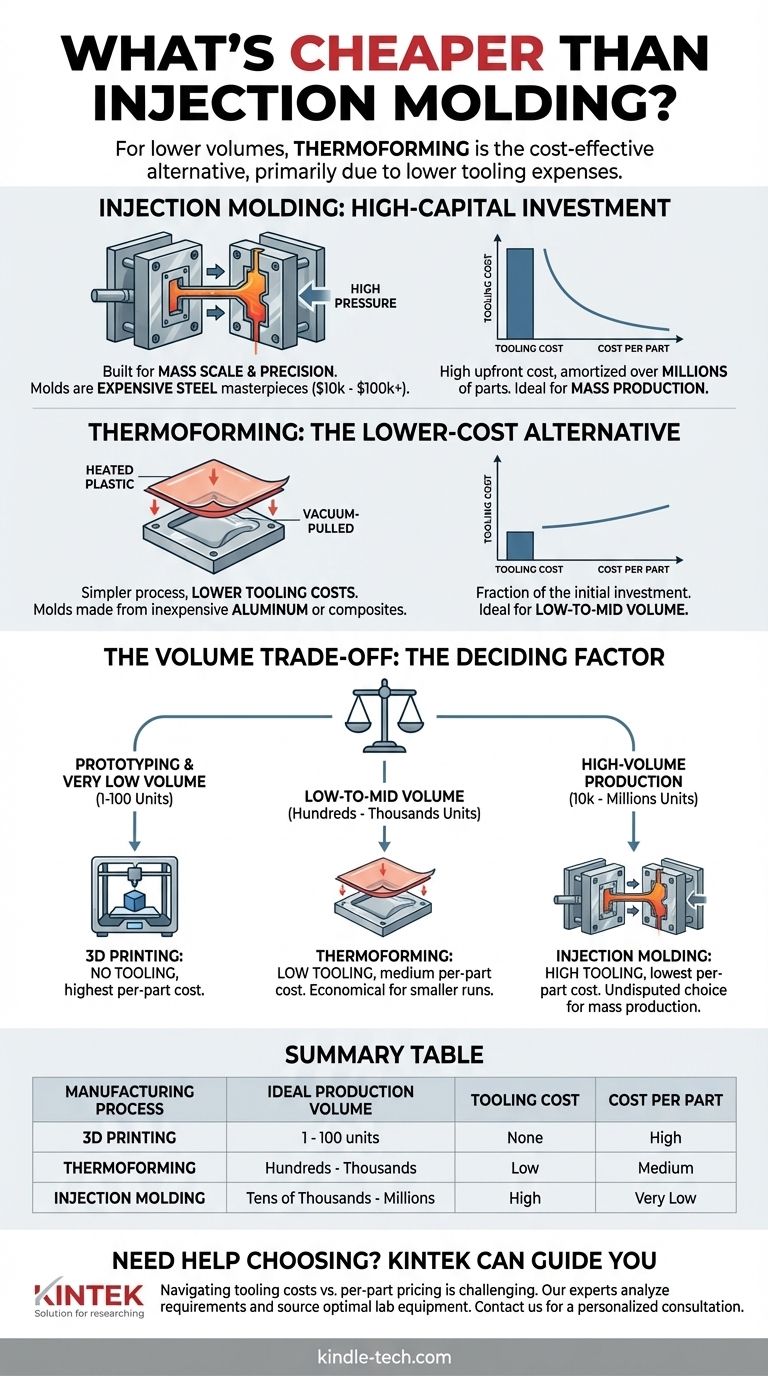
For projects with lower production volumes, the most common and cost-effective alternative to injection molding is thermoforming. The primary reason for this cost difference lies not in the plastic material itself, but in the massive upfront expense of the molds, or "tooling," required for injection molding. Thermoforming utilizes much simpler, less expensive molds, making it far more accessible for smaller-scale production runs.
The central decision between injection molding and its alternatives is a calculation of volume. While injection molding has the highest initial cost, it delivers the lowest price per part at scale. Cheaper alternatives have a lower entry cost but a higher price per part, making them ideal for smaller quantities.

