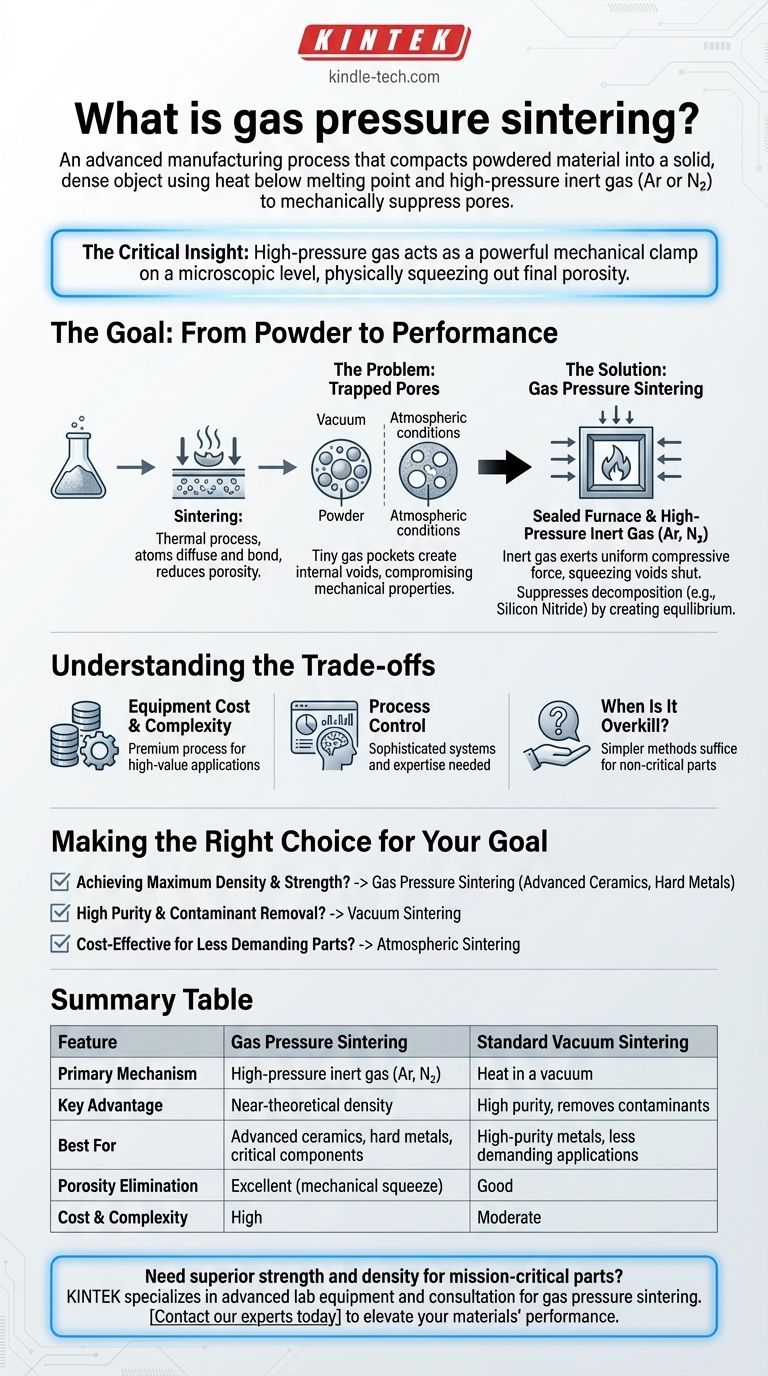
In short, gas pressure sintering is an advanced manufacturing process that compacts a powdered material into a solid, dense object by heating it below its melting point while subjecting it to high-pressure inert gas. Unlike vacuum sintering, which removes the atmosphere, this method uses the immense physical pressure of a gas like argon or nitrogen to mechanically suppress the formation of pores and defects. This results in a final component with superior density, strength, and overall performance.
The critical insight is that while heat enables atoms to bond, high-pressure gas acts as a powerful mechanical clamp on a microscopic level. It physically squeezes out the final traces of porosity that other sintering methods cannot, making it the definitive choice for creating materials that must perform under extreme conditions.

