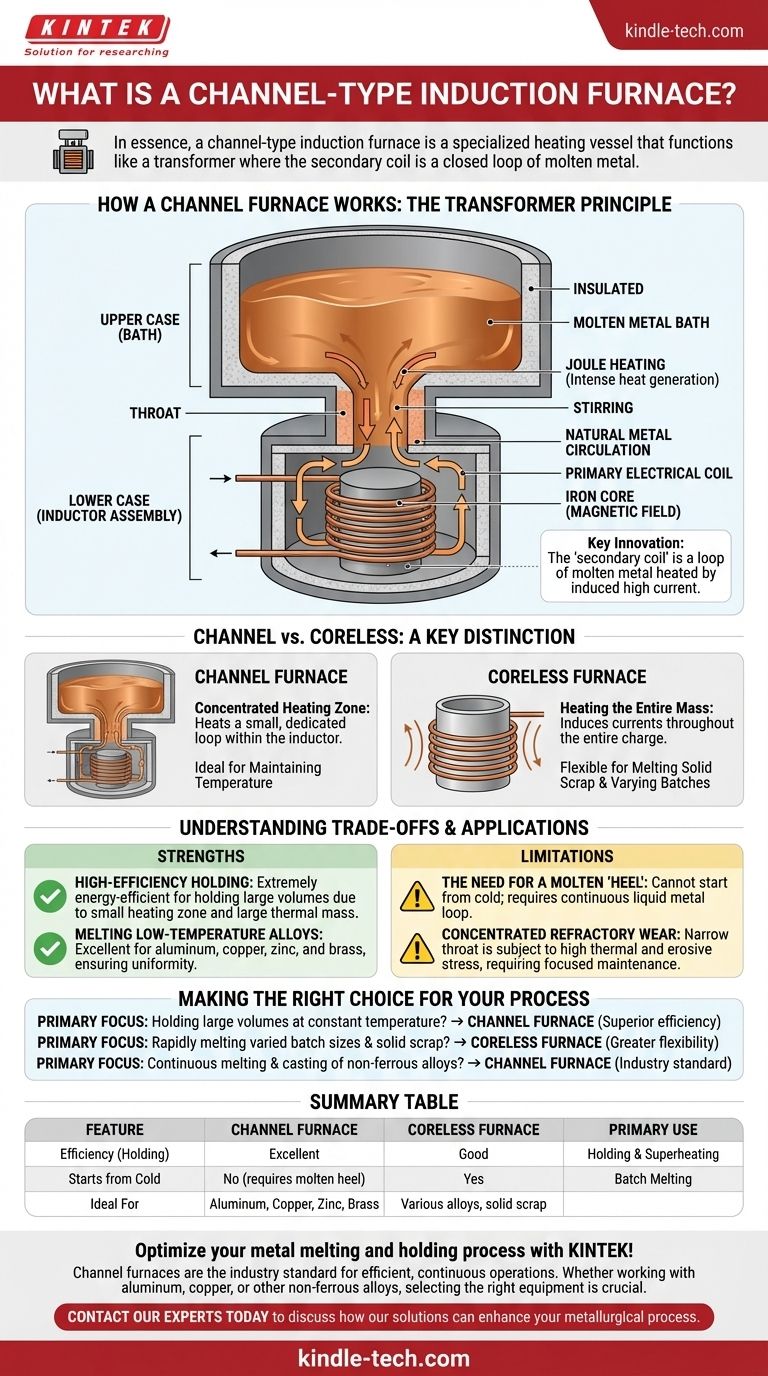
In essence, a channel-type induction furnace is a specialized heating vessel that functions like a transformer where the secondary coil is a closed loop of molten metal. It consists of a main refractory-lined chamber holding the bulk of the metal, connected by a narrow passage or "channel" to an induction unit that heats a small, circulating portion of the melt.
The critical distinction of a channel furnace is its design: it separates the main metal bath from the heating zone. By continuously heating a small, dedicated loop of metal, it becomes exceptionally efficient at holding large volumes of molten metal at a precise temperature.

How a Channel Furnace Works: The Transformer Principle
A channel furnace leverages the fundamental principles of electromagnetic induction in a unique and highly efficient configuration. Its operation is best understood by looking at its distinct components and their interaction.
