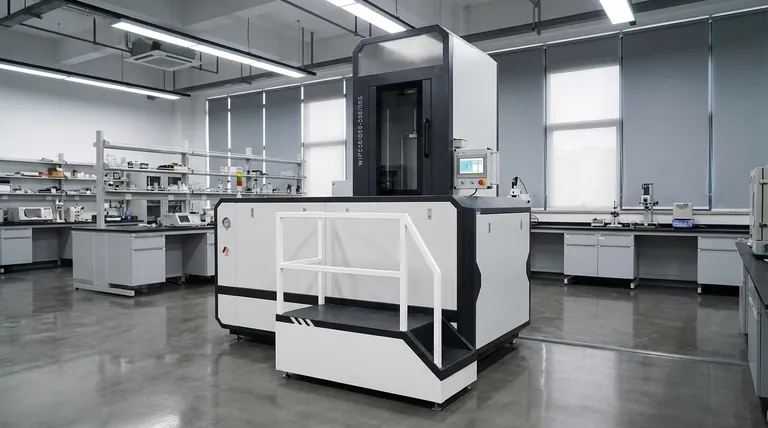
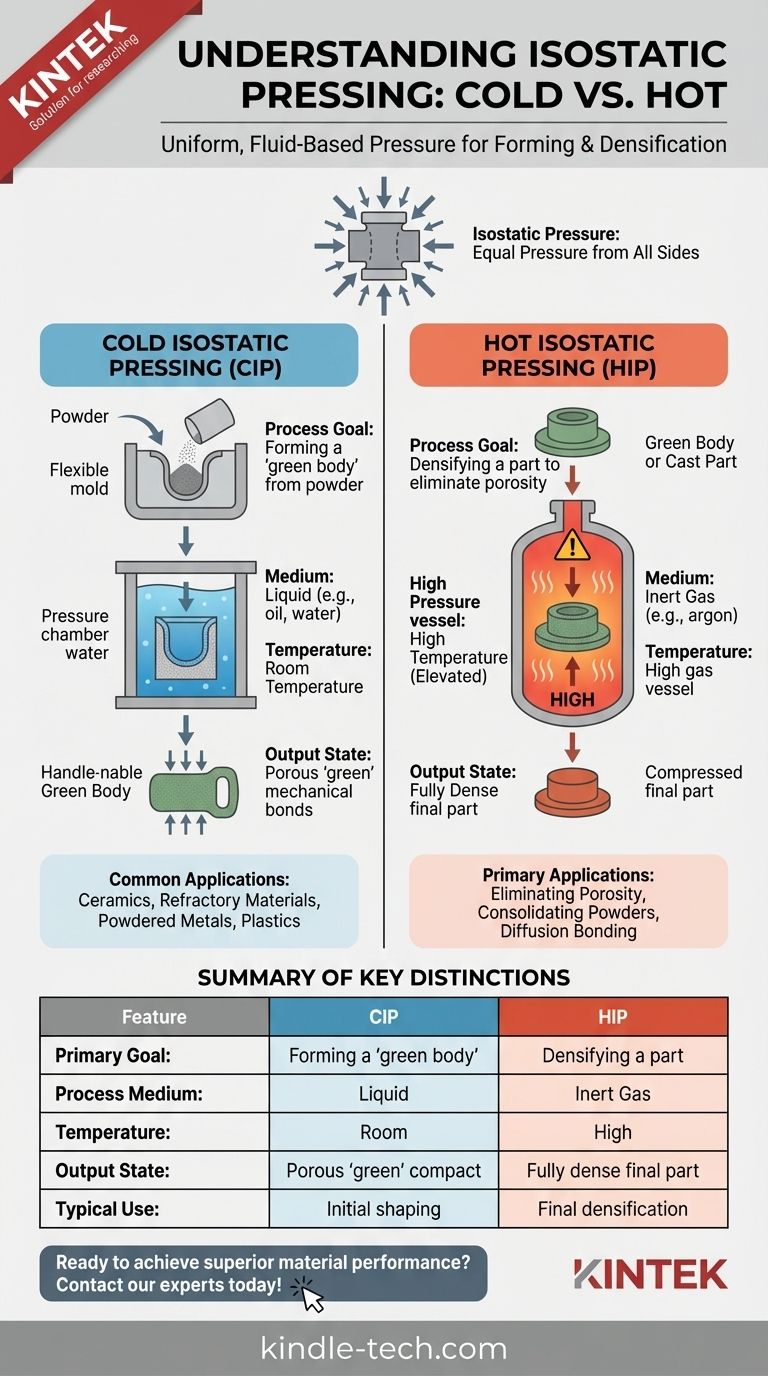
At its core, isostatic pressing is a manufacturing process that uses uniform, fluid-based pressure to compact powders or densify solid parts. Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) uses a liquid at room temperature to form a powdered material into a solid, handleable shape called a "green body." Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), by contrast, uses a heated, high-pressure inert gas to consolidate powders or eliminate microscopic voids in cast components, resulting in a fully dense final part.
