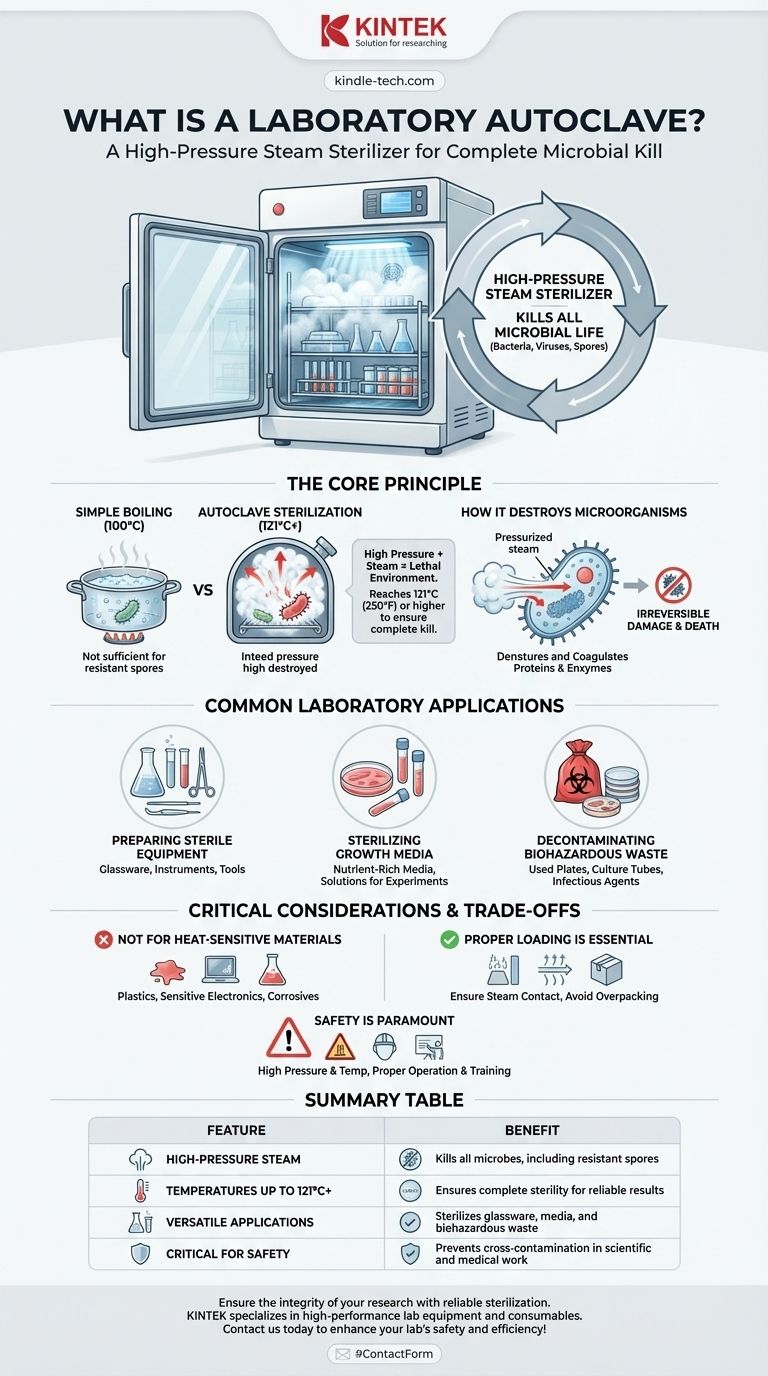
In short, a laboratory autoclave is a high-pressure steam sterilizer. It functions like a sophisticated pressure cooker, using high-temperature steam under pressure to kill all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and even highly resistant spores. This process is essential for decontaminating equipment and materials to ensure safety and prevent cross-contamination in scientific and medical settings.
The autoclave is not merely a cleaning device; it is a critical instrument of control. Its purpose is to achieve sterility—the complete absence of viable microorganisms—which is a non-negotiable requirement for reliable scientific research and safe medical practice.

The Core Principle: Why Steam Under Pressure is So Effective
An autoclave's power comes from a simple physical principle: the boiling point of water increases as pressure rises. By combining high pressure with steam, it creates an environment far more lethal to microbes than simple boiling water.
