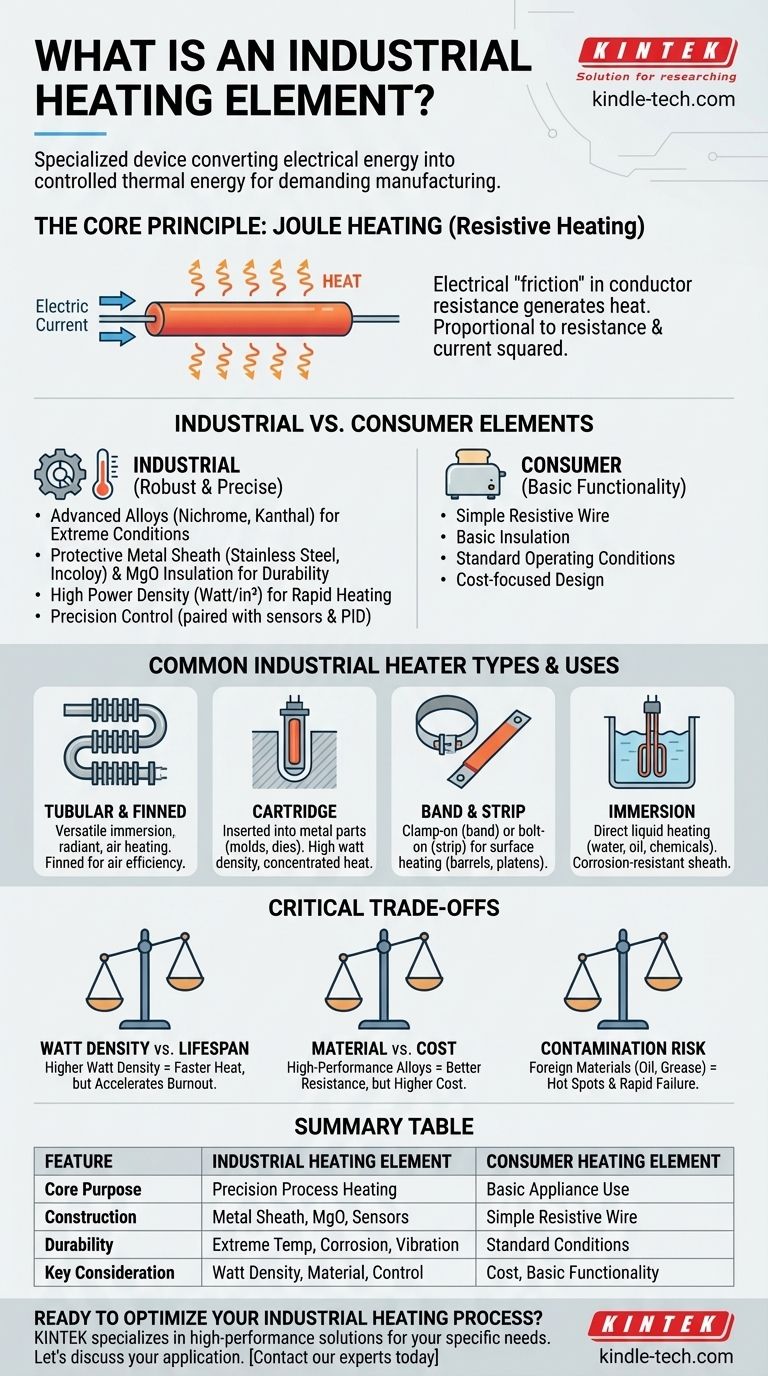
At its core, an industrial heating element is a specialized device engineered to convert electrical energy into precisely controlled thermal energy for manufacturing and processing applications. Unlike consumer-grade elements, they are designed for exceptional durability, high power output, and reliable performance under harsh operating conditions such as extreme temperatures, corrosive materials, and constant vibration.
The key distinction of an industrial heating element is not simply its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to deliver that heat with precision, reliability, and longevity within a demanding industrial environment. It is a critical component engineered for process integrity.

The Core Principle: How Electrical Energy Becomes Heat
The Concept of Joule Heating
Industrial heating elements operate on a fundamental principle of physics known as Joule heating, or resistive heating.
When an electric current is passed through a conductor, the material's natural resistance impedes the flow of electrons. This "electrical friction" generates heat.
The amount of heat produced is directly proportional to the material's resistance and the square of the current passing through it. This relationship is what allows engineers to design elements that produce specific amounts of heat.
Why This Matters for Industry
This simple principle is the foundation for countless industrial processes. By carefully selecting the resistive material and controlling the electrical current, manufacturers can melt plastics, cure coatings, heat process fluids, and maintain critical temperatures in molds and dies with incredible accuracy.
