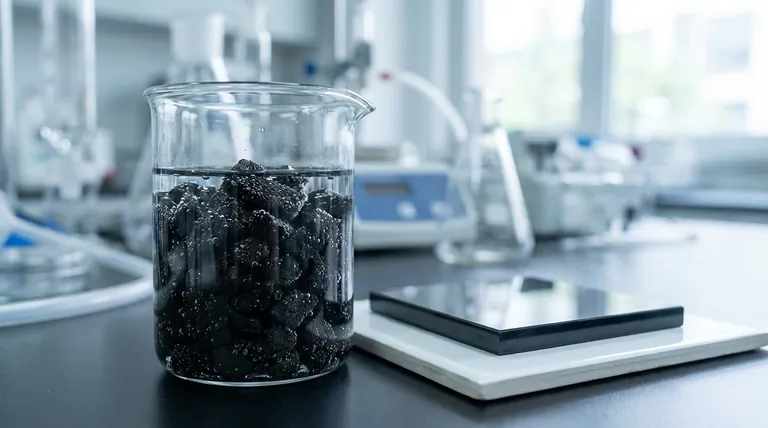
The activated carbon method is a purification process that uses a highly porous form of carbon to remove contaminants from a liquid or gas. It doesn't filter particles like a simple screen; instead, it uses a mechanism called adsorption, where contaminant molecules chemically stick to the carbon's vast internal surface. This material is typically produced from carbon-rich sources like coal or biomass.
At its core, the activated carbon method is not about mechanical filtering. Its effectiveness comes from creating a material with an enormous internal surface area that acts like a molecular magnet, attracting and holding impurities through the process of adsorption.

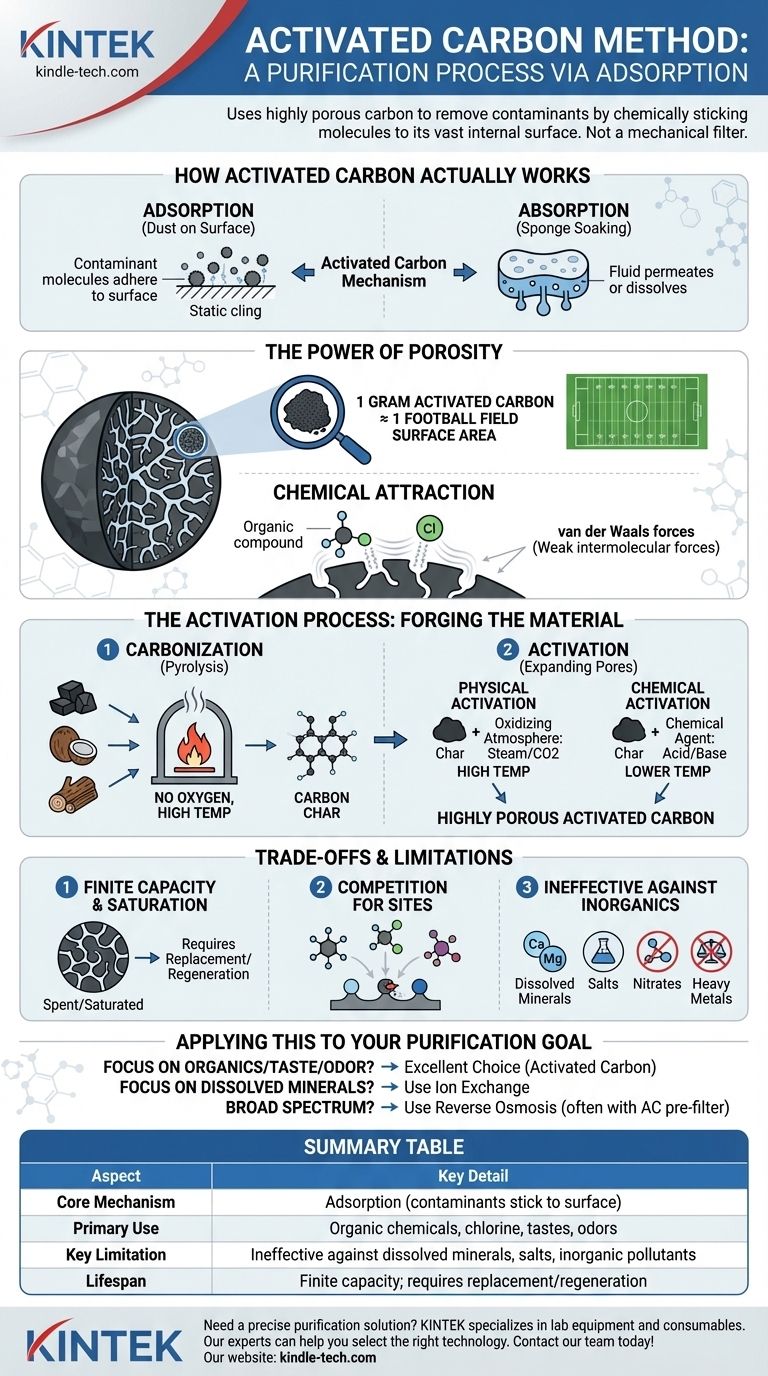
How Activated Carbon Actually Works
The power of activated carbon lies in its unique physical and chemical properties. Understanding the underlying mechanism is key to knowing when and how to use it effectively.
