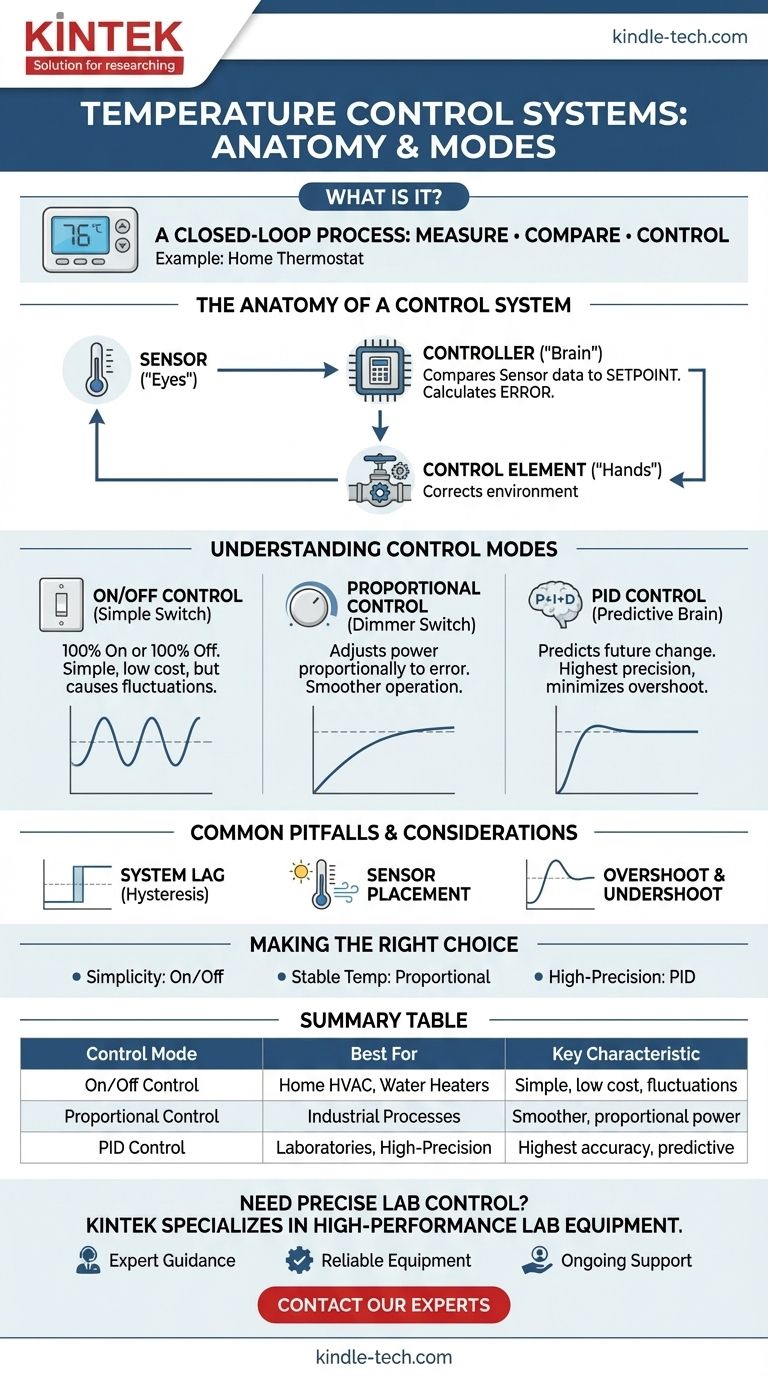
The most common example of a temperature control system is the thermostat in your home. It performs a simple yet critical loop: it measures the current room temperature, compares it to the temperature you've set (the "setpoint"), and turns your furnace or air conditioner on or off to close the gap between the two. This same fundamental principle applies to devices from a kitchen oven to a hot water heater.
A temperature control system is not a single component, but a closed-loop process. Its core function is to continuously measure a temperature, compare it to a desired setpoint, and control an output device to correct any deviation.
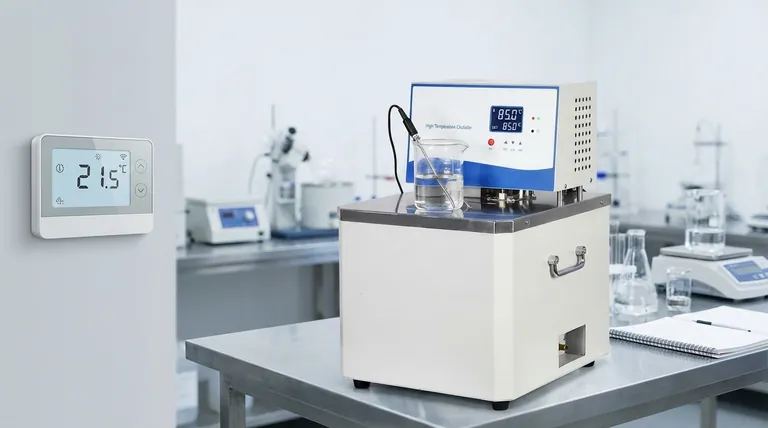

The Anatomy of a Control System
To understand how these systems work, it's best to break them down into their three essential components. We can use a home heating system as our guide.
