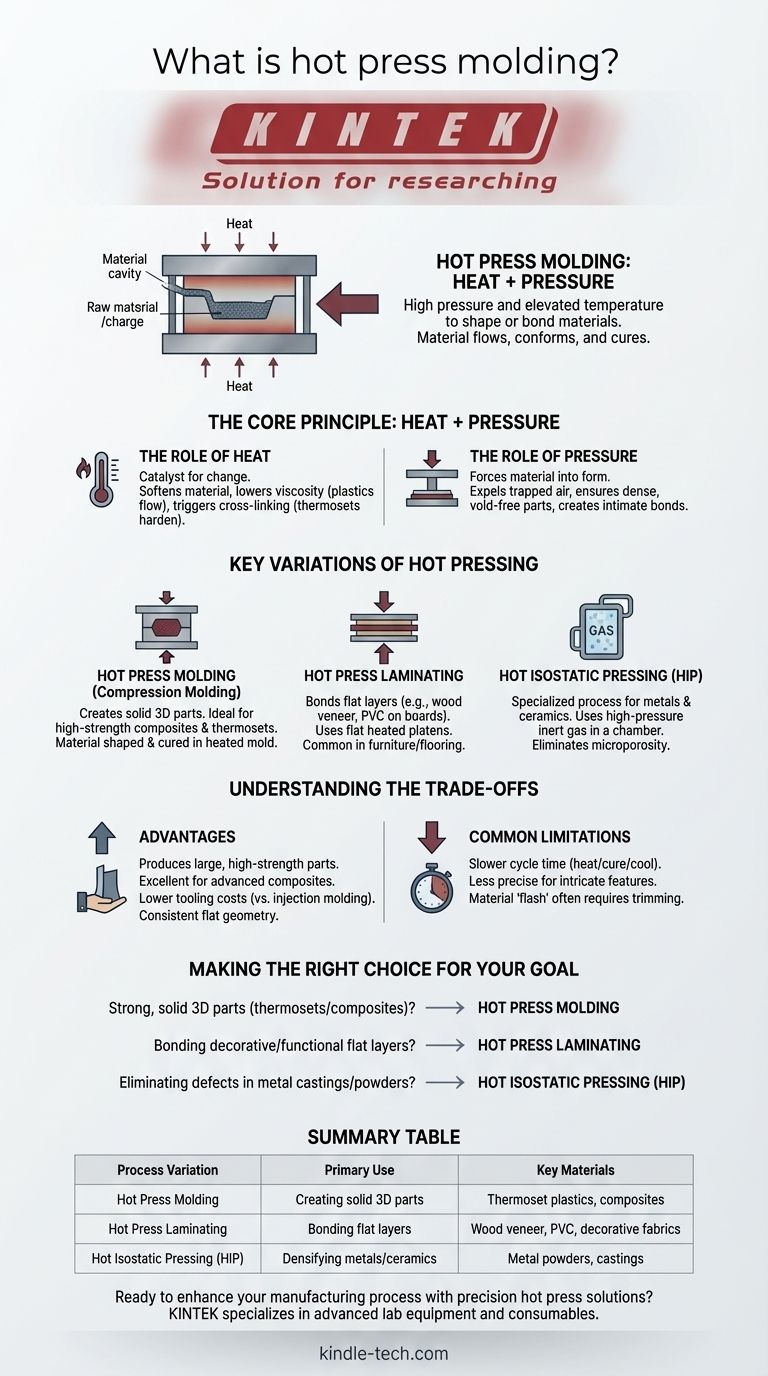
At its core, hot press molding is a manufacturing process that uses high pressure and elevated temperature to shape or bond materials. A raw material, often a thermoset plastic or a composite, is placed into a heated mold. A press then applies significant force, causing the material to flow, conform to the mold's shape, and cure into a solid, finished part.
The term "hot pressing" is a broad category where heat and pressure are the primary tools. The key is to understand that while the principle is simple, its application varies dramatically—from creating solid 3D parts to bonding flat decorative layers or even densifying metal castings.

The Core Principle: Heat + Pressure
The Role of Heat
Heat is the catalyst for change in the process. Its primary function is to soften the raw material or initiate a chemical reaction.
For plastics and composites, heat lowers the viscosity of the polymer resin, allowing it to flow easily and fill every detail of the mold cavity. In thermosetting materials, heat also triggers cross-linking, a chemical reaction that permanently hardens the material.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure provides the force needed to shape the material and ensure its integrity.
It forces the softened material into the desired form, expels any trapped air or volatile gases, and ensures the final part is dense and free of voids. In lamination, pressure creates an intimate bond between the layers.
Key Variations of Hot Pressing
The general term "hot pressing" can describe several distinct industrial processes. Understanding the differences is critical to selecting the right method for a specific application.
Hot Press Molding (Compression Molding)
This is the most common interpretation of the term. A pre-measured amount of molding compound (the "charge") is placed into the bottom half of a heated mold.
The press closes the mold, and the combination of heat and pressure shapes and cures the material. This method is ideal for high-strength composite parts and thermoset plastics.
Hot Press Laminating
This variation focuses on bonding flat layers together rather than creating a complex 3D shape. It's often used in furniture and flooring manufacturing.
As described in the references, a machine presses materials like decorative fabric, wood veneer, or PVC onto a substrate like plywood or MDF. The "mold" is typically two large, flat heated plates called platens.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
This is a highly specialized and distinct process that should not be confused with conventional molding. It is primarily used for metals and ceramics.
Instead of a physical press, parts are placed in a chamber that is filled with a high-pressure inert gas, like argon. The combination of extreme heat and uniform (isostatic) pressure from all directions eliminates internal microporosity in castings or consolidates metal powders into a fully dense solid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Advantages of Hot Press Molding
The primary benefit is its ability to produce very large, high-strength parts, particularly from advanced composite materials that cannot be processed by other means.
Tooling costs are often lower than those for high-volume processes like injection molding. It is also excellent for producing parts with a consistent, flat geometry.
Common Limitations
The main drawback is cycle time. The need to heat the mold, cure the part, and cool it down makes the process significantly slower than alternatives like injection molding.
It can also be less precise for creating highly intricate or complex features. Finally, a small amount of material often squeezes out between the mold halves, creating "flash" that must be trimmed in a secondary operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply these concepts effectively, match the process to your primary manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, solid 3D parts from thermoset plastics or composites: Hot press (compression) molding is the correct process.
- If your primary focus is bonding a decorative or functional surface layer onto a flat board: Hot press laminating is the most efficient method.
- If your primary focus is eliminating internal defects in metal castings or consolidating metal powders: You need the specialized process of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP).
Ultimately, selecting the right manufacturing technique begins with a clear understanding of your material and final part requirements.
Summary Table:
| Process Variation | Primary Use | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Press Molding | Creating solid 3D parts | Thermoset plastics, composites |
| Hot Press Laminating | Bonding flat layers | Wood veneer, PVC, decorative fabrics |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Densifying metals/ceramics | Metal powders, castings |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing process with precision hot press solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for high-strength part production, lamination, and material densification. Whether you're working with composites, laminates, or metals, our expertise ensures optimal performance and durability. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover the right hot press technology for your laboratory or production line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates



















