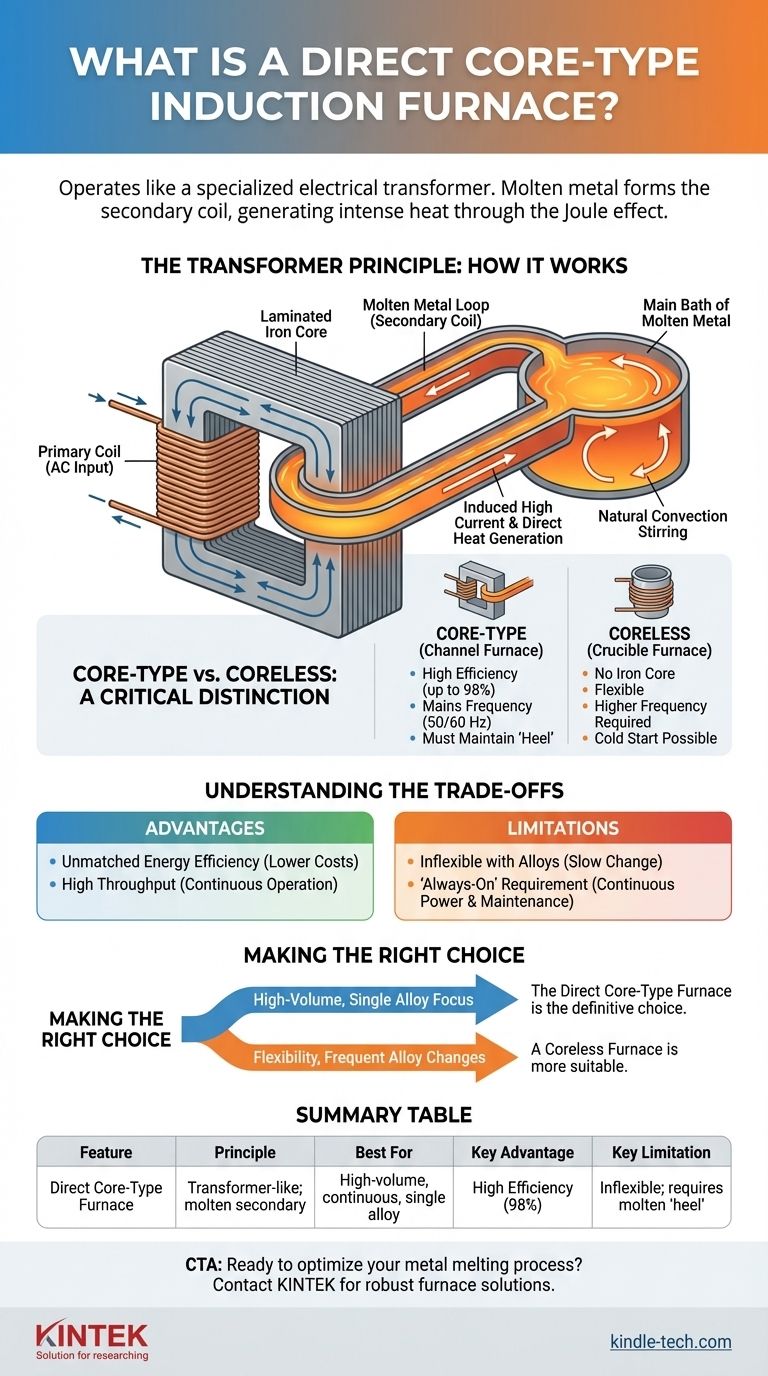
In essence, a direct core-type induction furnace operates like a specialized electrical transformer where the molten metal itself forms the secondary coil. An alternating current is passed through a primary coil wrapped around a central iron core, inducing a powerful secondary current within a closed loop or "channel" of liquid metal. This induced current generates intense heat directly within the material due to electrical resistance, a process known as the Joule effect.
Choosing the right furnace technology requires understanding its fundamental design and operational philosophy. The direct core-type furnace is engineered for exceptional efficiency in continuous, high-volume environments, but that same specialized design creates significant operational constraints.
