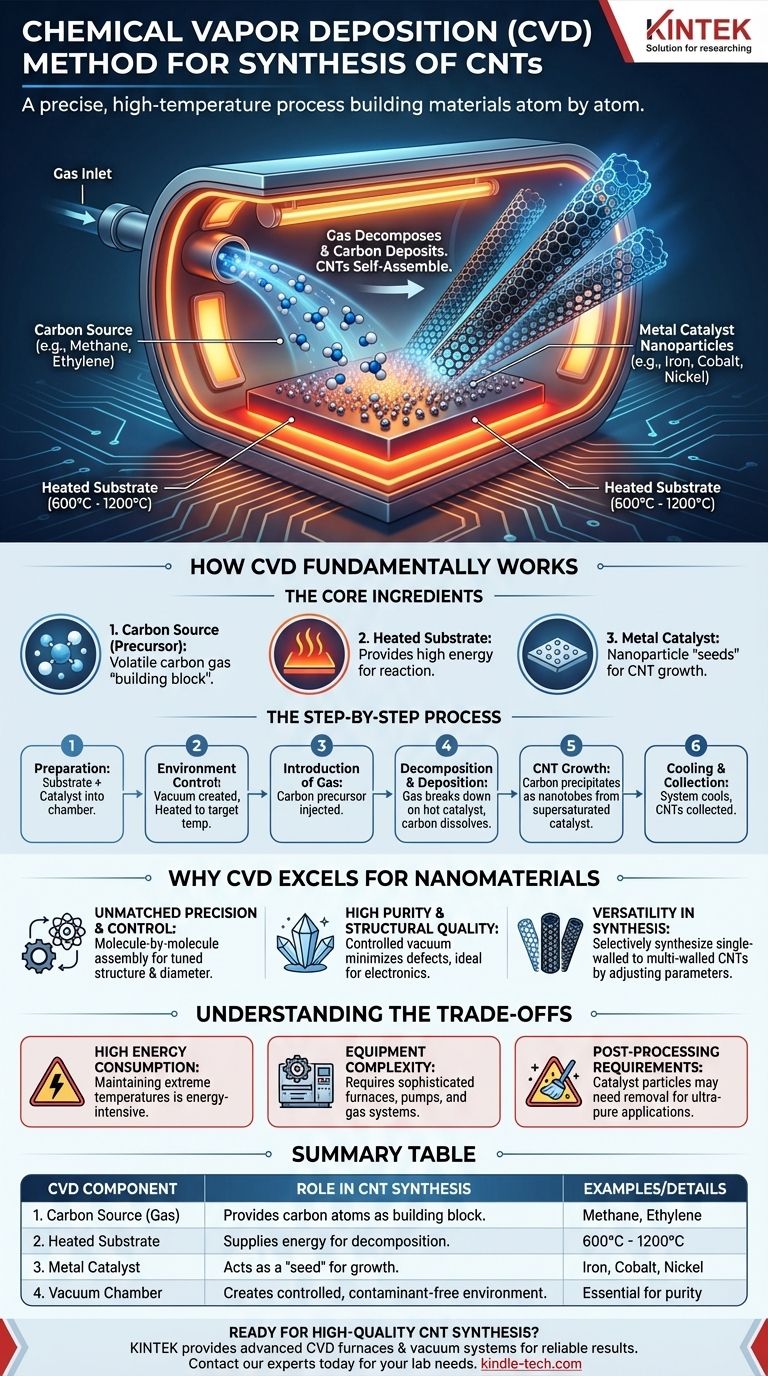
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a high-temperature manufacturing process that builds materials from the bottom up, atom by atom. For synthesizing Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs), a carbon-containing gas is introduced into a vacuum chamber where it decomposes upon contact with a heated, catalyst-coated surface. This reaction breaks the gas apart, allowing carbon atoms to deposit and self-assemble into the distinct cylindrical structure of a nanotube.
The critical insight is that CVD is not a simple coating technique; it's a precise chemical reaction in a controlled environment. It uses heat and a catalyst to transform a gas into a highly ordered, solid nanostructure, making it the dominant method for producing high-quality CNTs.
