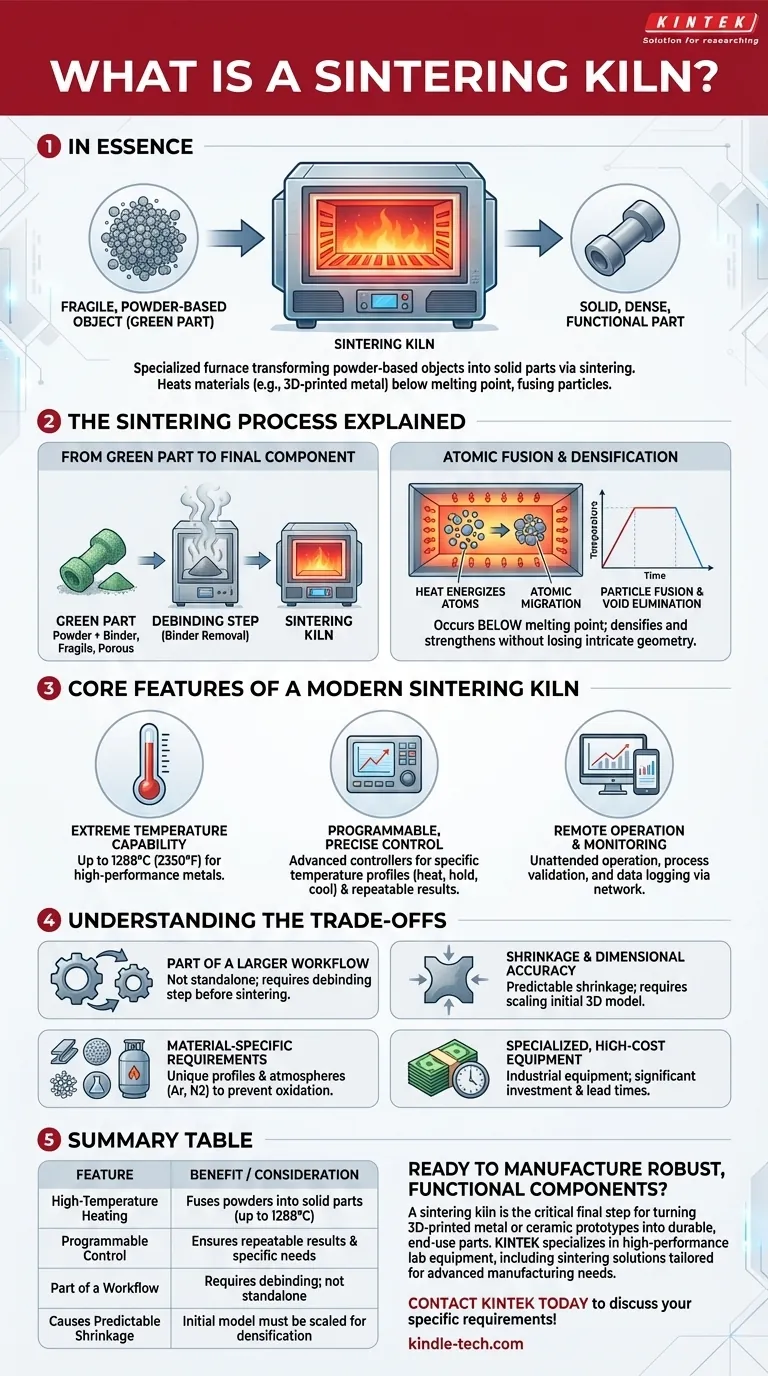
In essence, a sintering kiln is a specialized high-temperature furnace designed to transform fragile, powder-based objects into solid, dense, and functional parts. It accomplishes this through a process called sintering, where materials like 3D-printed metal or glass are heated to a temperature just below their melting point. This intense heat causes the individual particles to fuse, creating a strong, consolidated final component from materials such as stainless steel, bronze, and copper.
The core function of a sintering kiln is to serve as the critical final step in powder-based manufacturing, particularly metal 3D printing. It converts a delicate, unfinished "green part" into a durable, functional component by applying precise thermal energy without melting it.