The Sensor (The "Eyes")
The sensor is the part of the system that gathers information from the environment.
In a home thermostat, this is typically a thermistor or thermocouple. Its sole job is to accurately measure the ambient air temperature and convert that measurement into an electrical signal.
The Controller (The "Brain")
The controller is the decision-making hub of the system.
It takes the electrical signal from the sensor and compares that value to the setpoint you've programmed. The result of this comparison is what engineers call the error—the difference between where you are and where you want to be.
The Control Element (The "Hands")
Based on the error calculated by the controller, the control element takes action.
For a furnace, the controller sends a signal to open a gas valve and activate an igniter. For an air conditioner, it activates the compressor and fan. This element directly manipulates the environment to drive the temperature toward the setpoint.
Understanding Control Modes
Not all controllers make decisions the same way. The strategy a controller uses, known as its "control mode," has a significant impact on its accuracy and efficiency.
On/Off Control (The Simple Switch)
This is the most basic control mode, used in most home thermostats and hot water heaters.
The logic is simple: if the temperature is below the setpoint, the heater is 100% on. Once it passes the setpoint, the heater is 100% off. It is inexpensive and reliable but can lead to temperature fluctuations.
Proportional Control (The Dimmer Switch)
A more sophisticated approach is proportional control, common in industrial processes.
Instead of being fully on or off, the output of the control element is proportional to the error. If the temperature is very far from the setpoint, the heater runs at high power. As it gets closer, the power is gradually reduced, allowing for a much smoother approach to the target temperature.
PID Control (The Predictive Brain)
The gold standard for high-precision applications (like laboratory ovens or manufacturing) is PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control.
This advanced method not only looks at the current error (Proportional) but also considers the accumulated past error (Integral) and predicts the future rate of change (Derivative). This allows it to make incredibly fast and accurate corrections, preventing overshoot and maintaining a highly stable temperature.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Implementing a control system involves trade-offs that are critical to understand.
System Lag (Hysteresis)
A simple on/off controller doesn't turn off the instant the temperature hits 70°F and turn back on at 69.9°F. This rapid switching, or "cycling," would quickly destroy the equipment.
Controllers build in a deadband, or hysteresis, to prevent this. For example, the heater might turn on at 68°F and only turn off at 71°F, creating a stable operational range and preventing unnecessary wear.
Sensor Placement is Critical
A control system is only as good as the information it receives.
Placing a thermostat in direct sunlight, near a drafty window, or next to a heat-generating appliance will provide false readings. This forces the system to work incorrectly, wasting energy and failing to achieve the desired temperature in the actual living space.
Overshoot and Undershoot
The primary weakness of simple on/off control is overshoot. Because a furnace is still hot for a period after it shuts off, it will continue to heat the air, pushing the room temperature past the setpoint. Proportional and PID control are specifically designed to minimize or eliminate this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right type of temperature control system depends entirely on the requirements of the task.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and low cost: A basic on/off controller, like a residential thermostat, is the most practical and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is a steady, stable temperature: Proportional control is necessary to smooth out the fluctuations inherent in on/off systems.
- If your primary focus is high-precision industrial processes: A properly tuned PID controller is the industry standard for its unmatched accuracy and responsiveness.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively analyze, troubleshoot, or select the right control system for any application.
Summary Table:
| Control Mode | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| On/Off Control | Home HVAC, Water Heaters | Simple, cost-effective, but can cause temperature fluctuations |
| Proportional Control | Industrial Processes | Smoother operation by adjusting power proportionally to the error |
| PID Control | Laboratories, High-Precision Manufacturing | Highest accuracy; uses predictive algorithms to prevent overshoot |
Need Precise Temperature Control for Your Laboratory?
Understanding the right control system is the first step. Implementing it is the next. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment with advanced temperature control systems, including PID-controlled ovens and furnaces, designed for reliability and accuracy in demanding environments.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the perfect control mode (On/Off, Proportional, or PID) for your specific application.
- Reliable Equipment: Durable lab ovens, furnaces, and incubators built for precise thermal management.
- Ongoing Support: Ensure your systems operate at peak performance.
Let's discuss your lab's temperature control needs. Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your research or quality control processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath in CO2 absorption kinetics? Achieve High-Precision Research
- Why do manganese electrolysis processes require a thermostatic water bath? Master Thermal Control for High-Purity Metal
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- Why is a constant temperature water bath necessary for evaluating corrosion inhibitors? Ensure Precise Thermal Control
- Why are constant temperature water baths used in refractory testing? Accelerate MgO Hydration & Binder Evaluation



















