At its core, a CVD system is a sophisticated apparatus for Chemical Vapor Deposition. This is a process used to create high-purity, high-performance solid materials, often as thin films. By introducing specific reactant gases (precursors) into a chamber, the system uses heat and pressure to trigger a chemical reaction that deposits a new material, atom by atom, onto a surface or substrate. A prominent example of this is the creation of lab-grown diamonds from carbon-containing gas.
A CVD system is essentially a highly controlled chemical oven. It combines specific gaseous ingredients under precise temperature and pressure, causing them to react and deposit a solid material onto a target substrate, effectively "growing" a new layer of material with exceptional purity and control.

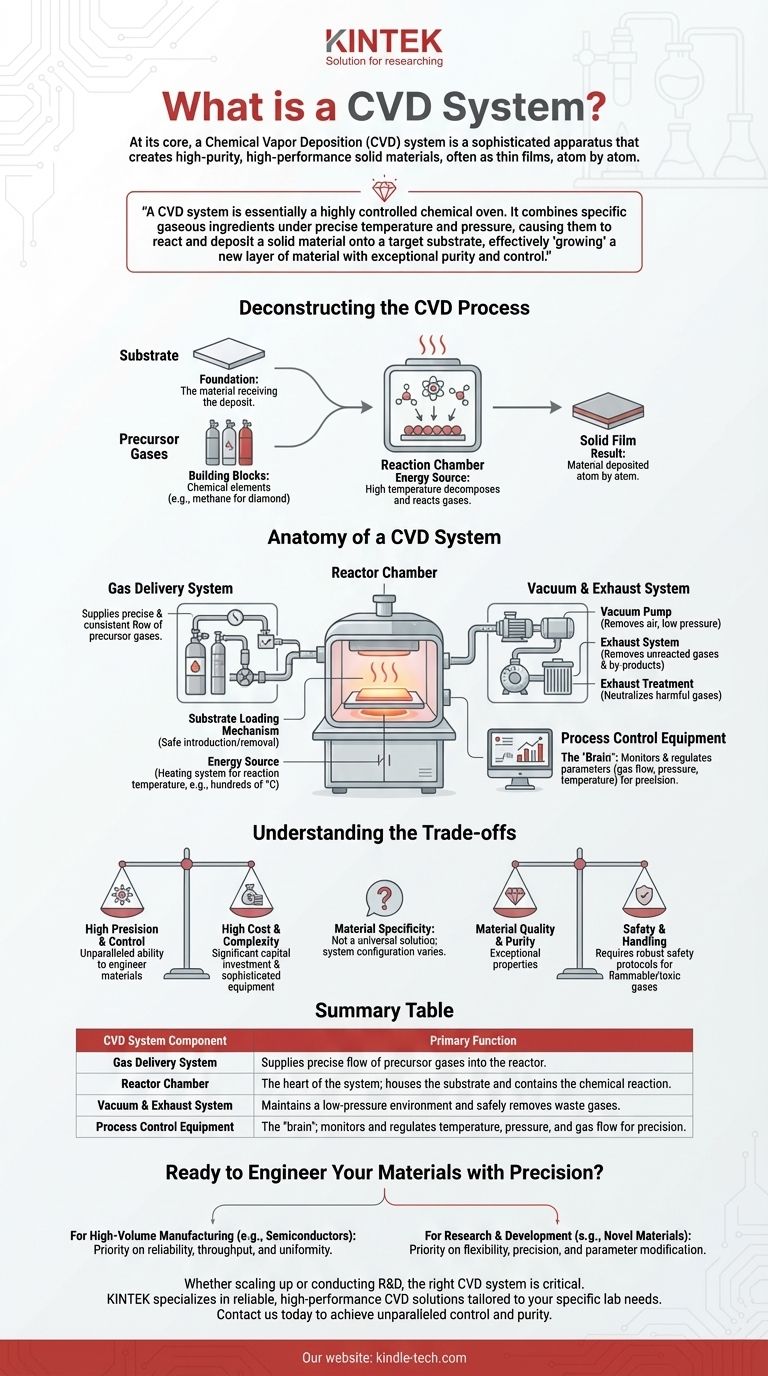
Deconstructing the CVD Process
To truly understand the system, you must first understand the fundamental process it is designed to facilitate. The goal is to move from a gaseous state to a solid state in a meticulously controlled manner.
