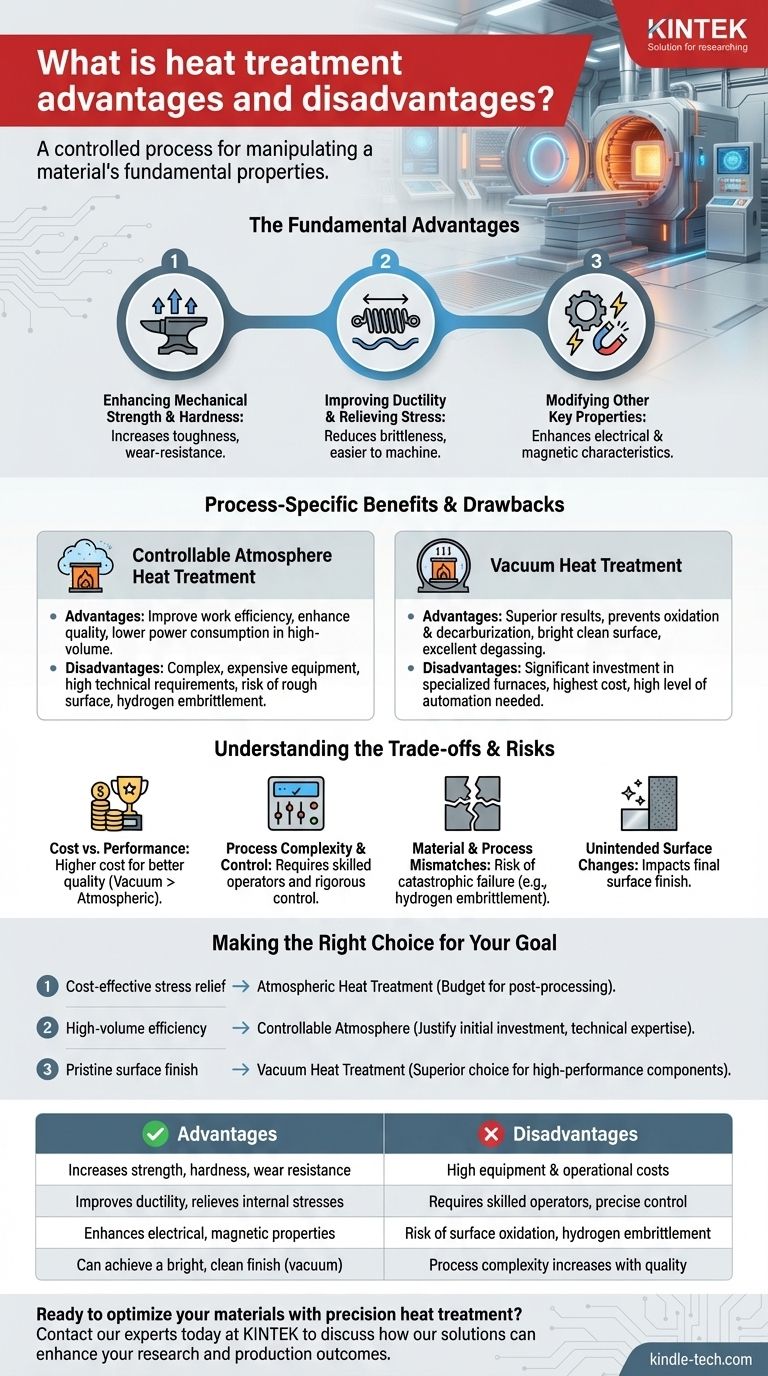
At its core, heat treatment is a powerful, controlled process for manipulating a material's fundamental properties. The primary advantages are significant improvements to mechanical characteristics like strength, hardness, and ductility, as well as relieving internal stresses for easier manufacturing. However, these benefits come with disadvantages, including the potential for high equipment costs, increased process complexity, and the risk of undesirable surface changes or material damage if not executed correctly.
The decision to use heat treatment is a strategic trade-off. While it unlocks superior material performance, you must weigh this benefit against the increased investment in equipment, technical expertise, and process control required to achieve the desired result without introducing new flaws.
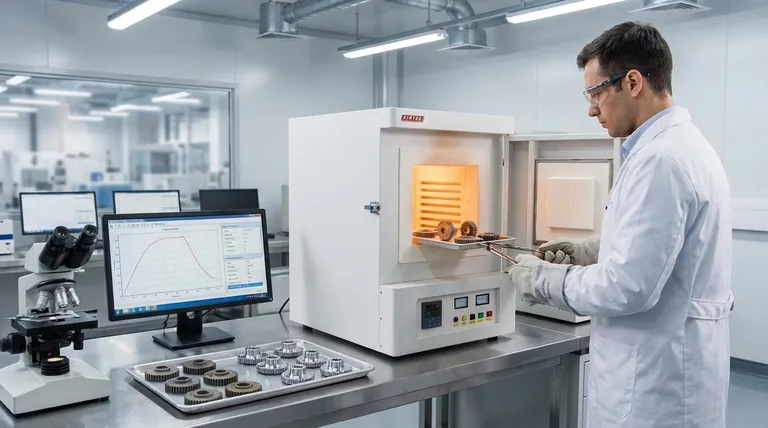

The Fundamental Advantages of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is applied to a wide range of materials, most notably steel, to achieve specific performance goals that the base material cannot meet on its own.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
By carefully controlling heating and cooling cycles, you can alter a material's crystalline structure. This allows you to significantly increase its strength, toughness, and wear-resistance. This is critical for components that will be subjected to high stress or abrasive conditions.