The critical distinction lies in their purpose and place in the manufacturing workflow. CIP is a forming step used to create an initial shape from powder, while HIP is a finishing or densification step used to achieve maximum material integrity.

The Fundamental Principle: Isostatic Pressure
How It Works
Both processes are built on the principle of applying uniform, hydrostatic pressure to a component. The part or powder is enclosed in a flexible mold or container, and pressure is transmitted through a surrounding fluid (a liquid for CIP, a gas for HIP).
The Key Advantage
Unlike mechanical pressing, which applies force from one or two directions, isostatic pressure is applied equally from all sides. This results in a part with highly uniform density and predictable, consistent shrinkage during subsequent processing like sintering.
A Closer Look at Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
The Process Explained
In CIP, a powder is placed into a flexible elastomer mold. This mold is then submerged in a pressure chamber filled with a liquid, typically oil or water, at room temperature. The chamber is pressurized, causing the mold to compress the powder particles together.
The "Green Body" Output
The result of CIP is not a finished part but a "green body." This is a solid object where the powder particles are held together by mechanical bonds. It has enough strength to be handled but requires a subsequent heating process (sintering or hot isostatic pressing) to achieve its final properties.
Common Applications
CIP is a versatile forming method used for a wide range of materials. It is ideal for producing parts from ceramics, refractory materials, powdered metals, plastics, and even in food processing.
A Closer Look at Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
The Process Explained
The HIP process takes place inside a high-temperature, high-pressure vessel. Parts are loaded into the vessel, which is then filled with an inert gas, typically argon. The temperature and pressure are raised simultaneously, holding the part at extreme conditions for a set period.
The Fully Dense Output
The combination of high heat and isostatic pressure allows the material's atoms to bond across internal pores. This process eliminates microscopic voids and internal defects, resulting in a component that is virtually 100% dense, with significantly improved mechanical properties.
Primary Applications
HIP serves three main functions:
- Eliminating Porosity: It removes microshrinkage and gas porosity from metal castings.
- Consolidating Powders: It can consolidate metal or ceramic powders into a fully dense, solid part, often with a complex geometry.
- Diffusion Bonding: It can join dissimilar materials together at a molecular level, a process known as cladding.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Process Goal
CIP is a forming step designed to create a preliminary shape from a powder. HIP is a densification step used to achieve final material properties in a green body or a pre-formed part.
Medium and Temperature
CIP uses a liquid medium at room temperature. HIP uses a high-purity inert gas at elevated temperatures.
Initial vs. Final State
CIP creates a handleable but porous "green" compact. HIP creates a fully dense, near-net-shape final part.
Typical Workflow
A component might be formed using CIP and then subsequently densified using HIP to achieve its ultimate performance characteristics. In other cases, HIP is used on its own to improve a part made by another method, such as casting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection between these processes depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex initial shape from powder: CIP is the ideal method to form a uniform "green body" for further processing.
- If your primary focus is eliminating porosity in a cast metal part: HIP is the essential finishing step to ensure maximum strength and fatigue life.
- If your primary focus is consolidating powder into a fully dense final part: You will use HIP, often on a part that has been pre-formed using CIP or another method.
Understanding this distinction between forming and finishing empowers you to select the most effective process for superior material performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Forming a 'green body' from powder | Densifying a part to eliminate porosity |
| Process Medium | Liquid (e.g., oil, water) | Inert Gas (e.g., argon) |
| Temperature | Room Temperature | High Temperature (elevated) |
| Output State | Porous 'green' compact | Fully dense final part |
| Typical Use | Initial shaping of ceramics, metals, plastics | Final densification of castings or powder compacts |
Ready to achieve superior material performance in your lab?
Whether you need to form complex shapes from powder with Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) or eliminate porosity and achieve maximum density with Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to help you create components with unparalleled integrity and consistency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our isostatic pressing solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance



















