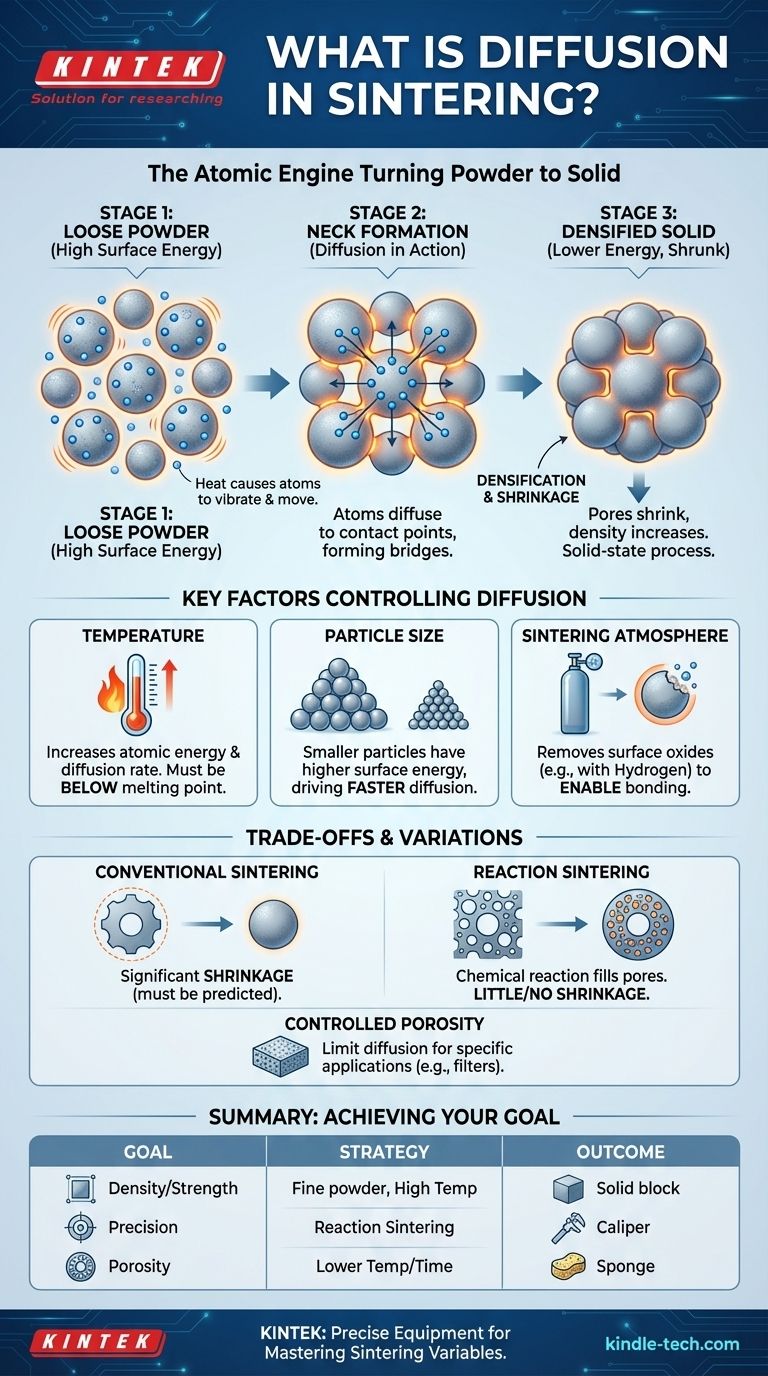
In the context of sintering, diffusion is the fundamental, atomic-level mechanism that bonds loose powder particles into a solid, coherent mass. Driven by heat, atoms migrate from the bulk of each particle to the points of contact between particles, forming bridges or "necks" that grow over time, increasing the component's density and strength. This entire process occurs in the solid state, well below the material's melting point.
Sintering is not a process of melting particles together. It is a solid-state transformation where atomic diffusion is the engine, driven by the thermodynamic need to reduce the high surface energy of a fine powder. Understanding and controlling diffusion is the key to controlling the final properties of the sintered part.
The Fundamental Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
What is Atomic Diffusion?
At its core, atomic diffusion is the movement of atoms within a material. When a solid is heated, its atoms gain thermal energy and begin to vibrate more intensely. This vibration allows them to jump from their fixed position in the crystal lattice to an adjacent empty spot.
This movement is not entirely random. Atoms tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, or from high-energy states to lower-energy states, to achieve a more stable configuration.
How Diffusion Drives Sintering
A collection of loose powder has an enormous amount of surface area, which corresponds to a high state of surface energy. The universe naturally favors lower energy states. Sintering leverages this principle.
