In a laboratory setting, a sieve is a fundamental instrument used for the critical task of particle size analysis. Its primary purpose is to separate granular materials, powders, or aggregates into distinct size fractions to determine their particle size distribution, ensure quality control, and prepare samples for further analysis.
At its core, a laboratory sieve is more than just a filter. It is a precision tool that provides the quantitative data needed to guarantee material consistency, which is a non-negotiable requirement for predictable performance in research, development, and manufacturing.

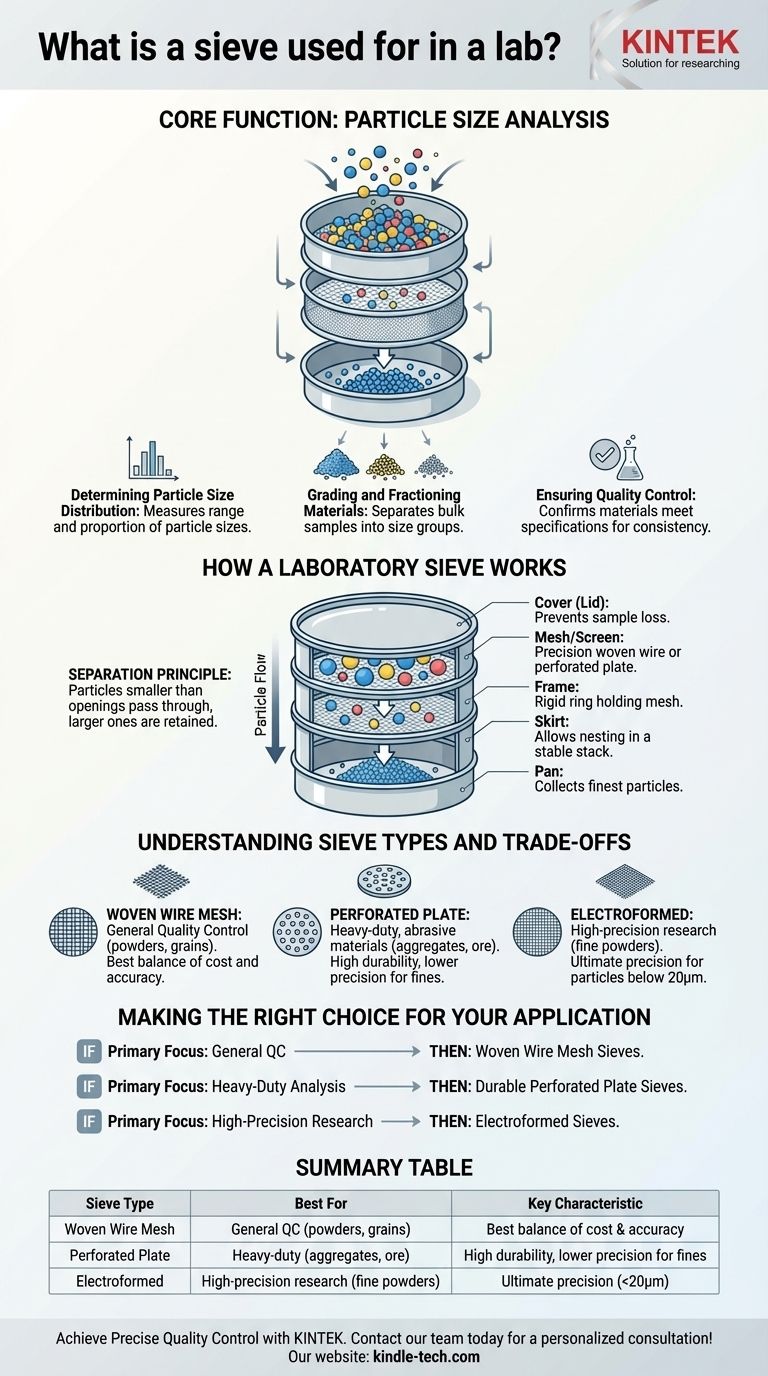
The Core Function: Particle Size Analysis
The most common and vital application of a laboratory sieve is analyzing the size of particles within a given sample. This process is essential across countless industries, from pharmaceuticals and food production to agriculture and mining.
Determining Particle Size Distribution
Particle size distribution refers to understanding the full range of particle sizes present in a sample and the proportion of each size.