What Distinguishes an "Industrial" Heating Element?
While a toaster and a plastics extruder both use resistive heating, the industrial component is a far more sophisticated and robust device. The difference lies in four key areas.
Robust Materials for Extreme Conditions
Industrial elements are made from advanced alloys selected for their performance at high temperatures. Common materials include Nichrome (nickel-chromium) for its high resistance and strength, and Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminum) for its excellent oxidation resistance at very high temperatures.
Construction Built for Durability
An industrial heater is more than just a resistive wire. The wire is typically protected by a metal sheath, often made of stainless steel, Incoloy, or Inconel, to guard against corrosion and physical damage.
Inside the sheath, the wire is electrically insulated and thermally bonded using compacted Magnesium Oxide (MgO) powder. This construction protects the element from vibration and moisture while ensuring efficient heat transfer to the outside sheath.
High Power Density and Scale
Industrial processes often require immense amounts of heat delivered to a small area. This is measured in watt density (watts per square inch). Industrial cartridge heaters, for example, can achieve extremely high watt densities to heat metal molds rapidly.
Precision and Controllability
These elements are designed to be part of a larger control system. They are almost always paired with temperature sensors like thermocouples or RTDs and a controller (like a PID controller) to maintain a process temperature with pinpoint accuracy, often within a single degree.
A Guide to Common Industrial Heater Types
The form factor of a heating element is dictated by its intended application.
Tubular and Finned Tubular Heaters
These are the most versatile types. Their robust tubular construction allows them to be bent into complex shapes for custom applications. They are used for immersion heating in liquids, radiant heating, and convection heating of air. Adding fins dramatically increases the surface area for more efficient air heating.
Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge heaters are high-performance elements designed to be inserted into drilled holes in metal parts like platens, dies, and molds. They provide concentrated, localized heat and are prized for their high watt density and fast response time.
Band and Strip Heaters
Band heaters are circular elements that clamp onto the outside of cylindrical parts, such as the barrels of plastic extruders or injection molding machines. Strip heaters are flat elements bolted or clamped onto surfaces to provide uniform heat over an area.
Immersion Heaters
As the name implies, these are designed for direct immersion in liquids like water, oils, solvents, and chemical solutions. Material selection for the sheath is critical to prevent corrosion from the liquid being heated.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting the right heater involves balancing performance, lifespan, and cost.
Watt Density vs. Element Lifespan
The most common cause of premature heater failure is running it at too high a watt density for the application. While a higher watt density provides faster heat-up, it also dramatically increases the internal wire temperature, accelerating oxidation and leading to burnout.
Material Selection vs. Cost
A heater sheathed in a high-performance alloy like Inconel can withstand highly corrosive environments but comes at a significant cost premium. For less demanding applications, like heating clean water, a standard stainless steel sheath is a far more economical and perfectly suitable choice.
The Risk of Contamination
Foreign materials like oil, grease, or even unsecured electrical connections can cause localized hot spots on the element's surface. These hot spots prevent heat from dissipating properly, leading to overheating and rapid failure. Proper installation and a clean operating environment are crucial for longevity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific industrial process you need to support.
- If your primary focus is heating liquids: Your decision rests on choosing an immersion heater with a sheath material that is chemically compatible with your fluid.
- If your primary focus is heating solid metal parts (molds, dies): You need cartridge heaters for concentrated heat or strip heaters for surface heating, ensuring a tight fit for good thermal transfer.
- If your primary focus is heating moving air: Finned tubular heaters are the most efficient choice, as the fins provide a large surface area for effective heat exchange.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature radiant heat: Ceramic or quartz-sheathed elements are often used, as they are highly effective at emitting infrared energy.
Ultimately, understanding the heating element as an engineered component is the first step toward building a more reliable and efficient industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Industrial Heating Element | Consumer Heating Element |
|---|---|---|
| Core Purpose | Precision process heating | Basic consumer appliance use |
| Construction | Metal sheath, MgO insulation, thermocouple compatibility | Simple resistive wire |
| Durability | Built for extreme temperatures, corrosion, and vibration | Standard operating conditions |
| Key Consideration | Watt density, sheath material, process control | Cost, basic functionality |
Ready to Optimize Your Industrial Heating Process?
Selecting the right heating element is critical for the efficiency, reliability, and safety of your operation. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and industrial heating solutions, providing the durable components you need for demanding applications.
We can help you:
- Identify the perfect heater type (cartridge, tubular, band, immersion) for your specific process.
- Select the optimal materials to withstand your operating environment, including temperature and corrosion factors.
- Avoid common pitfalls like premature burnout from incorrect watt density.
Let's discuss your application and ensure you have the right heating solution. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance