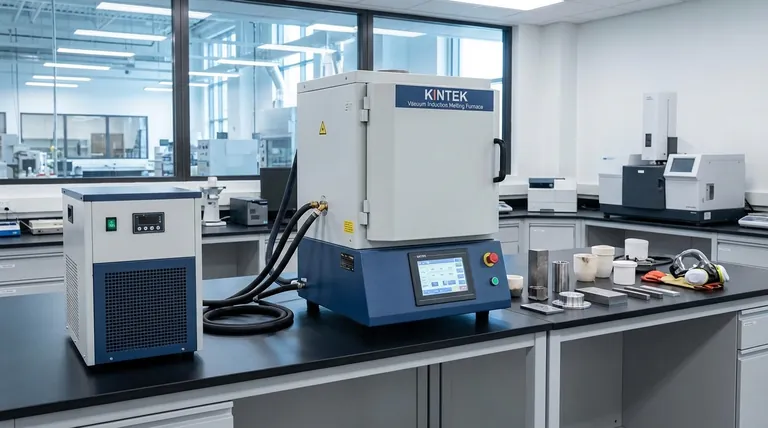

The Transformer Principle: How It Works
A direct core-type furnace, also known as a channel furnace, is a marvel of electrical engineering. Its efficiency stems from its direct application of transformer principles to the material being melted.
The Core and Primary Coil
At the heart of the system is a laminated iron core, just like in a standard power transformer. A primary coil, made of copper, is wound around this core. When mains-frequency alternating current (AC) flows through this primary coil, it generates a powerful, concentrated magnetic field within the iron core.
The Molten Metal Loop
This is the defining feature of the design. The furnace shell holds the main bath of molten metal, but a small, distinct loop or channel of this metal passes through the iron core, encircling it. This channel of conductive liquid metal acts as a single-turn secondary coil of the transformer.
Direct Heat Generation
The alternating magnetic field from the primary coil and core induces a very high-amperage, low-voltage current in the secondary coil—the molten metal loop. The inherent electrical resistance of the metal causes this massive current to generate extreme heat directly within the loop.
Natural Stirring Action
This intense heating within the channel causes the metal to expand and its density to decrease. This temperature and density difference creates a natural convection current, forcing the superheated metal from the channel to circulate out into the cooler main bath, providing a constant, gentle stirring action that ensures temperature and chemical uniformity.
Core-Type vs. Coreless: A Critical Distinction
The term "induction furnace" is broad. Understanding the difference between a core-type and a coreless furnace is essential for any technical evaluation.
The Role of the Iron Core
The most fundamental difference is the presence of the iron core. A core-type furnace uses it to concentrate the magnetic field, resulting in extremely high electrical efficiency (up to 98%). A coreless furnace has no iron core; the primary coil simply surrounds a crucible containing the metal, making it less efficient but far more flexible.
Operating Frequency
This structural difference dictates the operating frequency. Core-type furnaces are highly efficient at low, mains frequencies (50/60 Hz). Coreless furnaces often require medium-to-high frequency power supplies to induce sufficient current without a core, adding to system complexity.
Startup and Flexibility
A coreless furnace can melt a charge of solid metal from a cold start. A core-type furnace must be started with a "heel" of molten metal to complete the secondary circuit. It cannot be fully emptied or allowed to cool, as the metal in the channel would solidify and break the circuit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The unique design of the core-type furnace presents a clear set of advantages and disadvantages that define its use case.
The Advantage: Unmatched Energy Efficiency
By functioning as a highly coupled transformer, the core-type furnace offers the highest electrical efficiency of any induction furnace. This translates directly into lower energy costs for every ton of metal processed, a significant factor in high-production foundries.
The Advantage: High Throughput
These furnaces are designed as continuous or semi-continuous melters and holders. Their efficiency and large capacity make them ideal for operations that require a constant supply of molten metal with a consistent composition.
The Limitation: Inflexibility with Alloys
Because the furnace can never be fully drained, changing alloys is a slow and costly process of dilution. This makes the core-type furnace almost exclusively suited for operations dedicated to a single, consistent metal grade.
The Limitation: The "Always-On" Requirement
The need to maintain a liquid metal heel means the furnace must be kept under power continuously. It cannot be shut down for weekends or short maintenance periods without significant effort and risk. This demands constant monitoring and a robust maintenance plan for the refractory lining of the critical channel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Selecting the correct furnace is a strategic decision based entirely on your production goals and operational model.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of a single alloy: The core-type furnace is the definitive choice for its superior energy efficiency and high throughput.
- If your primary focus is flexibility, frequent alloy changes, or intermittent operation: A coreless induction furnace is the more suitable and practical choice, despite its lower electrical efficiency.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental design difference empowers you to select the furnace that serves as a strategic asset, not an operational constraint.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Core-Type Furnace |
|---|---|
| Principle | Operates like a transformer; molten metal is the secondary coil. |
| Best For | High-volume, continuous production of a single alloy. |
| Key Advantage | Extremely high electrical efficiency (up to 98%). |
| Key Limitation | Inflexible; requires a constant molten metal "heel." |
Ready to optimize your metal melting process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment, including advanced furnace solutions. Whether you're evaluating a core-type furnace for its unmatched efficiency or need a more flexible system, our experts can help you select the right technology for your specific alloy and production goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's productivity and reduce your operational costs. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