The Principle of Adsorption
Adsorption is the process where atoms or molecules from a substance (like a gas or liquid) adhere to the surface of another material, the adsorbent.
This is fundamentally different from absorption, where a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid. Think of adsorption as dust sticking to a surface via static cling, whereas absorption is a sponge soaking up water. Activated carbon is an adsorbent.
The Importance of a Massive Surface Area
The defining characteristic of activated carbon is its incredible porosity. The "activation" process riddles the carbon with a network of microscopic pores.
This creates a staggering internal surface area. A single gram of activated carbon can have a surface area equivalent to a football field, providing an immense number of sites for contaminant molecules to attach.
The Role of Chemical Attraction
Contaminants aren't just physically trapped in the pores. They are held to the carbon surface by weak intermolecular forces known as van der Waals forces.
This weak attraction is most effective on certain types of molecules, particularly organic compounds and disinfectants like chlorine, which is why activated carbon is so widely used in water and air purification.
The "Activation" Process: Forging the Material
Activated carbon begins as a raw, carbon-rich material. It's the two-step manufacturing process that transforms it into a powerful adsorbent.
Step 1: Carbonization
The process starts with source materials like coal, wood, or coconut shells. These materials are heated to very high temperatures in an environment without oxygen.
This step, called pyrolysis, burns off impurities and volatiles, leaving behind a concentrated carbon "char" with a rudimentary pore structure.
Step 2: Activation
The carbonized char is then "activated" to dramatically expand its internal pore network. This can be done in two primary ways.
Physical activation involves exposing the char to an oxidizing atmosphere (like steam or carbon dioxide) at high temperatures. The gas burns away parts of the carbon's internal structure, creating a sophisticated network of microscopic pores.
Chemical activation involves impregnating the raw material with a chemical agent, typically an acid or a strong base, before carbonization. This agent acts as a dehydrating and oxidizing catalyst, creating the porous structure at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the activated carbon method is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is subject to specific conditions and limitations.
Finite Capacity and Saturation
The surface of activated carbon has a limited number of adsorption sites. Once all these sites are occupied by contaminants, the carbon is considered "spent" or saturated.
At this point, it can no longer remove impurities and may even release previously captured contaminants back into the stream, a phenomenon known as desorption. The carbon must then be replaced or regenerated.
Competition for Adsorption Sites
Activated carbon is not perfectly selective. It will adsorb a wide range of molecules, not just the target contaminant.
If multiple types of contaminants are present, they will compete for the available adsorption sites. This can reduce the carbon's efficiency and shorten its lifespan for removing a specific substance.
Ineffectiveness Against Certain Contaminants
This method excels at removing organic chemicals, chlorine, and compounds that cause bad tastes and odors.
However, it is largely ineffective at removing many inorganic pollutants, such as dissolved minerals (calcium, magnesium), salts, nitrates, and most heavy metals.
Applying This to Your Purification Goal
Your choice of purification method should always be driven by the specific contaminants you need to remove.
- If your primary focus is removing organic chemicals, chlorine, and improving taste or odor: Activated carbon is an excellent and highly cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is removing dissolved minerals or "softening" water: You should use a method like ion exchange, as activated carbon will not be effective.
- If your primary focus is removing a very broad spectrum of contaminants, including salts and viruses: You may need a more comprehensive system like reverse osmosis, which often uses an activated carbon filter as a preliminary step.
Ultimately, understanding that the activated carbon method is a specialized tool for adsorption allows you to deploy it precisely where it delivers the most value.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Adsorption (contaminants stick to carbon surface) |
| Primary Use | Removing organic chemicals, chlorine, tastes, and odors |
| Key Limitation | Ineffective against dissolved minerals, salts, and many inorganic pollutants |
| Lifespan | Finite capacity; requires replacement or regeneration upon saturation |
Need a precise purification solution for your laboratory? The activated carbon method is just one tool in the purification toolkit. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including filtration and purification systems tailored to your specific needs—whether for water, air, or specialized gases. Our experts can help you select the right technology to ensure the purity and integrity of your work. Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the optimal solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- What is the proper procedure for cleaning a glassy carbon sheet after use? A Definitive Guide to Ensure Reliable Results
- What actions and conditions are strictly prohibited when working with a glassy carbon sheet? Protect Your Investment and Data Integrity