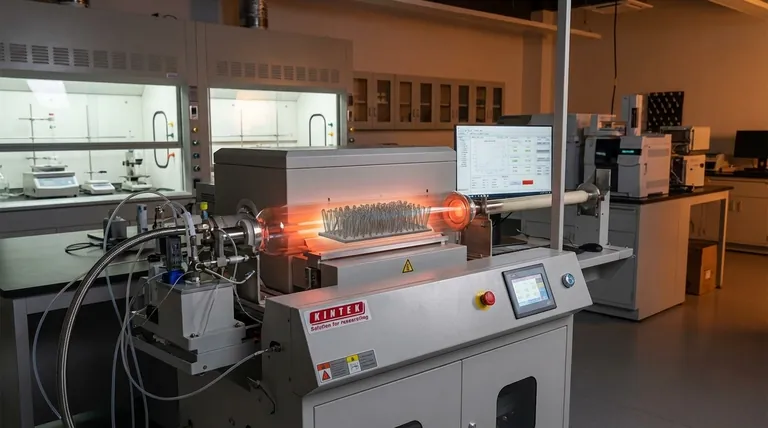

How CVD Fundamentally Works
To understand CVD, it is best to break it down into its core components and the sequence of events. The entire process is orchestrated inside a controlled vacuum chamber to ensure purity and precision.
The Core Ingredients
The success of the synthesis depends on three key elements working in concert.
1. The Carbon Source (Precursor) This is a volatile, carbon-containing gas that acts as the "building block" material. Common precursors include hydrocarbons like methane, ethylene, or acetylene.
2. The Heated Substrate This is the surface where the CNTs will grow. It is heated to a very high reaction temperature, often between 600°C and 1200°C, providing the energy needed for the chemical reaction.
3. The Metal Catalyst Tiny nanoparticles of a metal, such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, are deposited onto the substrate. These catalyst particles are the "seeds" from which the individual nanotubes nucleate and grow.
The Step-by-Step Process
The synthesis follows a clear, repeatable sequence.
- Preparation: A substrate coated with catalyst nanoparticles is placed inside a furnace or reaction chamber.
- Environment Control: The chamber is sealed, and a vacuum is created to remove air and potential contaminants. It is then heated to the target reaction temperature.
- Introduction of Gas: The carbon precursor gas is injected into the hot chamber.
- Decomposition & Deposition: Upon contact with the hot catalyst particles, the precursor gas decomposes. Carbon atoms dissolve into the catalyst.
- CNT Growth: When the catalyst becomes supersaturated with carbon, carbon atoms precipitate out in the form of a cylindrical, bonded tube. The nanotube grows as more precursor gas decomposes.
- Cooling & Collection: Once the desired growth is achieved, the system is cooled, and the CNTs on the substrate are collected.
Why CVD Excels for Nanomaterials
CVD has become the leading method for creating high-quality CNTs and other nanomaterials like graphene for several clear reasons.
Unmatched Precision and Control
The process deposits material molecule by molecule. This bottom-up assembly allows for significant control over the final product's structure, diameter, and orientation by carefully tuning parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow.
High Purity and Structural Quality
The controlled vacuum environment prevents unwanted side reactions and minimizes contamination. This results in CNTs with a very low defect count, which is critical for high-performance applications in electronics and sensors.
Versatility in Synthesis
The CVD method is not limited to just one type of nanotube. By adjusting the catalyst and growth conditions, it is possible to selectively synthesize different types of CNTs, from single-walled to multi-walled structures, for various applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the CVD process is not without its challenges and considerations. Acknowledging them is key to understanding its practical application.
High Energy Consumption
The process relies on maintaining extremely high temperatures for the duration of the synthesis, which can be energy-intensive and costly, especially at an industrial scale.
Equipment Complexity
Operating under high vacuum and high temperatures requires sophisticated and expensive equipment, including specialized furnaces, vacuum pumps, and gas handling systems.
Post-Processing Requirements
Catalyst particles can sometimes get trapped within or at the tip of the finished CNTs. For ultra-pure applications, a subsequent purification step is often required to remove this residual metal contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of CVD synthesis is directly tied to the desired outcome for the Carbon Nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: CVD is the definitive choice due to its ability to produce uniform, high-purity CNTs with minimal structural defects.
- If your primary focus is bulk production for composites or mechanical reinforcement: CVD offers an excellent balance of quality and scalability, making it a robust industrial method.
- If your primary focus is academic research or material discovery: The high degree of control offered by CVD makes it an ideal platform for experimenting with growth parameters to create novel nanostructures.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition provides the controlled environment necessary to guide the self-assembly of atoms into one of modern science's most remarkable materials.
Summary Table:
| CVD Component | Role in CNT Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Carbon Source (Gas) | Provides carbon atoms as the building block (e.g., methane, ethylene). |
| Heated Substrate | Supplies energy for the decomposition reaction (600°C - 1200°C). |
| Metal Catalyst | Acts as a 'seed' for nanotube nucleation and growth (e.g., iron, cobalt). |
| Vacuum Chamber | Creates a controlled, contaminant-free environment for precise synthesis. |
Ready to synthesize high-quality Carbon Nanotubes for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment—including precision CVD furnaces, vacuum systems, and gas handling components—needed for reliable and efficient CNT synthesis. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools to achieve superior material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your nanomaterials innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries



