Beyond Simple Boiling
While boiling water at 100°C (212°F) can kill many bacteria, it is not sufficient to eliminate highly resistant bacterial spores. An autoclave pressurizes its chamber, allowing steam to reach temperatures of 121°C (250°F) or higher, ensuring a complete kill.
How It Destroys Microorganisms
The combination of intense heat and moisture is key. The hot, pressurized steam rapidly penetrates materials and transfers heat, which denatures and coagulates essential proteins and enzymes within microbial cells. This process irreversibly damages the microorganism's structure and metabolic functions, leading to its death.
Ensuring Complete Sterilization
The goal of autoclaving is not just to reduce microbial count but to achieve total sterility. The process is validated to destroy all forms of life, making it the gold standard for sterilizing materials that can withstand the high temperature and moisture.
Common Laboratory Applications of an Autoclave
The autoclave is a workhorse in nearly every microbiology, medical, and life science laboratory. Its applications are centered on preparing sterile materials and safely disposing of used ones.
Preparing Sterile Equipment
The most common use is sterilizing reusable items. This includes glassware (flasks, beakers, test tubes), surgical instruments, and other heat-resistant laboratory tools.
Sterilizing Growth Media and Solutions
For microbiologists, it is critical that the nutrient-rich media used to grow bacteria or cells is completely sterile beforehand. The autoclave ensures that no contaminating organisms are present, so experiments only grow the intended microbes.
Decontaminating Biohazardous Waste
Before disposal, all materials that have come into contact with potentially infectious agents must be rendered safe. Autoclaves are used to sterilize used petri dishes, culture tubes, and other biohazardous waste, neutralizing any dangerous pathogens.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Considerations
While incredibly effective, an autoclave is a powerful machine that demands respect and proper technique. Its limitations and operational risks must be understood to ensure both safety and successful sterilization.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
The primary limitation is heat. Any materials that cannot withstand high temperatures and moisture will be destroyed. This includes many plastics that will melt, sensitive electronics, and corrosive or volatile chemicals that could degrade or react dangerously.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Effective sterilization depends on steam making contact with every surface. If the chamber is overpacked or items are wrapped improperly, it can create air pockets that prevent steam penetration. This failure results in unsterile items and compromised experiments.
Safety is Paramount
An autoclave operates at extremely high pressures and temperatures, making it a potential workplace hazard. All users must be trained on its proper operation, including correctly sealing the door, using appropriate personal protective equipment, and allowing the machine to cool and depressurize fully before opening.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Proper use of an autoclave is dictated by the material being sterilized. Your approach should change based on the specific task to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing solid items like glassware: Ensure items are clean and arrange them to allow for maximum steam circulation and penetration.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or growth media: Use vented caps or cover flasks with foil to prevent the containers from shattering due to pressure changes during the cycle.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Use specialized, steam-penetrable autoclave bags and run a longer cycle time to ensure the heat fully penetrates the entire dense load.
Ultimately, mastering the autoclave is fundamental to guaranteeing the safety, validity, and integrity of any modern scientific or medical work.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure Steam | Kills all microbes, including resistant spores |
| Temperatures up to 121°C+ | Ensures complete sterility for reliable results |
| Versatile Applications | Sterilizes glassware, media, and biohazardous waste |
| Critical for Safety | Prevents cross-contamination in scientific and medical work |
Ensure the integrity of your research with reliable sterilization. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing autoclaves trusted by laboratories worldwide. Let our experts help you select the right sterilizer for your specific needs—from glassware and media preparation to safe waste decontamination. Contact us today to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave play in 3D-GO synthesis? Optimize Your Graphene Composites
- What are the 4 principles of autoclave? Master Steam Sterilization for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of autoclaving in the laboratory? Ensure Sterile Safety & Integrity
- What are the materials that can be sterilized using an autoclave? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- Why is it necessary to use a low-pressure autoclave for aluminum foam casting? Ensure Perfect Infiltration
- How often do we need to perform maintenance on the autoclave machine? A Guide to High-Risk vs. General Use
- Which factors contribute to successful sterilization using an autoclave? Master the 3 Keys to Sterility
- Can you sterilize instruments without an autoclave? Discover Effective Alternatives for Your Lab



