Why Injection Molding is a High-Capital Investment
To understand the alternatives, we must first understand why injection molding carries such a significant upfront cost. The entire process is built for massive scale and precision.
The Cost of High-Precision Molds
Injection molding works by forcing molten plastic into a steel mold under immense pressure. These molds are masterpieces of engineering.
They must be machined from hardened steel to withstand thousands of tons of clamping pressure and repeated heat cycles without degrading. This requires expensive materials, specialized machinery, and significant design and validation time, often costing tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
The Breakeven Point
This high tooling cost is an investment that is amortized, or spread out, across the total number of parts produced.
If a mold costs $50,000, that cost is prohibitive for making 1,000 parts ($50 per part in tooling alone). However, for one million parts, the tooling cost drops to just 5 cents per part, making the process incredibly economical at scale.
The Lower-Cost Alternative: Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a fundamentally simpler process that avoids the high pressures and complexities of injection molding, leading to dramatic savings in tooling.
How Thermoforming Works
In thermoforming, a sheet of plastic is heated until it becomes pliable. It is then stretched over or into a single-sided mold and cooled to its final shape. Air pressure or a vacuum is often used to pull the sheet tightly against the mold for better detail.
The Tooling Advantage
Because the process does not involve extreme pressures, the molds don't need to be made from hardened steel.
Molds for thermoforming are often machined from inexpensive aluminum or even composite materials. This drastically reduces the cost and lead time, making the initial investment a fraction of what is required for injection molding.
Per-Part Cost Dynamics
While the upfront cost is lower, the per-part cost in thermoforming is typically higher than in injection molding. Cycle times are longer, and the process starts with a sheet of plastic, from which the final part must be trimmed, creating more material waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a manufacturing process is never just about the price tag. Each method comes with critical limitations and advantages.
Part Complexity and Geometry
Injection molding excels at creating complex, three-dimensional parts with intricate features like ribs, bosses, and varying wall thicknesses.
Thermoforming is best suited for simpler, shell-like parts with relatively uniform wall thickness, such as trays, enclosures, and packaging. It cannot produce the same level of fine detail as injection molding.
Production Volume is the Deciding Factor
This is the most critical trade-off.
Thermoforming is ideal for low-to-mid volume production, typically from a few hundred to several thousand units. The low tooling cost makes these smaller runs economically viable.
Injection molding is the undisputed choice for mass production, from tens of thousands into the millions of units, where the low per-part cost justifies the high initial investment.
A Note on 3D Printing
For prototyping and very low volumes (typically 1-100 units), 3D printing is the cheapest option of all.
It requires no custom tooling, allowing you to go directly from a digital design to a physical part. However, its high per-part cost and slow speed make it unsuitable for any significant production scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your production volume is the single most important factor in determining the most economical manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or producing 1-100 units: 3D printing offers the lowest initial cost because it requires no tooling.
- If your primary focus is low-to-mid volume production (hundreds to thousands of units): Thermoforming provides a cost-effective solution with a much lower tooling investment than injection molding.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production (tens of thousands to millions of units): Injection molding becomes the most cost-effective option, as the high initial tooling cost is offset by an extremely low price per part.
Ultimately, choosing the right process means matching the method's economic model to the scale of your ambition.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Process | Ideal Production Volume | Tooling Cost | Cost Per Part |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | 1 - 100 units | None | High |
| Thermoforming | Hundreds - Thousands | Low | Medium |
| Injection Molding | Tens of Thousands - Millions | High | Very Low |
Need Help Choosing the Right Manufacturing Process?
Navigating the trade-offs between upfront tooling costs and per-part pricing can be challenging. The team at KINTEK specializes in helping labs and manufacturers select the optimal equipment for their specific production needs and budget constraints.
We can help you:
- Analyze your project requirements and production volume
- Identify the most cost-effective manufacturing method
- Source reliable lab equipment for prototyping and production
Contact us today for a personalized consultation, and let our experts guide you to the most efficient and economical solution for your project.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What is a hydraulic floor press used for? A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Lab Applications
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification


















