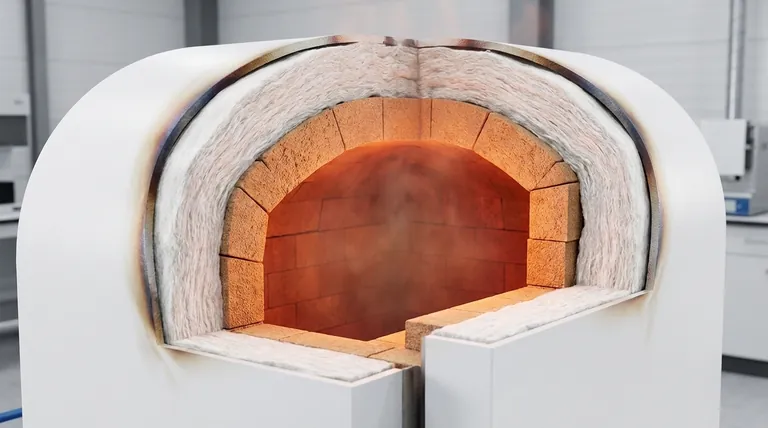
In essence, furnace lining is the protective, heat-resistant inner layer of any high-temperature furnace or kiln. This critical system is composed of specialized materials known as refractories, which are designed to withstand extreme heat, chemical attack, and physical wear. Far from being simple insulation, the lining is a multi-functional barrier that directly impacts the furnace's safety, efficiency, and operational lifespan.
Furnace lining is not just a passive shell; it is an engineered system that contains extreme thermal energy, protects the furnace's structural integrity, and prevents contamination of the final product. The selection of the right lining is a fundamental decision that balances thermal performance, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability.
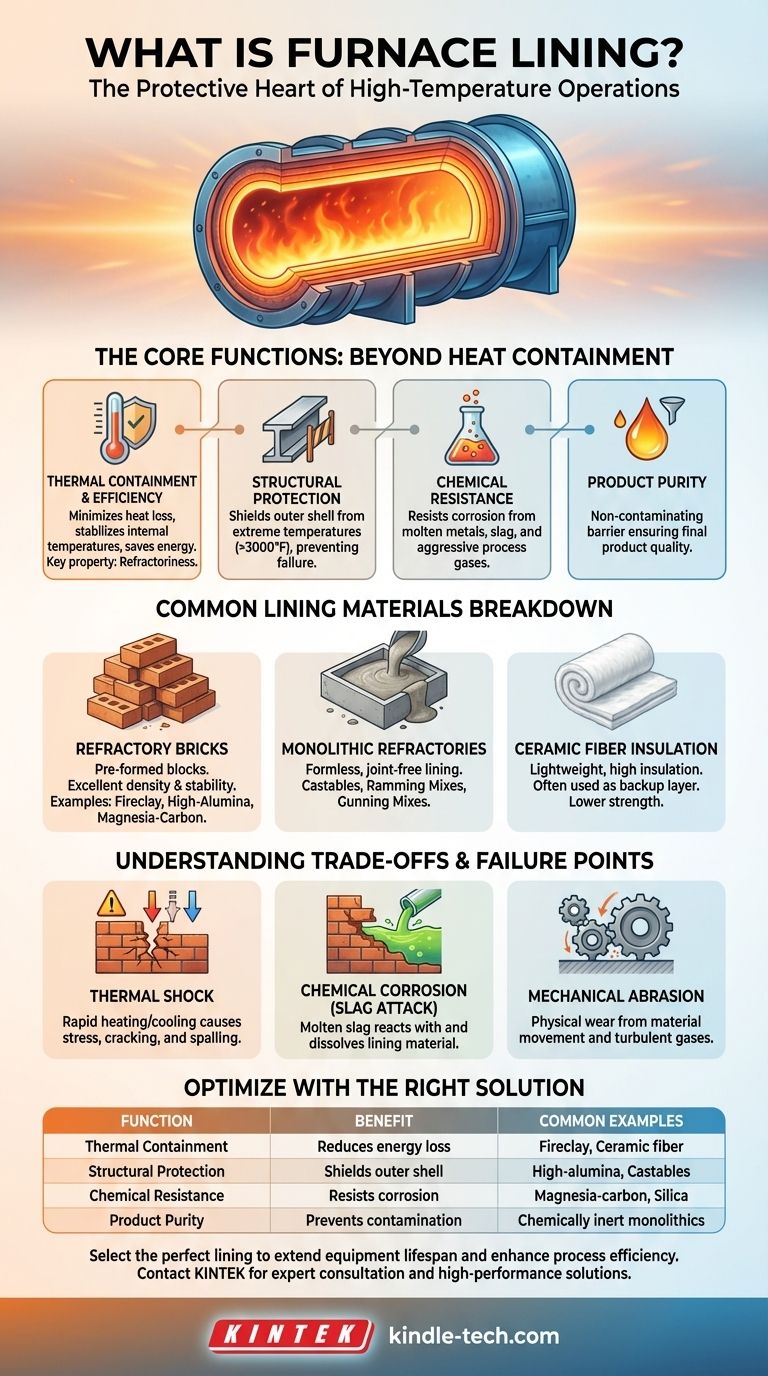
The Core Functions of Furnace Lining
Understanding the purpose of a furnace lining requires looking beyond simple heat containment. It serves several distinct and equally critical roles that enable high-temperature industrial processes.