Improving Ductility and Relieving Stress
Conversely, certain heat treatment processes can soften a material, increasing its ductility and reducing brittleness. This is often used to relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing processes like welding or hot forming, making the part easier to machine and less prone to cracking under load.
Modifying Other Key Properties
Beyond mechanical traits, heat treatment can be used to refine a material's properties for specialized applications. This includes enhancing specific electrical and magnetic characteristics, which is vital for components used in motors, sensors, and other electronic devices.
Process-Specific Benefits and Drawbacks
Not all heat treatment is the same. The environment in which the process occurs—air, a controlled gas atmosphere, or a vacuum—dramatically changes the outcome, advantages, and disadvantages.
Controllable Atmosphere Heat Treatment
This method involves heating the material in a furnace filled with a specific mixture of gases to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
- Advantages: It can improve work efficiency, save manpower, and enhance product quality. In high-volume production, it leads to lower consumption of power and auxiliary materials.
- Disadvantages: This process requires complex and expensive equipment with high technical operating requirements. It can leave a rough, non-bright surface and poses a risk of hydrogen embrittlement in certain steels.
Vacuum Heat Treatment
This is a more advanced process where the material is heated in a high vacuum, eliminating nearly all atmospheric gases.
- Advantages: Vacuum treatment offers superior results by completely preventing oxidation and decarburization. This preserves the material's inherent mechanical properties and results in a bright, clean surface that requires no further processing. It also provides excellent degassing and degreasing.
- Disadvantages: The primary drawback is the significant investment in specialized vacuum furnaces and the high level of automation and control required. It is generally the most expensive option.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a heat treatment process requires a clear understanding of its potential downsides and the balance between cost and desired outcome.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct relationship between the cost of the heat treatment process and the quality of the result. While simple atmospheric heating is cheapest, it offers little protection against surface oxidation. Vacuum treatment provides the highest quality but comes at the highest cost.
Process Complexity and Control
Advanced methods like controllable atmosphere and vacuum heat treatment are not simple procedures. They demand rigorous process control and skilled operators to manage gas mixtures or vacuum levels, as errors can easily ruin the workpiece.
Material and Process Mismatches
Not every material is suitable for every type of heat treatment. As noted, using a high-hydrogen atmosphere on certain steels can cause hydrogen embrittlement, a catastrophic failure mode. It is critical to match the material to a compatible and beneficial process.
Unintended Surface Changes
The process environment directly impacts the final surface of the part. A controllable atmosphere may leave a rough finish, while a vacuum process results in a bright, purified surface. This can eliminate the need for costly and time-consuming secondary cleaning or finishing steps.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate heat treatment, you must first define your most critical objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective stress relief and basic property enhancement: A standard atmospheric heat treatment may be sufficient, but you must budget for post-processing steps like cleaning or shot-blasting.
- If your primary focus is high-volume efficiency with good quality control: Controllable atmosphere treatment is a strong option, provided you can justify the initial equipment investment and have the necessary technical expertise on hand.
- If your primary focus is pristine surface finish and ultimate material integrity: Vacuum heat treatment is the superior choice for high-performance, precision components where preventing any surface degradation is paramount.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heat treatment method is a strategic engineering decision that directly impacts the performance, lifespan, and quality of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Increases strength, hardness, and wear resistance | High equipment and operational costs |
| Improves ductility and relieves internal stresses | Requires skilled operators and precise control |
| Enhances electrical and magnetic properties | Risk of surface oxidation or hydrogen embrittlement |
| Can achieve a bright, clean finish (vacuum process) | Process complexity increases with quality |
Ready to optimize your materials with precision heat treatment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're working with standard alloys or high-performance materials, our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect balance of material properties, cost, and quality.
Let us help you select the right furnace and process for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Lab's Needs
- What are the methods of ash analysis? Dry Ashing, Wet Ashing, and More Explained
- What is the temperature range of a furnace? From 1100°C to Over 2000°C Explained
- What are the 3 official methods in determining ash and water content? A Guide to Proximate Analysis
- Dry Ashing vs Wet Ashing: Which Method is Best for Your Sample Analysis?



















