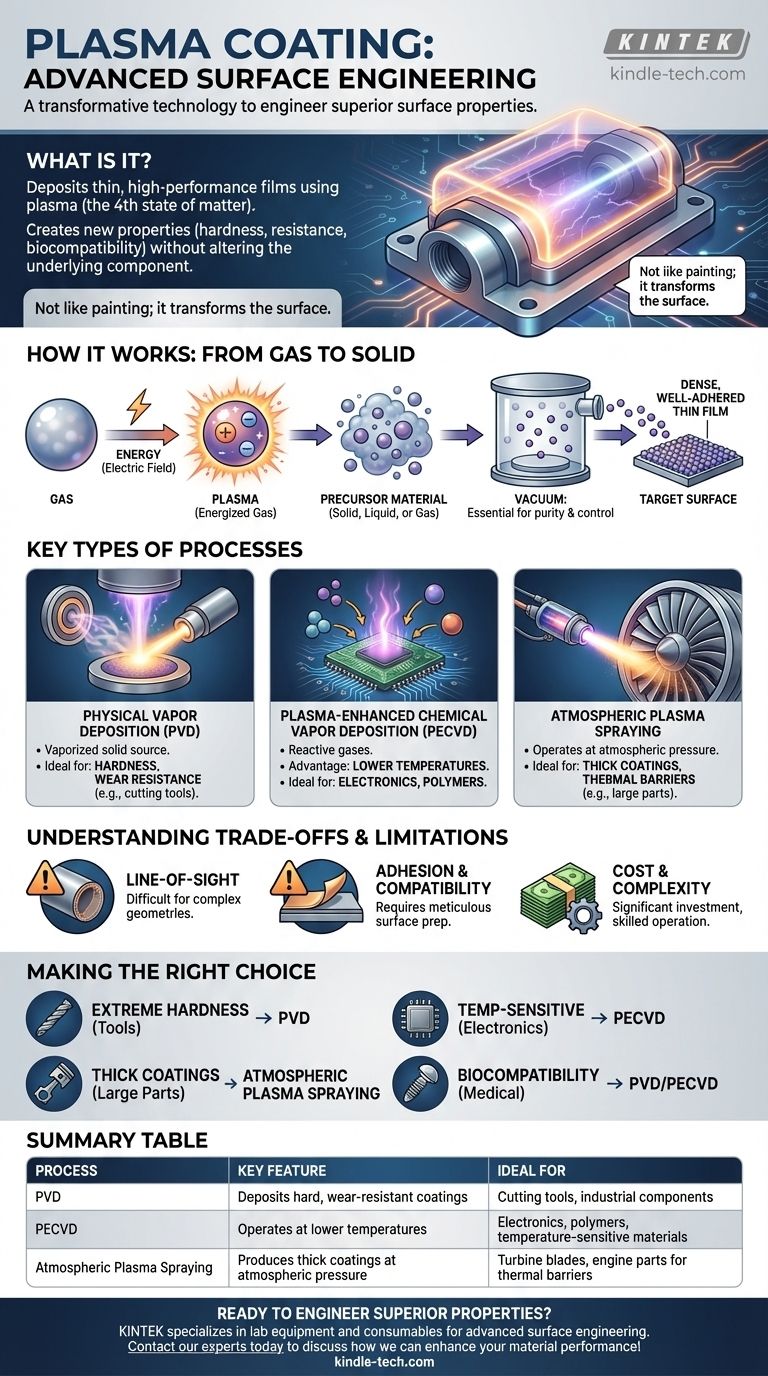
At its core, a plasma coating is an advanced surface engineering process that uses plasma—the fourth state of matter—to deposit a thin, high-performance film onto a material's surface. This technique isn't like painting; instead of a simple layer, it creates a new surface with fundamentally different properties, such as extreme hardness, chemical resistance, or biocompatibility, all without altering the underlying component.
Plasma coating is a family of vacuum-based techniques that transform a material's surface properties by depositing a precisely controlled thin film. It is the go-to solution when a component's bulk material is perfect for the job, but its surface is not.
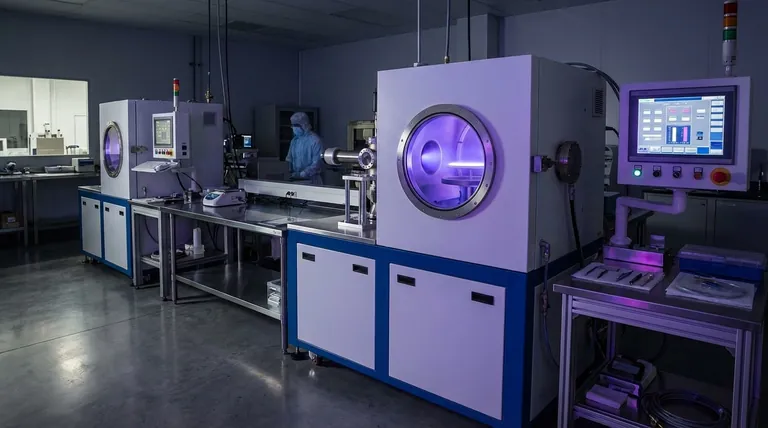

How Plasma Coating Works: From Gas to Solid
To understand plasma coating, you must first understand its key components: the plasma, the precursor material, and the vacuum environment.