By passing a material through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller openings, you can measure how much of the sample is retained on each screen. This data creates a precise "fingerprint" of the material's physical character.
Grading and Fractioning Materials
Sieving is used to physically separate, or fractionate, a bulk sample into different size groups.
For example, a soil scientist might use sieves to separate sand, silt, and clay components for analysis. In another application, a manufacturer might grade aggregates to ensure they meet construction specifications.
Ensuring Quality Control
Consistency is the ultimate goal in most production environments. Sieving provides a simple yet effective method for quality control.
If a batch of raw material (like flour or a chemical powder) has an incorrect particle size distribution, it can drastically affect the final product's properties, such as dissolution rate, flowability, or texture. Routine sieve analysis confirms that materials meet required specifications.
How a Laboratory Sieve Works
The operational principle of a sieve is straightforward, but its components are engineered for precision and repeatability.
The Basic Principle of Separation
A sieve operates by allowing particles smaller than its mesh openings to pass through while retaining any particles that are larger.
The process typically involves two stages. First, fine particles well below the opening size pass through quickly. The second, more time-consuming stage involves separating the "near-size" particles that have a high probability of passing but require agitation and time to orient correctly.
Key Components of a Sieve
A test sieve is an assembly of a few critical parts working together.
- Mesh/Screen: This is the most technical component. It is a screen with precisely measured and uniform openings, typically made from stainless steel woven wire or a perforated metal plate. Opening sizes range from several inches down to just 20 microns (0.02 mm).
- Frame: A rigid, circular metal ring that holds the mesh under tension. Common diameters are 8 inches (200 mm) and 12 inches (300 mm).
- Skirt: A small lip on the bottom of the frame that allows sieves to be nested in a stable stack without tipping over.
- Cover and Pan: A lid (cover) is placed on the top sieve to prevent sample loss, and a solid pan is placed at the bottom of the stack to collect the finest particles.
Understanding the Sieve Types and Trade-offs
Choosing a sieve involves balancing precision, durability, and cost. The type of mesh is the primary factor in this decision.
Woven Wire Mesh Sieves: The Workhorse
These are the most common type of laboratory sieves. They offer an excellent balance of performance and cost, making them suitable for a vast range of materials from fine powders to sands and grains. Their main limitation is potential stretching or damage with highly abrasive materials.
Perforated Plate Sieves: For Durability
Instead of woven wire, these sieves use a thick metal plate with round or square holes punched into it. They are significantly more durable and are the ideal choice for grading large, heavy, or abrasive materials like construction aggregates, coal, or large seeds. Their precision is lower than wire mesh for fine particles.
Electroformed Sieves: For Ultimate Precision
These sieves are made by an electro-deposition process that creates extremely precise and consistent square openings, especially at very fine sizes (below 20 microns). They are used for high-stakes applications like analyzing fine pharmaceutical powders or metal dusts where accuracy is paramount. However, they are the most expensive and delicate type of sieve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine the most appropriate sieve configuration for your lab.
- If your primary focus is general quality control for powders or grains: A standard set of woven wire mesh sieves provides the best balance of cost and accuracy for most routine analyses.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty analysis of aggregates, ore, or soil: Durable perforated plate sieves are necessary to withstand the abrasive nature of the material.
- If your primary focus is high-precision research on fine or specialty powders: An electroformed sieve is the only option that delivers the required level of accuracy, despite its higher cost and fragility.
Ultimately, the laboratory sieve is a simple tool that enables a profound level of control over the physical properties of materials, ensuring safety, quality, and performance.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Type | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Woven Wire Mesh | General quality control (powders, grains) | Best balance of cost and accuracy |
| Perforated Plate | Heavy-duty, abrasive materials (aggregates, ore) | High durability, lower precision for fines |
| Electroformed | High-precision research (fine powders, pharmaceuticals) | Ultimate precision for particles below 20µm |
Achieve precise quality control and reliable results in your lab.
Choosing the right sieve is critical for accurate particle size analysis, directly impacting your product's quality, consistency, and performance. Whether you work with fine pharmaceutical powders, abrasive construction aggregates, or food ingredients, the correct sieve ensures your materials meet exact specifications.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of sieves for every application. Our experts can help you select the perfect sieve type—from durable perforated plates to ultra-precise electroformed meshes—to meet your specific needs and budget.
Let us help you guarantee material consistency. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