The Role of Sintering in Modern Manufacturing
From "Green Part" to Final Component
Many advanced manufacturing processes, especially binder jetting or metal FDM 3D printing, produce what is known as a "green part."
This initial object is a mixture of metal powder held together by a temporary binding agent. While it has the correct shape, it is extremely fragile, porous, and lacks the mechanical properties of a solid metal object.
The Sintering Process Explained
The sintering kiln applies a precise, pre-programmed heating cycle to the green part (often after a debinding step to remove the binder).
This heat energizes the atoms in the metal particles, causing them to diffuse across the boundaries of neighboring particles. This atomic migration effectively welds the particles together, eliminating the voids between them and densifying the entire part.
Crucially, this occurs below the material's melting point, allowing the component to solidify and strengthen without losing its intricate geometry.
Core Features of a Modern Sintering Kiln
Extreme Temperature Capability
To process high-performance metals and materials, these kilns must reach very high temperatures. For example, a maximum temperature of 1288°C (2350°F) is common for handling materials like stainless steel and other alloys.
Programmable, Precise Control
Achieving successful sintering requires exacting control over the heating and cooling cycles.
Modern kilns utilize advanced controllers, often with touchscreens, to program specific temperature profiles (how fast to heat, how long to hold, how fast to cool). This precision is essential for repeatable results and for meeting the unique needs of different materials.
Remote Operation and Monitoring
In a professional or industrial setting, the ability to monitor a sintering cycle remotely via a computer or phone is a key feature.
This allows for unattended operation, process validation, and data logging, which are critical for quality control and operational efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Part of a Larger Workflow
A sintering kiln is not a standalone solution. It is one step in a multi-stage process that begins with 3D printing and almost always includes a separate "debinding" phase to remove the binding agent before sintering can begin.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Accuracy
The process of eliminating voids between particles inherently causes the part to shrink. This shrinkage is predictable but must be accounted for in the initial design phase. Engineers must scale up the initial 3D model to ensure the final, sintered part meets its required dimensional tolerances.
Material-Specific Requirements
There is no universal "sintering" button. Different materials require unique temperature profiles and, in many cases, controlled atmospheres (like an argon or nitrogen environment) to prevent oxidation at high temperatures. The kiln must be capable of meeting these specific process requirements.
Specialized, High-Cost Equipment
These are not commodity appliances. Sintering kilns are specialized pieces of industrial equipment, often built to order with significant lead times and investment costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding whether you need a sintering kiln depends entirely on your manufacturing goals and the materials you intend to use.
- If your primary focus is producing functional metal parts from powder-based 3D printing: A sintering kiln is an essential, non-negotiable component of your process.
- If your primary focus is prototyping with standard polymers or plastics (e.g., PLA, ABS, PETG): This equipment is completely unnecessary, as those materials do not undergo a sintering post-process.
- If you are exploring advanced materials like technical ceramics or specific high-performance alloys: You must verify that the kiln's maximum temperature and atmospheric control capabilities align with the strict requirements of your chosen materials.
Ultimately, integrating a sintering kiln into your workflow is the step that bridges the gap between simply printing a shape and truly manufacturing a robust, functional component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit / Consideration |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Heating | Fuses metal/ceramic powders into solid parts (e.g., up to 1288°C / 2350°F). |
| Programmable Control | Ensures repeatable results and meets specific material requirements. |
| Part of a Workflow | Requires a debinding step before sintering; not a standalone solution. |
| Causes Predictable Shrinkage | Initial 3D model must be scaled to account for densification. |
Ready to manufacture robust, functional components?
A sintering kiln is the critical final step for turning your 3D-printed metal or ceramic prototypes into durable, end-use parts. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including sintering solutions tailored for advanced manufacturing needs.
Our experts can help you select the right kiln to ensure precise temperature control, repeatable results, and successful integration into your workflow.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and unlock the full potential of your powder-based manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