When a compacted powder is heated, the system's primary goal is to reduce its total surface area. The most efficient way to do this is for atoms to move from the surface of the particles into the voids between them, effectively bonding the particles together and reducing the total exposed surface.
The Formation and Growth of "Necks"
The sintering process begins at the points where individual powder particles touch. Driven by heat, atoms diffuse towards these contact points, creating a small bridge of solid material known as a neck.
As the process continues, more atoms migrate to these necks, causing them to grow wider. This growth pulls the centers of the adjacent particles closer together, which shrinks the pores between them and increases the overall density of the component. This process is called densification.
Key Factors That Control Diffusion
Temperature
Temperature is the most critical variable in sintering. Higher temperatures provide atoms with more thermal energy, dramatically increasing the rate of diffusion.
However, the temperature must remain below the material's melting point. The goal is to enable solid-state diffusion, not to melt the powder, which would result in a loss of shape and control.
Particle Size
Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This creates a stronger thermodynamic driving force for the system to reduce its surface energy.
As a result, finer powders generally sinter at lower temperatures and faster rates than coarser powders, leading to higher final densities.
Sintering Atmosphere
The gas surrounding the powder during heating—the sintering atmosphere—plays a crucial role. A primary function is to prevent or remove surface oxides.
Oxide layers on metal particles act as a barrier, physically blocking the atomic diffusion required for necks to form. A reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen or cracked ammonia) can strip these oxides away, allowing diffusion to proceed efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
The Challenge of Shrinkage
Because solid-state diffusion involves moving material to fill in the gaps between particles, conventional sintering almost always results in component shrinkage.
This densification is often desirable for strength, but it must be precisely predicted and accounted for in the initial mold design to achieve the correct final dimensions.
An Alternative Path: Reaction Sintering
Some advanced processes, like reaction sintering, introduce a chemical reaction alongside diffusion. For example, a porous silicon preform can be infiltrated with molten carbon, which reacts to form silicon carbide (SiC) in the pores.
This method can produce highly dense parts with very little or no shrinkage, as the new material is formed in-situ, filling the voids. This makes it ideal for large or complex shapes where dimensional stability is critical.
Porosity vs. Densification
While the goal is often to achieve maximum density, sometimes a certain level of porosity is desired, such as in the manufacturing of filters or self-lubricating bearings.
By controlling the diffusion rate—using lower temperatures, shorter times, or larger particles—engineers can limit neck growth and preserve a network of interconnected pores within the final part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Mastering a sintering process means controlling the rate and extent of diffusion to achieve a specific outcome. Your approach should be tailored to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Use finer powders, higher sintering temperatures, and a controlled reducing atmosphere to promote the highest possible rate of diffusion.
- If your primary focus is precise dimensional control: Consider reaction sintering to minimize shrinkage, or use precise modeling to predict and compensate for the shrinkage in a conventional process.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity (e.g., for filters): Use lower temperatures, shorter cycle times, or larger initial particles to limit the extent of diffusion and neck growth.
By viewing sintering through the lens of atomic diffusion, you can move from simple observation to precise control, turning loose powder into a highly engineered and reliable component.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Diffusion & Sintering |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases atomic energy and diffusion rate; must be below melting point. |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles have higher surface energy, driving faster diffusion and densification. |
| Atmosphere | Removes surface oxides (e.g., with hydrogen) to enable unobstructed atomic diffusion. |
| Time | Longer sintering times allow for more extensive neck growth and densification. |
Ready to master the sintering process for your materials?
Understanding and controlling atomic diffusion is key to achieving the perfect balance of density, strength, and dimensional accuracy in your sintered components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consumables needed to precisely manage every variable—from temperature profiles to sintering atmospheres.
Whether your goal is maximum density, controlled porosity, or minimal shrinkage, our solutions are designed to help you achieve reliable, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering needs and help you turn powder into high-performance parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do infrared thermal imagers or thermocouple monitoring systems evaluate SiC coating thermal oxidation resistance?
- What are the three sample preparation techniques? Master the Key Stages for Accurate Analysis
- What is the main advantage of annealing? Restore Ductility and Relieve Internal Stress for Better Workability
- How does RF sputtering work? Deposit Thin Films on Insulating Materials
- How do precision dripping systems or syringes contribute to sodium alginate bead formation? Achieve Scientific Uniformity
- What is the purpose of a rotavap? Achieve Gentle, Efficient Solvent Removal for Your Lab
- How do ULT freezers increase energy efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Cooling for Cost and Sustainability
- Is pyrolysis of plastic harmful? The Truth About Toxic Byproducts and Environmental Risks



















