In materials science, field assisted sintering (FAST) is a family of advanced processing techniques that uses an electric current to rapidly consolidate powders into a dense solid. Often called Electric Current Assisted Sintering (ECAS), its most common form is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). By passing a current directly through the powder or its mold, the process generates intense internal heat, drastically reducing the time and temperature required compared to conventional methods.
Traditional sintering is a slow process limited by the speed of external furnace heating. Field assisted sintering revolutionizes this by using an electric current for direct, internal heating, enabling dramatically faster production times and achieving superior material properties.
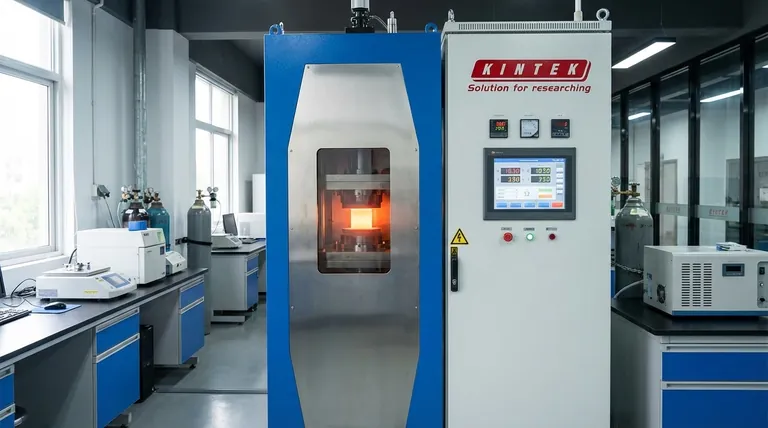

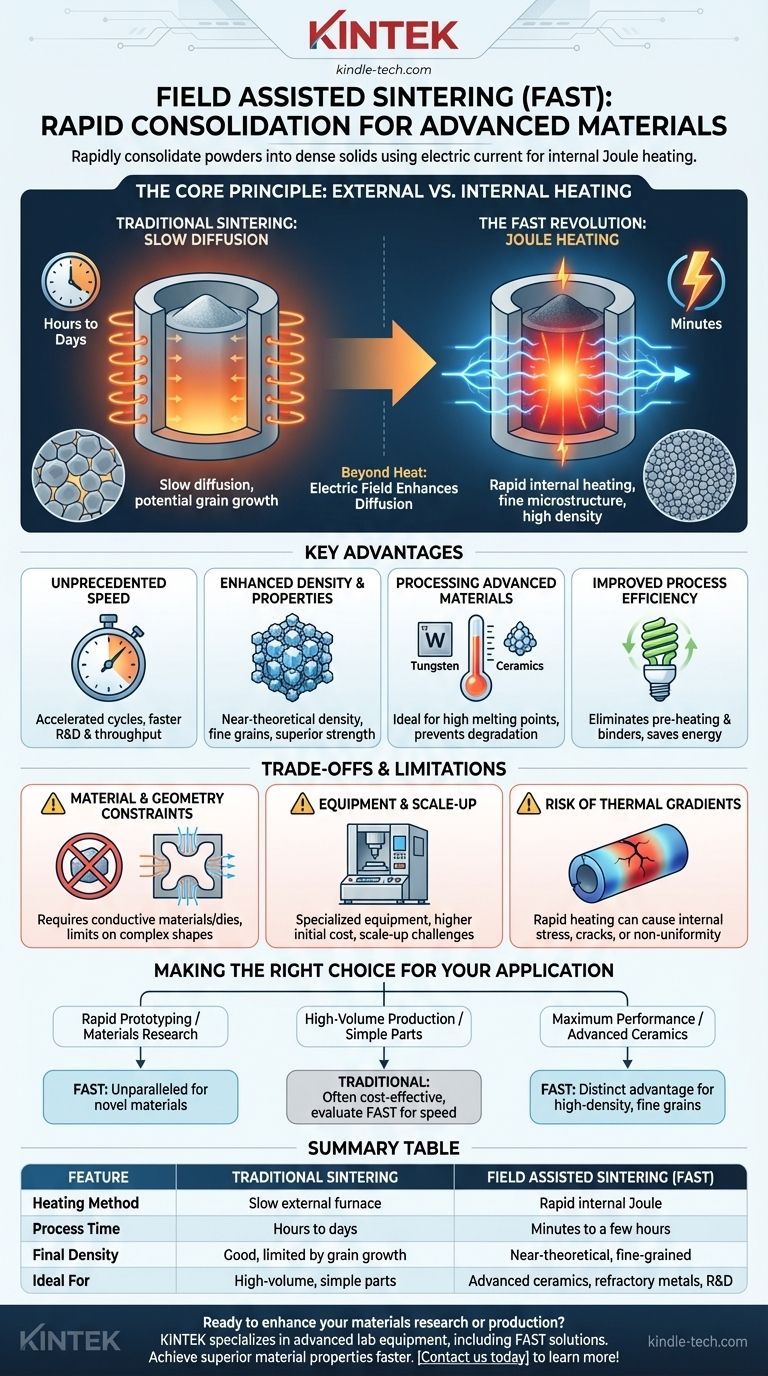
The Core Principle: From External Furnaces to Internal Heating
To understand the value of FAST, you must first understand the limitations of the process it improves upon.