The Role of Plasma: An Energized Gas
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter, after solid, liquid, and gas. It is created by applying a large amount of energy (typically an electric field) to a gas, causing its atoms to break apart into a mix of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons.
This energized, reactive cloud of particles is the engine of the coating process. It has the unique ability to break down precursor materials and propel them toward a target surface with high energy.
The Deposition Process: Building the Film
The process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. First, a precursor material—which can be a solid, liquid, or gas—is introduced.
When the plasma is generated, it bombards and reacts with this precursor. This interaction breaks the precursor down into its fundamental atomic or molecular components, which are then accelerated and deposited atom by atom onto the substrate (the part being coated), forming a dense, well-adhered thin film.
Why a Vacuum is Critical
The vacuum environment is essential for two reasons. First, it removes air and other contaminants that would otherwise interfere with the coating and cause defects.
Second, it allows the plasma particles to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with air molecules, ensuring a pure, controlled, and uniform deposition.
Key Types of Plasma Coating Processes
The term "plasma coating" covers several distinct techniques, each suited for different materials and outcomes.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
In PVD, a solid source material (a "target") is physically vaporized into the plasma. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto the substrate, forming the coating.
This method is ideal for depositing very hard, wear-resistant metallic or ceramic coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) on cutting tools and industrial components.
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD)
In PECVD, reactive gases are introduced into the chamber. The plasma's energy causes these gases to react and form a solid film on the substrate's surface.
A key advantage of PECVD is its ability to operate at much lower temperatures than traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This makes it perfect for coating temperature-sensitive materials like plastics and electronics.
Atmospheric Plasma Spraying
Unlike PVD and PECVD, this process can operate at normal atmospheric pressure. A high-temperature plasma jet melts a powder material and propels it at high velocity onto a surface.
Plasma spraying produces much thicker coatings (from micrometers to millimeters) and is used for thermal barriers, corrosion protection, and wear resistance on large industrial components like turbine blades and engine parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, plasma coating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful application.
The "Line-of-Sight" Problem
Many vacuum-based plasma processes, particularly PVD, are "line-of-sight." This means the coating can only deposit on surfaces directly visible to the plasma source.
Coating complex, non-visible internal geometries or deeply recessed features can be challenging and often requires sophisticated part rotation and manipulation during the process.
Adhesion and Substrate Compatibility
The success of any coating is its ability to stick to the substrate. This requires meticulous surface preparation, as any oil, oxide layer, or contaminant will prevent proper adhesion.
Furthermore, a significant mismatch in the thermal expansion coefficients between the coating and the substrate can cause the coating to crack or peel off when exposed to temperature changes.
Cost and Complexity
Plasma coating systems represent a significant capital investment and require highly skilled operators. The process is far more complex and costly than conventional methods like painting or wet plating.
Because of this, it is typically reserved for high-value applications where the performance benefits clearly justify the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right plasma process depends entirely on your end goal and the material you are working with.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance on tools: PVD is the standard for depositing hard ceramic coatings like TiN, TiCN, or AlTiN.
- If you need a protective, functional layer on temperature-sensitive electronics or polymers: Low-temperature PECVD is the ideal choice.
- If your goal is to apply a thick, robust thermal barrier or wear coating to a large part: Atmospheric Plasma Spraying is the most practical and cost-effective method.
- If you must ensure biocompatibility for a medical implant: PVD or PECVD can be used to deposit inert, body-safe materials like titanium or diamond-like carbon (DLC).
Ultimately, plasma coating is a transformative technology that allows you to engineer a surface to overcome challenges the bulk material cannot solve alone.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Deposits hard, wear-resistant coatings | Cutting tools, industrial components |
| Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) | Operates at lower temperatures | Electronics, polymers, temperature-sensitive materials |
| Atmospheric Plasma Spraying | Produces thick coatings at atmospheric pressure | Turbine blades, engine parts for thermal barriers |
Ready to engineer superior surface properties for your components?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced surface engineering. Our expertise in plasma coating technologies can help you achieve extreme hardness, chemical resistance, or biocompatibility tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your material performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