Thermal Containment and Efficiency
The most obvious function is to keep the intense heat inside the furnace. A properly designed lining minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, which directly translates to lower energy consumption and more stable internal process temperatures.
The key property here is refractoriness, the material's ability to withstand high temperatures without deforming or melting.
Structural Protection
Industrial furnaces are typically built with an outer steel shell. This steel would quickly fail if exposed directly to the internal operating temperatures, which can exceed 3000°F (1650°C).
The refractory lining acts as a thermal shield, keeping the temperature of the steel shell within safe operational limits and protecting it from catastrophic failure.
Chemical Resistance
The internal environment of a furnace is often chemically aggressive. Molten metals, slag (impurities), and process gases can corrode and degrade materials.
The lining is selected to be as chemically inert as possible to the specific substances it will contact, preventing it from being eaten away and extending its service life.
Product Purity
In applications like metal casting or glass manufacturing, the purity of the final product is paramount.
The furnace lining serves as a non-contaminating barrier, ensuring that elements from the furnace structure do not leach into the molten material and compromise its quality.
A Breakdown of Common Lining Materials
The choice of refractory material is dictated by the furnace's specific operating conditions. Materials are generally categorized into three main families.
Refractory Bricks
These are pre-formed, fired blocks that are assembled with mortar to create the lining. They offer excellent density and stability.
Common types include fireclay for general use, high-alumina for higher temperatures and abrasion resistance, and specialized bricks like silica, magnesite, or magnesia-carbon for specific chemical environments found in steel and glass making.
Monolithic Refractories
These are formless materials, similar to high-tech concrete, that are installed and then hardened in place. Their key advantage is creating a joint-free lining, which is less susceptible to penetration.
This category includes castables (poured like concrete), ramming mixes (compacted into place), and gunning mixes (sprayed onto a surface).
Ceramic Fiber Insulation
These are lightweight materials, such as ceramic fiber blankets, boards, and modules, known for their exceptional insulating properties.
Due to their lower mechanical strength and chemical resistance, they are often used as a "backup" insulation layer behind a denser hot-face lining of brick or monolithic refractory.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
No furnace lining lasts forever. Understanding the common failure mechanisms is crucial for maintenance, safety, and selecting the right material.
Thermal Shock
Rapid changes in temperature—either heating up too quickly or cooling down too fast—create internal stresses in the refractory material.
This stress can cause cracking and spalling, where pieces of the lining face break away, exposing the layers behind it to damage.
Chemical Corrosion (Slag Attack)
This is a primary cause of failure in metal-melting furnaces. The molten slag, which is a byproduct of the process, can chemically react with the refractory lining, dissolving it over time.
Choosing a refractory with the correct chemical composition (e.g., an acidic refractory for an acidic slag) is critical to mitigate this.
Mechanical Abrasion and Erosion
The physical movement of materials inside the furnace, such as charging scrap metal or the flow of molten material and turbulent gases, can physically wear away the lining.
In these high-wear zones, materials with high mechanical strength and density, like high-alumina bricks or abrasion-resistant castables, are required.
Selecting the Right Lining for Your Application
The optimal furnace lining is always a tailored solution based on the specific demands of the process.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (e.g., steelmaking): High-refractoriness materials like magnesia-carbon or high-alumina bricks are essential for the primary hot-face lining.
- If your primary focus is resisting chemical attack (e.g., from acidic slags): You must prioritize materials with a compatible chemical nature, such as silica or specific alumina-silicate refractories.
- If your primary focus is complex shapes or rapid repairs: Monolithic castables or gunning mixes provide unparalleled flexibility for installation in difficult-to-reach areas or for patching existing linings.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency in intermittent-use furnaces: A lightweight, low-thermal-mass lining using ceramic fiber modules can significantly reduce the energy needed for each heat-up cycle.
Ultimately, viewing your furnace lining as a high-performance engineered system is the first step toward achieving a safer, more efficient, and more profitable operation.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Containment | Reduces energy loss, stabilizes temperature | Fireclay bricks, Ceramic fiber |
| Structural Protection | Shields outer steel shell from extreme heat | High-alumina bricks, Castables |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists corrosion from slag and process gases | Magnesia-carbon bricks, Silica bricks |
| Product Purity | Prevents contamination of molten materials | Chemically inert monolithic refractories |
Optimize your furnace performance and safety with the right lining solution. The selection of refractory materials is critical to your operation's efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including furnace systems and refractory solutions tailored to your specific thermal and chemical requirements. Let our experts help you select the perfect lining to extend your equipment's lifespan and enhance your process. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do SiC sandpaper and alumina polishing suspension play in steel pretreatment? Achieve Optimal Coating Adhesion
- What are the classification of refractory materials? A Guide to Chemical and Thermal Selection
- Why are silicon carbide and silicon oxide polishing consumables required for surface treatment? Ensure Accurate Data
- What is the function of combining an ultrasonic disperser and a mechanical stirrer? Achieve Flawless Slurry Dispersion
- Why use fluoroelastomer seals for ball milling halide electrolytes? Ensure Pure LiCl and ZrCl4 Synthesis
- What is the maximum pressure for a vacuum pump? Understanding Ultimate Vacuum for Your Lab Needs
- What is the function of a laboratory magnetic stirrer in Ni–Cr–P electrodeposition? Optimize Ion Transport & Coating
- What environmental conditions must a ball mill jar meet? Prevent Fe3Al Oxidation with Advanced Sealing



