Traditional Sintering: Slow Diffusion
Conventional sintering involves placing compacted powder into a large furnace. The furnace slowly heats the material from the outside-in.
This prolonged heat, applied below the material's melting point, gives atoms the energy to slowly diffuse across the boundaries of individual powder particles, fusing them into a single solid piece. This process is effective but often takes many hours.
The FAST Revolution: Joule Heating
Field assisted sintering abandons the external furnace. Instead, a powerful DC electric current is passed directly through the conductive mold and, in many cases, the powder itself.
The material's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up internally—a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This direct, volumetric heating is incredibly fast and efficient.
Beyond Heat: The Role of the Electric Field
The "field" in FAST is critical. Beyond just generating heat, the strong electric field is thought to enhance the diffusion of atoms and help break down oxide layers on particle surfaces. This further accelerates the densification process beyond what heat alone could accomplish.
Key Advantages of Field Assisted Sintering
The shift from slow, external heating to rapid, internal heating provides several major advantages in manufacturing and materials development.
Unprecedented Speed
FAST can reduce processing cycles from many hours in a traditional furnace to just a few minutes. This dramatic reduction in time accelerates research and development and increases manufacturing throughput.
Enhanced Density and Properties
The rapid cycle prevents unwanted grain growth that can occur during long furnace treatments. This allows for the creation of materials with extremely fine microstructures and near-theoretical densities.
Lower porosity and finer grains directly translate to superior mechanical properties, such as increased strength and hardness.
Processing Advanced Materials
FAST is exceptionally well-suited for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten, molybdenum, and advanced ceramics. Traditional methods struggle to process these materials effectively without causing degradation or excessive grain growth.
Improved Process Efficiency
By eliminating long furnace pre-heating cycles and the need for processing aids (binders) in the powder, FAST saves significant energy and simplifies the overall manufacturing workflow.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, FAST is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application.
Material and Geometry Constraints
The most fundamental requirement is that either the material itself or the die containing it must be electrically conductive to allow for Joule heating. This can limit its use for some non-conductive polymers or ceramics without a special setup.
Additionally, achieving a uniform current distribution in very large or complex shapes can be difficult, potentially leading to inconsistent heating and density.
Equipment and Scale-Up
The equipment required for FAST, particularly for Spark Plasma Sintering, is more specialized and often carries a higher initial cost than conventional furnace systems.
Scaling the process for mass production of very large parts remains a significant engineering challenge.
Risk of Thermal Gradients
The same rapid heating that provides FAST its speed can also create steep temperature differences within the part. If not carefully controlled, these thermal gradients can lead to internal stress, cracks, or a non-uniform microstructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your material, geometry, and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or materials research: FAST is an unparalleled tool for quickly creating dense samples of novel or difficult-to-process materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple parts: Traditional press-and-sinter powder metallurgy may remain more cost-effective, though FAST should be evaluated for its potential to slash cycle times.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum performance in advanced ceramics or refractory metals: FAST provides a distinct advantage in producing high-density, fine-grained materials whose properties are unachievable with conventional methods.
Ultimately, adopting field assisted sintering is a strategic decision to leverage its unique capabilities for unprecedented speed, efficiency, and final material quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Sintering | Field Assisted Sintering (FAST) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Slow external furnace heating | Rapid internal Joule heating |
| Process Time | Hours to days | Minutes to a few hours |
| Final Density | Good, but limited by grain growth | Near-theoretical, fine-grained |
| Ideal For | High-volume, simple parts | Advanced ceramics, refractory metals, R&D |
Ready to enhance your materials research or production with rapid, high-performance sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including field assisted sintering solutions. Our expertise helps you achieve superior material density and properties faster than traditional methods. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, refractory metals, or developing new materials, KINTEK has the tools and support to accelerate your innovation.
Contact us today to learn how our sintering technology can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification



















