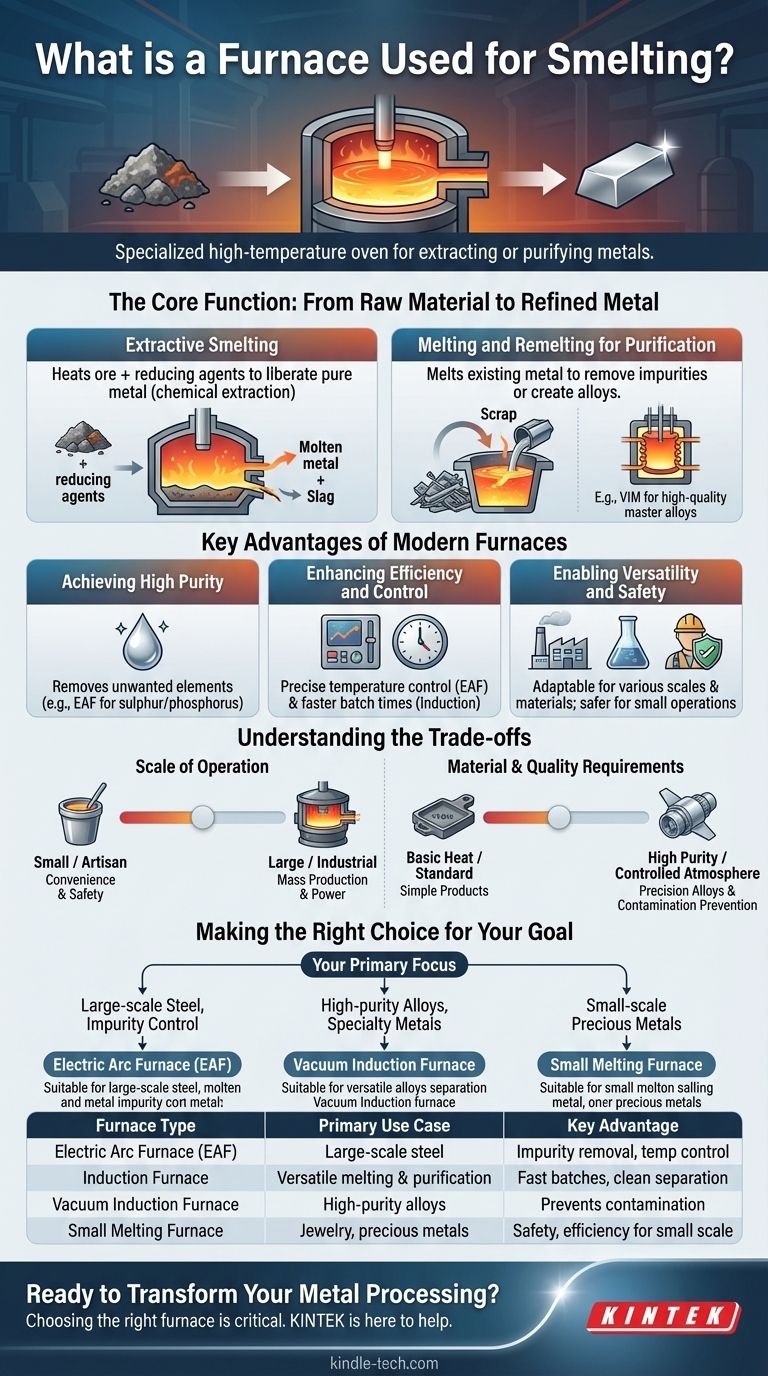
At its core, a furnace for smelting is a specialized high-temperature oven used to extract a base metal from its ore or to melt and purify existing metals. The process involves heating the raw material, often with a chemical reducing agent, to drive chemical and physical transformations that separate the desired metal from unwanted impurities.
The fundamental purpose of a smelting furnace is to create a precisely controlled, high-heat environment. This control allows for either the chemical extraction of metal from raw ore or the physical melting and purification of existing metals into a more refined, usable form.
