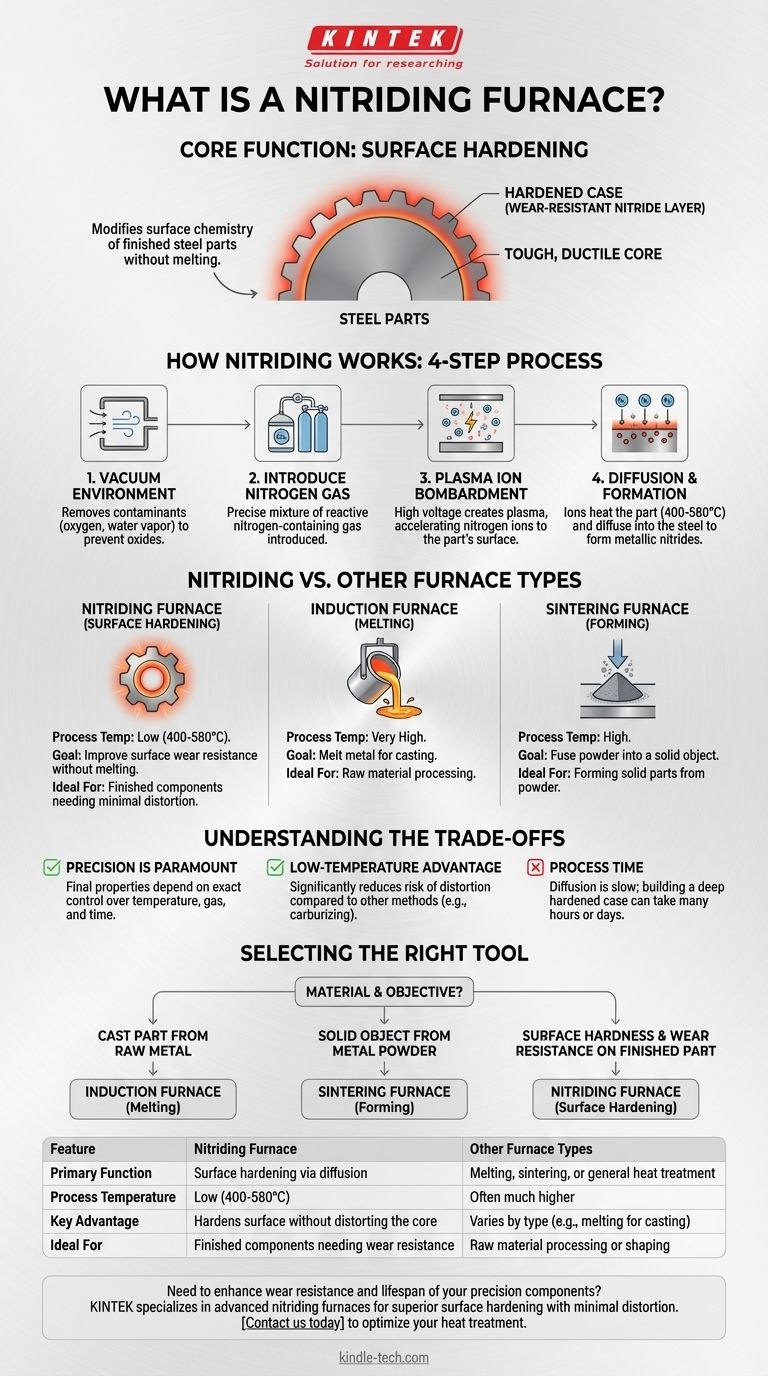
At its core, a nitriding furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed for a surface-hardening heat treatment process called nitriding. Unlike furnaces that melt or shape metal, a nitriding furnace modifies the surface chemistry of a finished steel part to create an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer layer while leaving the core material tough and ductile.
The crucial distinction to understand is that a nitriding furnace is not for general heating or melting. It is a precise tool for altering the surface properties of a metal part in a solid state, using a controlled atmosphere of reactive nitrogen.