The Core Components: Bath and Inductor
The furnace is built in two main parts. The upper case is the main vessel or bath that holds the majority of the molten metal. The lower case is the inductor assembly, which contains the iron core and primary coil. These two sections are connected by one or more narrow refractory passages, known as throats.
Primary Coil vs. Secondary Loop
The inductor assembly contains a primary electrical coil wound around an iron core, just like a standard transformer. The key innovation is that the "secondary coil" is not made of wire but is formed by the loop of molten metal that flows from the main bath, through the throat, and around the inductor's core.
Generating Heat Through Induction
When an alternating current is applied to the primary coil, it creates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field in the iron core. This field induces a very high secondary current in the molten metal loop. The inherent electrical resistance of the metal causes this current to generate intense heat (Joule heating), rapidly raising the temperature of the metal within the channel.
The Importance of Metal Circulation
This intense heating within the confined channel, combined with electromagnetic forces, causes the metal to flow continuously. Hot metal from the channel rises into the main bath, and cooler metal from the bath sinks to take its place. This natural circulation provides constant, gentle stirring, ensuring excellent temperature uniformity and chemical homogeneity throughout the entire melt.
Channel vs. Coreless: A Key Distinction
While both are induction furnaces, the way they apply heat creates fundamental differences in their performance and ideal applications.
The Heating Zone: A Concentrated Channel
A channel furnace applies all its energy to a small, specific portion of the metal—the loop within the inductor. The rest of the metal in the main bath is heated only by the circulation of this superheated metal.
The Coreless Approach: Heating the Entire Mass
In a coreless induction furnace, the primary coil surrounds the entire crucible. The magnetic field induces eddy currents throughout the entire charge, heating the whole mass of metal simultaneously.
Implications for Operation
This structural difference means a channel furnace excels at maintaining the temperature of an already liquid bath, while a coreless furnace is often more flexible for melting solid scrap in varying batch sizes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The unique design of the channel furnace makes it ideal for some tasks but less suitable for others.
Strength: High-Efficiency Holding
Because the heating zone is small and well-insulated, and the main bath has a large thermal mass with a relatively small surface area, channel furnaces are extremely energy-efficient for holding metal at temperature for long periods. They are often used as holding and superheating units downstream from a primary melting furnace.
Strength: Melting Low-Temperature Alloys
These furnaces are a standard choice for melting and holding non-ferrous alloys with lower melting points, such as aluminum, copper, zinc, and brass. The constant circulation is excellent for maintaining alloy composition.
Limitation: The Need for a Molten "Heel"
A channel furnace cannot be started from cold, solid material. It requires a continuous liquid metal loop to complete the secondary circuit. Therefore, the furnace must always maintain a molten "heel" of metal, even when idle, or be started with an initial charge of molten metal from another source.
Limitation: Concentrated Refractory Wear
All the heat and metal flow are concentrated in the narrow throat. This makes the refractory lining in this area subject to high thermal and erosive stress, often requiring more focused maintenance compared to the main bath lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology is critical for both operational efficiency and final product quality.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal at a constant temperature: The channel furnace's unparalleled thermal efficiency makes it the superior choice for holding applications.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting varied batch sizes, including solid scrap: A coreless induction furnace provides greater operational flexibility and is better suited for batch melting.
- If your primary focus is a continuous melting and casting operation for non-ferrous alloys: The channel furnace is a highly effective and energy-efficient industry standard.
Understanding this fundamental design difference empowers you to select the most efficient and cost-effective melting technology for your specific metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Channel Furnace | Coreless Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Holding & Superheating | Batch Melting |
| Efficiency (Holding) | Excellent | Good |
| Starts from Cold | No (requires molten heel) | Yes |
| Ideal For | Aluminum, Copper, Zinc, Brass | Various alloys, solid scrap |
Optimize your metal melting and holding process with KINTEK!
Channel furnaces are the industry standard for efficient, continuous operations. Whether you're working with aluminum, copper, or other non-ferrous alloys, selecting the right equipment is crucial for productivity and cost-effectiveness.
As a specialist in lab and industrial equipment, KINTEK can help you determine if a channel furnace is the right solution for your specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your metallurgical process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