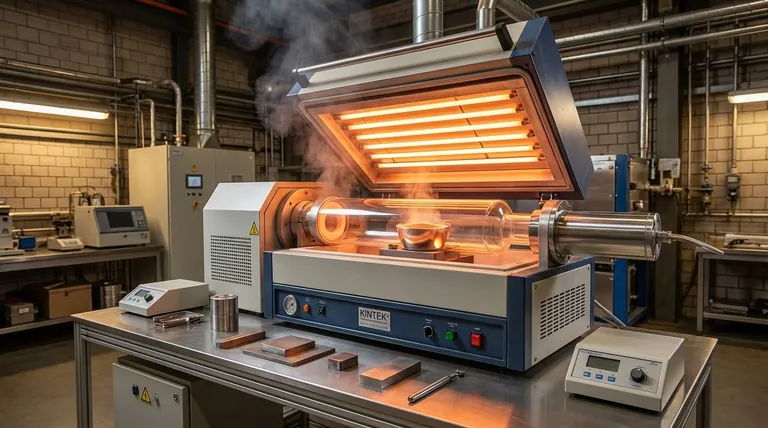

The Core Function: From Raw Material to Refined Metal
A furnace's role in metallurgy is transformative. It facilitates two primary processes: extracting new metal or improving the quality of existing metal.
Extractive Smelting
This is the classic definition of smelting. A furnace heats a mixture of metal ore and reducing agents, causing a chemical reaction that liberates the pure, molten metal from its mineral compounds.
Melting and Remelting for Purification
Modern furnaces are also critical for secondary processing. They melt down existing metals to remove impurities or to create specific metal mixtures, known as alloys.
For example, a vacuum induction melting furnace is used in a remelting process to produce high-quality consumable electrodes or create precise master alloys for casting.
Key Advantages Offered by Modern Furnaces
Different types of furnaces are engineered to provide specific benefits, from industrial-scale production to small, specialized applications.
Achieving High Purity
A key advantage is the ability to remove unwanted elements. An electric arc furnace (EAF) is highly effective at removing impurities like sulphur and phosphorus during steelmaking.
Similarly, an induction furnace allows for the complete emptying of its contents, ensuring a clean separation of melted gold from any residual impurities.
Enhancing Efficiency and Control
Modern furnaces offer superior control over the process. An EAF allows for easy and precise control of the furnace temperature, which is critical for producing high-quality alloy steel.
Induction furnaces also save significant time and money because preparing the furnace for the next batch is a much faster process.
Enabling Versatility and Safety
Furnaces can be adapted for various scales and materials. The technological flexibility of an EAF makes it suitable for smelting a wide range of high-quality steels.
For smaller operations, such as jewelry making or gold stores, a small melting furnace offers a combination of safety, efficiency, and convenience for working with precious metals like gold, silver, and copper.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of furnace is not universal; it is dictated entirely by the material, the required purity, and the scale of the operation. There is no single "best" type of furnace, only the most appropriate tool for a specific task.
Scale of Operation
A large, industrial electric arc furnace is designed for the mass production of steel, covering a large area and consuming immense power.
In contrast, a small induction furnace is perfect for a local gold buyer or artisan, prioritizing convenience and safety over massive throughput.
Material and Quality Requirements
Standard melting may only require basic heat. However, producing high-quality alloys for precision casting demands a sophisticated tool like a vacuum induction furnace, which can operate in a controlled atmosphere to prevent contamination.
The furnace is chosen based on the final product's specifications. A simple cast iron product has very different furnace requirements than a component for an aerospace application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is about aligning the equipment's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production with impurity control: An electric arc furnace (EAF) offers the necessary flexibility, temperature control, and refining capability.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity master alloys or specialty metals: A vacuum induction furnace provides the controlled environment essential for preventing contamination and achieving precise chemical compositions.
- If your primary focus is small-scale, high-value precious metal work: A small, specialized melting furnace delivers the ideal balance of safety, efficiency, and convenience for gold, silver, or copper.
Ultimately, the furnace is the critical instrument that enables the precise transformation of raw materials into valuable, refined metals.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Large-scale steel production | Excellent impurity removal (sulphur, phosphorus) & temperature control |
| Induction Furnace | Versatile melting & purification | Fast batch times, clean separation of metals (e.g., gold) |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | High-purity alloys & specialty metals | Prevents contamination in a controlled atmosphere |
| Small Melting Furnace | Jewelry, precious metals (gold, silver) | Safety, efficiency, and convenience for small-scale operations |
Ready to Transform Your Metal Processing?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to the success of your operation, whether you're extracting metal from ore or purifying existing materials for high-value applications. The precise control and capabilities of your equipment directly impact the quality, purity, and efficiency of your output.
KINTEK is here to help. We specialize in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces tailored for metallurgy. Our experts can guide you to the ideal solution—be it an industrial-scale electric arc furnace or a compact unit for precious metals—ensuring it meets your specific material, scale, and quality requirements.
Let's discuss your project. Contact us today to explore how our solutions can enhance your metal smelting and purification processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab



