How Nitriding Works: The Core Mechanism
Nitriding is a thermochemical diffusion process. A plasma nitriding furnace, a common type, uses a specific sequence of steps to achieve this transformation.
Creating the Environment: Vacuum
First, the furnace chamber containing the metal part is pumped down to a vacuum. This is a critical step to remove oxygen, water vapor, and other contaminants that could interfere with the process and create unwanted oxides on the part's surface.
Introducing the Active Agent: Nitrogen Gas
Once a sufficient vacuum is achieved, a precisely controlled mixture of nitrogen-containing gas (often nitrogen and hydrogen) is introduced into the chamber. This ensures the atmosphere is pure and contains only the necessary reactive elements.
The Role of Plasma: Ion Bombardment
A strong DC electric field is applied within the furnace. This high voltage ionizes the rarefied gas, creating a plasma. The metal workpiece is made the cathode, causing positively charged nitrogen ions to accelerate and bombard its surface with high energy.
Forming the Hardened Layer: Diffusion
This ionic bombardment does two things: it heats the workpiece to the required nitriding temperature (typically 400-580°C) and sputters the surface, cleaning it at an atomic level. Most importantly, it provides the active nitrogen that diffuses into the steel, reacting with iron and other alloying elements to form a very hard layer of metallic nitrides.
Nitriding vs. Other Furnace Types
Understanding what a nitriding furnace is also means understanding what it is not. Its purpose is fundamentally different from other common industrial furnaces.
Nitriding vs. Melting (Induction Furnaces)
Induction furnaces are designed to melt metal. They use powerful electromagnetic fields to rapidly heat a metal charge from a solid to a liquid state for casting. A nitriding furnace operates at a much lower temperature and never melts the workpiece.
Nitriding vs. Forming (Sintering Furnaces)
Sintering furnaces are used to fuse metallic or ceramic powders into a solid mass without melting them. Their goal is to create a solid object from powder. A nitriding furnace, by contrast, treats the surface of an already-solid, fully-formed component.
Nitriding vs. General Heat Treating (Muffle Furnaces)
Muffle furnaces are general-purpose ovens used for a wide range of processes like annealing (softening) or firing ceramics. While they control temperature, a nitriding furnace adds a layer of complexity by precisely controlling both the atmosphere and an electrical field to drive a specific surface reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the nitriding process involves specific considerations and is not a universal solution for hardening.
Precision is Paramount
The final properties of the nitrided layer—its depth, hardness, and composition—depend entirely on precise control over temperature, gas mixture, pressure, and process time. Any deviation can lead to a suboptimal or failed treatment.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
A key benefit of nitriding is its relatively low process temperature compared to other surface hardening methods like carburizing. This significantly reduces the risk of the part distorting or warping, which is critical for high-precision components.
The Limitation: Process Time
Nitriding is a diffusion-based process, which can be inherently slow. Building a deep hardened case can take many hours, sometimes even days. This can make it more costly or time-consuming than some alternative treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process requires a clear understanding of your material and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a cast part from raw metal: An induction furnace for melting is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is forming a solid object from metal powder: A sintering furnace is required to bond the powder into a dense part.
- If your primary focus is improving the surface hardness and wear resistance of a finished component with minimal distortion: A nitriding furnace is the specialized equipment for the job.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool to the specific material transformation you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Nitriding Furnace | Other Furnace Types |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Surface hardening via diffusion | Melting, sintering, or general heat treatment |
| Process Temperature | Low (400-580°C) | Often much higher |
| Key Advantage | Hardens surface without distorting the part's core | Varies by type (e.g., melting for casting) |
| Ideal For | Finished components needing wear resistance | Raw material processing or shaping |
Need to enhance the wear resistance and lifespan of your precision components? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including nitriding furnaces, to help you achieve superior surface hardening with minimal distortion. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your laboratory's specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our nitriding furnaces can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the function of a corundum furnace tube in chlorine corrosion tests? Ensure Purity in High-Heat Experiments
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