The Goal: From Powder to Performance
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process for turning a powdered material into a solid mass. This is achieved using heat and pressure, but critically, the temperature remains below the material's melting point.
Instead of melting and re-solidifying, the heat energizes the atoms in the powder particles, causing them to diffuse and form strong bonds with neighboring particles. This process reduces the empty space, or porosity, between the particles, dramatically increasing the material's density and strength.
The Problem: Trapped Pores
In simpler sintering methods, like those done in a vacuum or at atmospheric pressure, tiny pockets of gas can become trapped within the material as it densifies.
These trapped pockets create internal pores or voids. Even a small amount of porosity can severely compromise the mechanical properties of the final part, acting as a starting point for cracks and failures.
How Gas Pressure Sintering Solves the Problem
The Role of Inert Gas
Gas pressure sintering takes place inside a sealed furnace that can withstand extreme pressures. After initially removing ambient air (often with a vacuum), the chamber is backfilled with a chemically inert gas, most commonly argon or nitrogen, to pressures many times higher than normal atmosphere.
This gas is "inert," meaning it will not chemically react with the material being sintered. Its purpose is purely mechanical.
The Power of External Pressure
As the material is heated to its sintering temperature, this high-pressure gas exerts a uniform, compressive force on the exterior of the component.
This external pressure works against the internal pressure of any trapped gas inside the pores. It effectively squeezes these voids shut, forcing the gas to dissolve into the surrounding material and allowing the pores to close completely. This leads to a final part with near-theoretical density.
Suppressing Decomposition
For some advanced ceramics, like silicon nitride, high temperatures can cause the material itself to decompose or vaporize.
In these specific cases, using a high-pressure nitrogen atmosphere (the same gas that is part of the material's chemistry) creates an equilibrium. This high-pressure environment prevents the material from breaking down, enabling it to be sintered at the required high temperatures without damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Furnaces capable of handling both high temperatures and extreme gas pressures are significantly more complex and expensive than vacuum or atmospheric furnaces. This makes gas pressure sintering a premium process reserved for high-value applications.
Process Control
Simultaneously managing extreme temperature and pressure requires sophisticated control systems and deep process expertise. Any deviation can impact the quality and consistency of the final product.
When Is It Overkill?
For many metals or ceramics in non-critical applications, the near-perfect density achieved by gas pressure sintering is not necessary. Simpler, more cost-effective methods like vacuum or atmospheric sintering are often sufficient for the job.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best sintering method depends entirely on the material and the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and mechanical strength: Gas pressure sintering is the superior choice, especially for advanced ceramics, hard metals, and mission-critical components.
- If your primary focus is high purity and removing contaminants: Vacuum sintering is highly effective, as the vacuum helps pull out volatile impurities before and during densification.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of less demanding parts: Conventional atmospheric sintering may be perfectly adequate and is the most economical option.
Ultimately, choosing gas pressure sintering is an investment in achieving the highest possible material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gas Pressure Sintering | Standard Vacuum Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | High-pressure inert gas (Ar, N₂) | Heat in a vacuum |
| Key Advantage | Achieves near-theoretical density | High purity, removes contaminants |
| Best For | Advanced ceramics, hard metals, critical components | High-purity metals, less demanding applications |
| Porosity Elimination | Excellent (mechanically squeezes out pores) | Good |
| Cost & Complexity | High | Moderate |
Need to create components with superior strength and density?
Gas pressure sintering is the definitive process for manufacturing mission-critical parts that must perform under extreme stress, heat, or pressure. If your project involves advanced ceramics, hard metals, or any application where material failure is not an option, this advanced technique is your solution.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consultation needed to implement gas pressure sintering effectively. Our solutions are designed for researchers and manufacturers who demand the highest material integrity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how gas pressure sintering can elevate your materials' performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press furnace for sintering CNT/Cu composites? Superior Density & Bonding
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot-pressing furnace in the preparation of Cu-2Ni-7Sn/45 steel composites?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in Al-20% Si/Graphite fabrication? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?



















