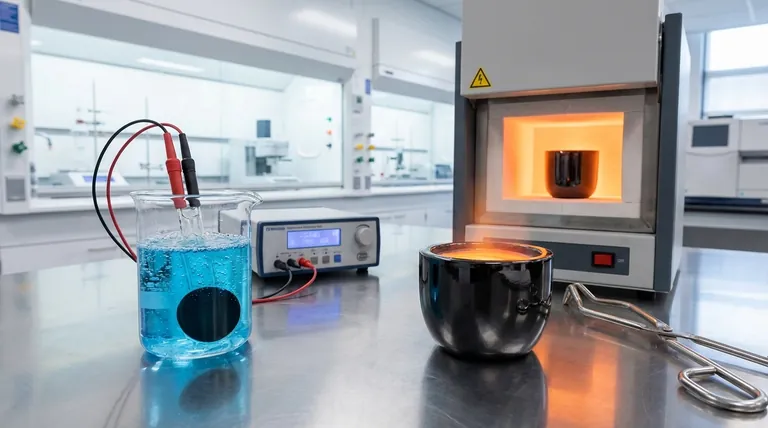
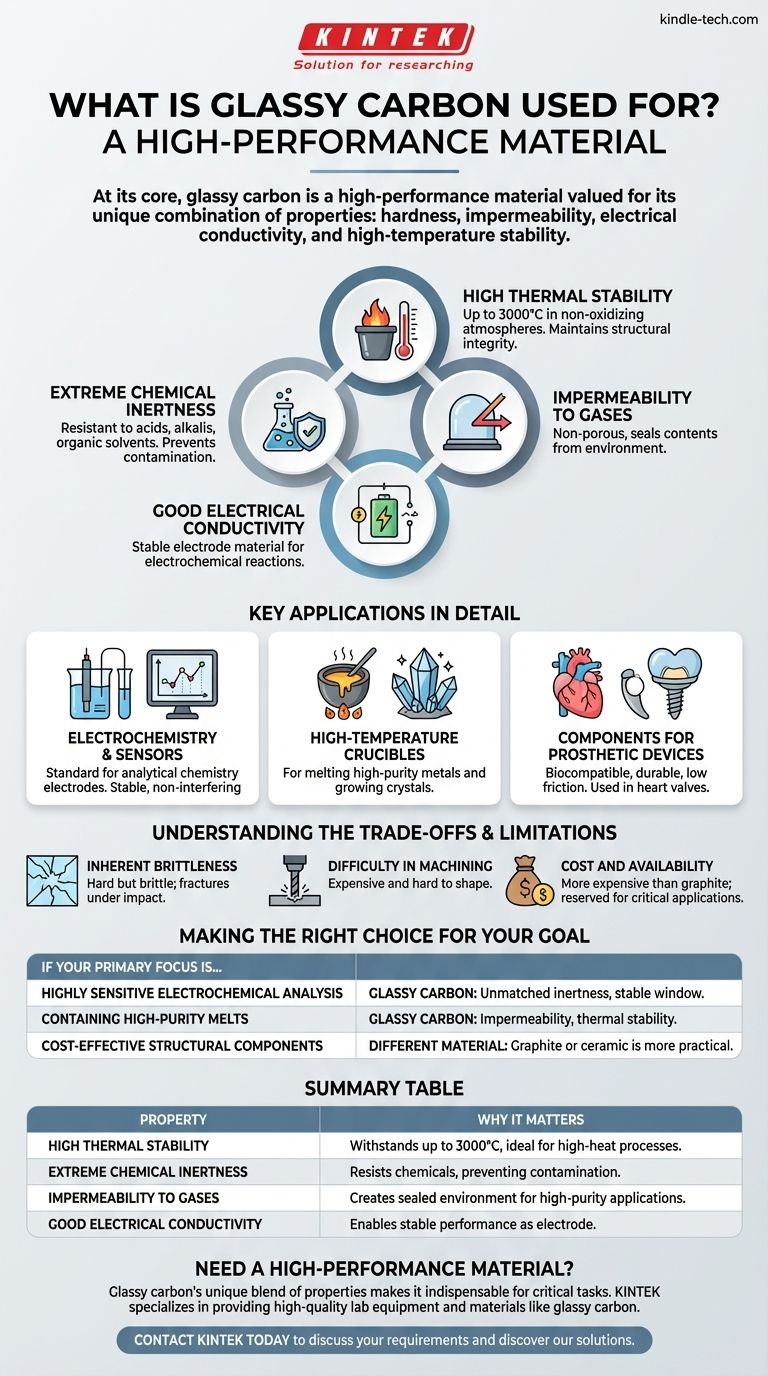
At its core, glassy carbon is a high-performance material valued for its unique combination of properties. It is widely used as an electrode material in electrochemistry, for high-temperature crucibles used in metallurgy and crystal growth, and as a durable component in some prosthetic devices. Its selection for these demanding roles is a direct result of its exceptional chemical and thermal stability.