The Role of the Substrate
The substrate is the foundation. It is the material onto which the new film will be deposited. The system begins by placing this substrate inside the reaction chamber.
The Power of Precursor Gases
Precursor gases are the chemical building blocks for the final material. For creating a diamond film, this would be a carbon-rich gas like methane. These gases are carefully selected and mixed to provide the necessary elements for the desired solid film.
The Reaction Environment
The system heats the substrate to a high temperature. This energy causes the precursor gas molecules to decompose and react, both in the gas phase and on the hot substrate surface. This reaction results in the deposition of a solid film on the substrate, building it up one atomic layer at a time.
Anatomy of a CVD System
A complete CVD system is an integration of several critical subsystems working in concert. We can group these into three primary functions: gas delivery, reaction, and exhaust.
Gas Delivery System
This is the system's intake. It is responsible for supplying a precise and consistent flow of one or more precursor gases into the reactor. This requires highly accurate flow controllers to maintain the correct chemical recipe for the deposition.
The Reactor Chamber
This is the heart of the CVD system. It's a sealed chamber that houses the substrate and contains the chemical reaction. Key components of the reactor itself include:
- A Substrate Loading Mechanism: A method for safely introducing and removing substrates without contaminating the chamber.
- An Energy Source: Typically a heating system that brings the substrate to the required reaction temperature, often several hundred or even a thousand degrees Celsius.
The Vacuum and Exhaust System
This subsystem manages the chamber's environment and waste. A vacuum pump is used to remove air and maintain a low-pressure environment, preventing unwanted reactions with atmospheric gases. The exhaust system then removes unreacted precursor gases and volatile by-products from the chamber. Often, this includes an exhaust treatment stage to neutralize harmful or toxic gases before they are released.
Process Control Equipment
This is the brain of the operation. A sophisticated control system monitors and regulates all critical parameters, including gas flow rates, chamber pressure, substrate temperature, and reaction time. This precision control is what ensures the final material has the desired properties and thickness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD systems are not a universal solution. Their design and operation involve inherent complexities and trade-offs.
High Precision vs. High Cost
The need for precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas composition requires sophisticated and expensive equipment. This makes CVD a significant capital investment compared to simpler deposition techniques.
Material Specificity
A CVD system is not a one-size-fits-all tool. The choice of precursor gases, operating temperatures, and pressures is highly specific to the material being deposited. Changing from depositing one material (e.g., silicon nitride) to another (e.g., diamond) can require significant changes to the system's configuration and cleaning procedures.
Safety and Handling
Many precursor gases used in CVD are highly flammable, toxic, or corrosive. This necessitates robust safety protocols and dedicated exhaust treatment systems, adding to the operational complexity and cost.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your focus will determine which aspect of the CVD system is most critical for you.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing (e.g., semiconductors, protective coatings): Your priority will be the system's reliability, throughput (substrate loading speed), and the uniformity of the deposited film across large substrates.
- If your primary focus is research and development (e.g., creating novel materials): You will value the system's flexibility, the precision of its process controls, and the ability to easily modify reaction parameters to explore new material properties.
Ultimately, a CVD system provides an unparalleled ability to engineer materials from the atom up, enabling the creation of components that are fundamental to modern technology.
Summary Table:
| CVD System Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Gas Delivery System | Supplies precise flow of precursor gases (e.g., methane) into the reactor. |
| Reactor Chamber | The heart of the system; houses the substrate and contains the chemical reaction. |
| Vacuum & Exhaust System | Maintains a low-pressure environment and safely removes waste gases. |
| Process Control Equipment | The 'brain'; monitors and regulates temperature, pressure, and gas flow for precision. |
Ready to Engineer Your Materials with Precision?
Whether you are scaling up a manufacturing process for semiconductors and coatings or conducting advanced R&D on novel materials, the right CVD system is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable, high-performance CVD solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve unparalleled control and purity in your material deposition projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings


















