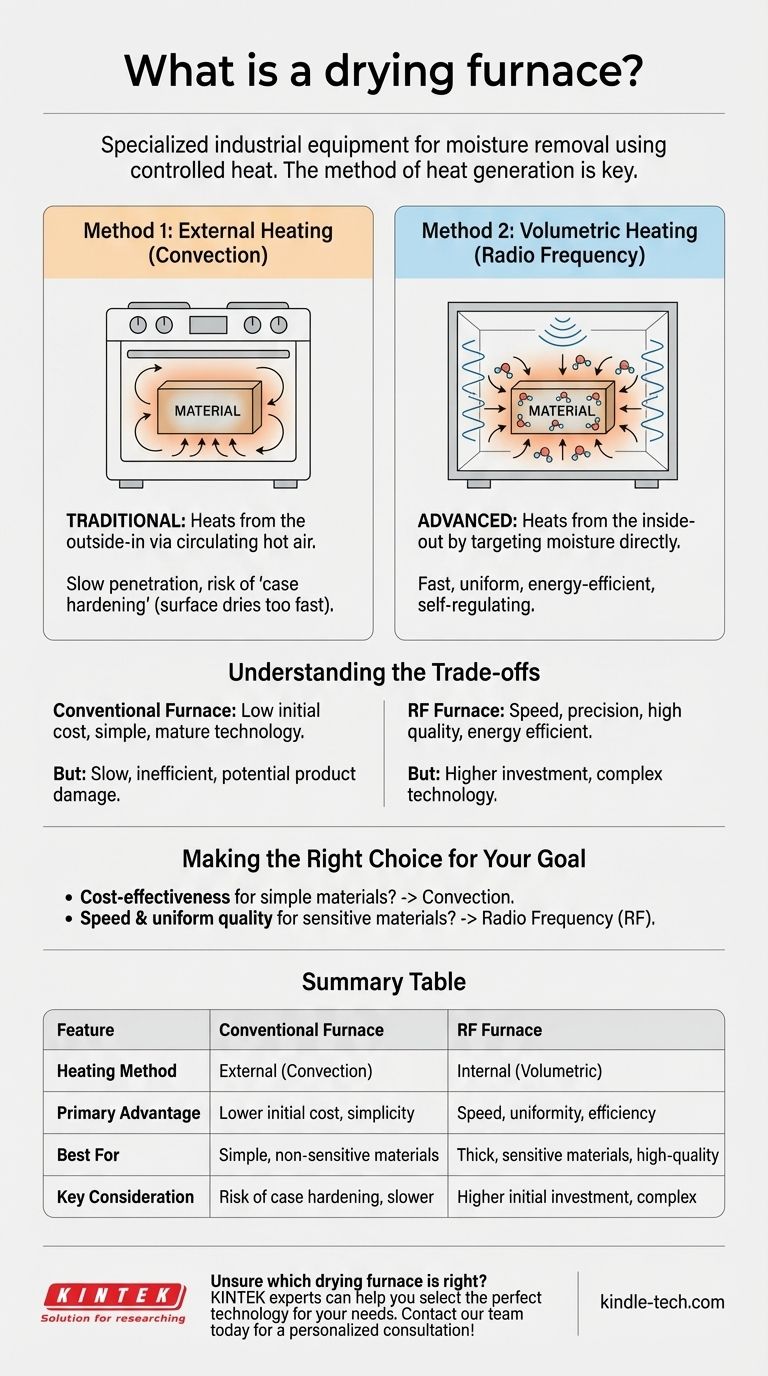
In industrial processes, a drying furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to remove moisture or other volatile liquids from a material using controlled heat. While this sounds simple, the method used to generate and apply this heat is what defines the technology, ranging from conventional ovens that heat from the outside-in to advanced systems that heat the material internally using electromagnetic fields.
The term "drying furnace" covers any industrial system using heat for moisture removal. The critical distinction, however, is not the furnace itself, but how the heat is generated—either externally through convection or internally through radio frequency (RF) energy that targets moisture directly.
