carbon is the primary element that gives steel its hardness, decarburization creates a soft, weak surface layer. An inert atmosphere protects the carbon content, ensuring the part maintains its intended mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Inert Gas
While both Nitrogen and Argon are inert, their properties and cost dictate their use in different applications.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Industry Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most widely used atmosphere gas in heat treating. It offers an excellent balance of performance and cost.
It is suitable for the vast majority of processes involving carbon steels, alloy steels, and copper. Nitrogen is typically supplied in liquid form for high-volume use or generated on-site from compressed air.
Argon (Ar): For Highly Reactive Metals
Argon is chemically more inert than nitrogen and is reserved for materials that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures.
It is the required choice for heat treating titanium, refractory metals (like molybdenum and tantalum), and certain grades of stainless steel. Argon is significantly more expensive than nitrogen, so its use is limited to these necessary applications.
Helium (He): For Specialized Applications
Helium is used far less frequently. Its primary advantage is its high thermal conductivity.
This property allows it to transfer heat very effectively, making it useful in some vacuum furnace applications as a quenching gas to achieve rapid, uniform cooling rates. Its extremely high cost restricts its use to niche processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an atmosphere is a technical decision balanced by economic realities.
Cost vs. Required Purity
The fundamental trade-off is cost. Nitrogen is the default choice unless a specific metallurgical reason demands a more inert gas.
Using Argon for a simple carbon steel part would produce an excellent result, but at an unnecessarily high cost. Conversely, using Nitrogen to heat treat titanium would result in the formation of titanium nitrides, ruining the part's surface.
Reactivity at Extreme Temperatures
The term "inert" is relative. While Nitrogen is non-reactive in most situations, it can form nitrides with certain reactive elements at very high heat treating temperatures.
This is the key technical reason why Argon is essential for metals like titanium. Argon will not react under any heat treating conditions, providing true inertness.
Gas Density and Purging
Argon is about 40% denser than air, while Nitrogen is slightly less dense than air. This affects how the furnace is purged.
Heavier gases like Argon can effectively displace air from the bottom up. This can sometimes lead to more efficient purging cycles, but proper furnace design and operation are more critical factors for success.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material and process goal should dictate your gas selection.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of carbon steels, alloy steels, or copper: Nitrogen is the most cost-effective and technically sound choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or specific stainless grades: Argon is required to prevent unwanted nitride formation and ensure surface integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving extremely rapid cooling (quenching) in a vacuum furnace: Helium may be considered for its superior heat transfer properties, despite its high cost.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is a fundamental step in achieving precise and repeatable metallurgical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Use Cases | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Carbon steels, alloy steels, copper | Cost-effective, industry standard |
| Argon (Ar) | Titanium, refractory metals, certain stainless steels | Highly inert, prevents nitride formation |
| Helium (He) | Specialized quenching in vacuum furnaces | High thermal conductivity, high cost |
Optimize your heat treating process with the right atmosphere gas.
Choosing between Nitrogen and Argon is critical for preventing oxidation, decarburization, and surface defects in your metal parts. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice and reliable solutions for your heat treating applications.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure you achieve precise, repeatable results. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting



