Glassy carbon's value comes not from a single attribute, but from its rare combination of properties: the hardness and impermeability of glass, the electrical conductivity of a conductor, and the high-temperature stability and chemical inertness of carbon. Understanding this blend is key to seeing why it excels in such specific, challenging environments.

The Defining Properties of Glassy Carbon
Glassy carbon, also known as vitreous carbon, is a non-graphitizing form of carbon. This means its atomic structure is a disorganized tangle of carbon atoms, unlike the neat, layered sheets found in graphite. This unique structure is the source of its most valuable characteristics.
High Thermal Stability
Glassy carbon can withstand extremely high temperatures, often up to 3000°C, in non-oxidizing atmospheres. It maintains its structural integrity without melting or significant degradation, making it ideal for high-heat processes.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
This material is highly resistant to attack by acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This inertness ensures that it does not corrode or contaminate the substances it comes into contact with, a critical feature for both chemical analysis and high-purity material processing.
Impermeability to Gases
Unlike graphite, which is porous, glassy carbon has a structure that is impermeable to gases and liquids. This makes it an excellent material for creating sealed containers, such as crucibles, that protect their contents from the outside environment.
Good Electrical Conductivity
While not as conductive as metals or graphite, glassy carbon conducts electricity well enough to function effectively as an electrode material. Its conductivity, combined with its inertness, provides a stable surface for electrochemical reactions.
Key Applications in Detail
The properties of glassy carbon make it the material of choice for several specialized industrial and scientific applications.
Electrochemistry and Sensors
Glassy carbon is a standard material for electrodes in analytical chemistry. Its wide potential window and low chemical reactivity mean it provides a stable, non-interfering surface on which to measure chemical reactions, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
High-Temperature Crucibles
For melting high-purity metals, alloys, or growing semiconductor crystals, contamination is a critical failure point. Crucibles made from glassy carbon are used because they do not react with the molten material inside and their impermeability prevents contamination from atmospheric gases.
Components for Prosthetic Devices
The combination of hardness, low friction, wear resistance, and excellent biocompatibility makes glassy carbon suitable for certain medical implants. It has been used in components for prosthetic heart valves because the body does not reject it and it withstands the constant mechanical stress of operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and glassy carbon's unique properties come with practical constraints that are important to understand.
Inherent Brittleness
Like glass, glassy carbon is very hard but also brittle. It cannot withstand sharp impacts or high mechanical shock and will fracture rather than bend or deform.
Difficulty in Machining
The extreme hardness of glassy carbon makes it very difficult and expensive to machine into complex shapes. Parts are typically formed into their final or near-final shape during the initial production process.
Cost and Availability
The complex and energy-intensive manufacturing process makes glassy carbon significantly more expensive than other forms of carbon, such as graphite. Its use is therefore reserved for applications where its unique properties are indispensable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a carbon-based material, the intended application dictates the best choice.
- If your primary focus is highly sensitive electrochemical analysis: Glassy carbon is the superior choice due to its unmatched chemical inertness and broad, stable operating window.
- If your primary focus is containing high-purity melts without contamination: Glassy carbon's impermeability and thermal stability make it ideal for crucibles where purity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective structural components or easily machined parts: A different material, such as isotropic graphite or a specialized ceramic, would be a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, glassy carbon is a specialty material chosen when its specific combination of inertness, stability, and impermeability is mission-critical and justifies its manufacturing constraints.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures up to 3000°C, ideal for high-heat processes. |
| Extreme Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, alkalis, and solvents, preventing contamination. |
| Impermeability to Gases | Creates a sealed environment for high-purity applications. |
| Good Electrical Conductivity | Enables stable performance as an electrode material. |
Need a high-performance material for a demanding application?
Glassy carbon's unique blend of properties makes it indispensable for critical tasks in electrochemistry, high-temperature processing, and medical technology. If your project requires exceptional chemical inertness, thermal stability, and impermeability, the right material is key to your success.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including materials like glassy carbon, to meet the precise needs of laboratories and research facilities. Let our experts help you select the perfect solution to enhance your efficiency and ensure purity in your processes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can benefit your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-purity graphite electrodes as cathodes? Optimize Your Micro-Arc Oxidation Setup
- How can auxiliary equipment be installed on the PTFE electrode stand? Ensure Stable & Interference-Free Setup
- Why does graphite have a high melting point? The Power of Its Giant Covalent Structure
- What are the temperature guidelines for a platinum electrode? Ensure Accurate Measurements & Longevity
- Which polishing cloths should be used with specific sizes of alumina powder? Match Cloth to Powder for a Perfect Finish
- What physical protection measures are necessary when cleaning and handling RVC electrodes? Protect Your Carbon Lattice
- What is the recommended maintenance for electrodes used with an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Longevity and Data Accuracy
- What are the necessary pre-treatment steps for a platinum disk electrode before an experiment? Achieve Reliable Electrochemical Data



