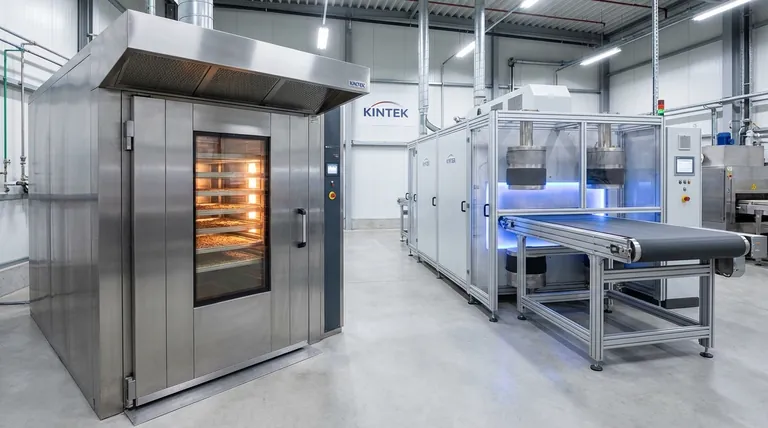

How Drying Furnaces Work: Two Core Methods
The fundamental goal of any drying process is to transfer enough energy into a material to cause its liquid content (typically water) to evaporate. The efficiency and quality of this process depend entirely on the method of heat transfer.
Method 1: External Heating (Convection)
This is the most traditional approach, functioning much like a conventional home oven.
Heat is generated by a source outside the material, such as a gas burner or electric element. This heat is then transferred to the surface of the material, typically by circulating hot air (convection). The heat must then slowly penetrate from the surface toward the core of the material to complete the drying process.
Method 2: Volumetric Heating (Radio Frequency)
This advanced method heats the material from the inside out, targeting the moisture itself.
An RF generator creates an alternating electric field. The material to be dried is placed within this field, causing polar molecules—like water—to rapidly flip back and forth. This constant molecular motion creates friction, which generates heat uniformly throughout the entire volume of the material at once.
Critically, areas with higher moisture content absorb more energy and therefore heat up faster. This self-regulating effect results in exceptionally fast and even drying.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a conventional furnace and an RF system involves balancing cost, speed, and the specific requirements of the material being processed.
Conventional Furnace: Simplicity and Cost
Conventional drying ovens are a mature, well-understood technology. They are generally simpler in design and represent a lower initial capital investment, making them a practical choice for many standard applications.
The Downside: Inefficiency and Quality Risk
Because conventional ovens heat from the outside, the process can be slow as heat struggles to reach the material's core. This can also cause "case hardening," where the surface dries and hardens too quickly, trapping moisture inside and potentially damaging the product.
RF Furnace: Speed and Precision
Radio Frequency systems are significantly faster and more energy-efficient because they don't waste energy heating the surrounding air or the material itself. Instead, they directly target and heat the water molecules. This precision leads to a higher quality final product with consistent moisture levels.
The Downside: Complexity and Investment
The technology behind RF drying is more complex and requires a higher initial investment. It is best suited for applications where speed, precision, and final product quality are paramount and justify the additional cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal technology is defined entirely by the needs of your material and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simple, non-sensitive materials: A standard convection furnace is often the most practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is speed, efficiency, and uniform quality for thick or sensitive materials: A Radio Frequency (RF) furnace offers superior performance by heating moisture directly from within the material.
Ultimately, understanding how heat is applied is the key to selecting the most effective drying furnace for your specific industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Furnace | RF Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | External (Convection) | Internal (Volumetric) |
| Primary Advantage | Lower initial cost, simplicity | Speed, uniformity, energy efficiency |
| Best For | Simple, non-sensitive materials | Thick, sensitive materials, high-quality requirements |
| Key Consideration | Risk of case hardening, slower | Higher initial investment, more complex technology |
Unsure which drying furnace is right for your lab's materials?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect drying technology—whether a cost-effective conventional oven or a high-performance RF system—to ensure efficient moisture removal and protect your material's integrity.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- Why is a freeze dryer used for metagenomic analysis on sludge? Ensure Genomic Integrity for Accurate Profiling
- How does the use of a vacuum freeze dryer benefit cys-CDs powder preparation? Preserve Nanoparticle Integrity
- Why is a laboratory freeze dryer used before biomass characterization? Preserve Structural Integrity for Accurate Data
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why use a laboratory freeze dryer for microalgae? Preserve Sample Integrity for Accurate Analysis












