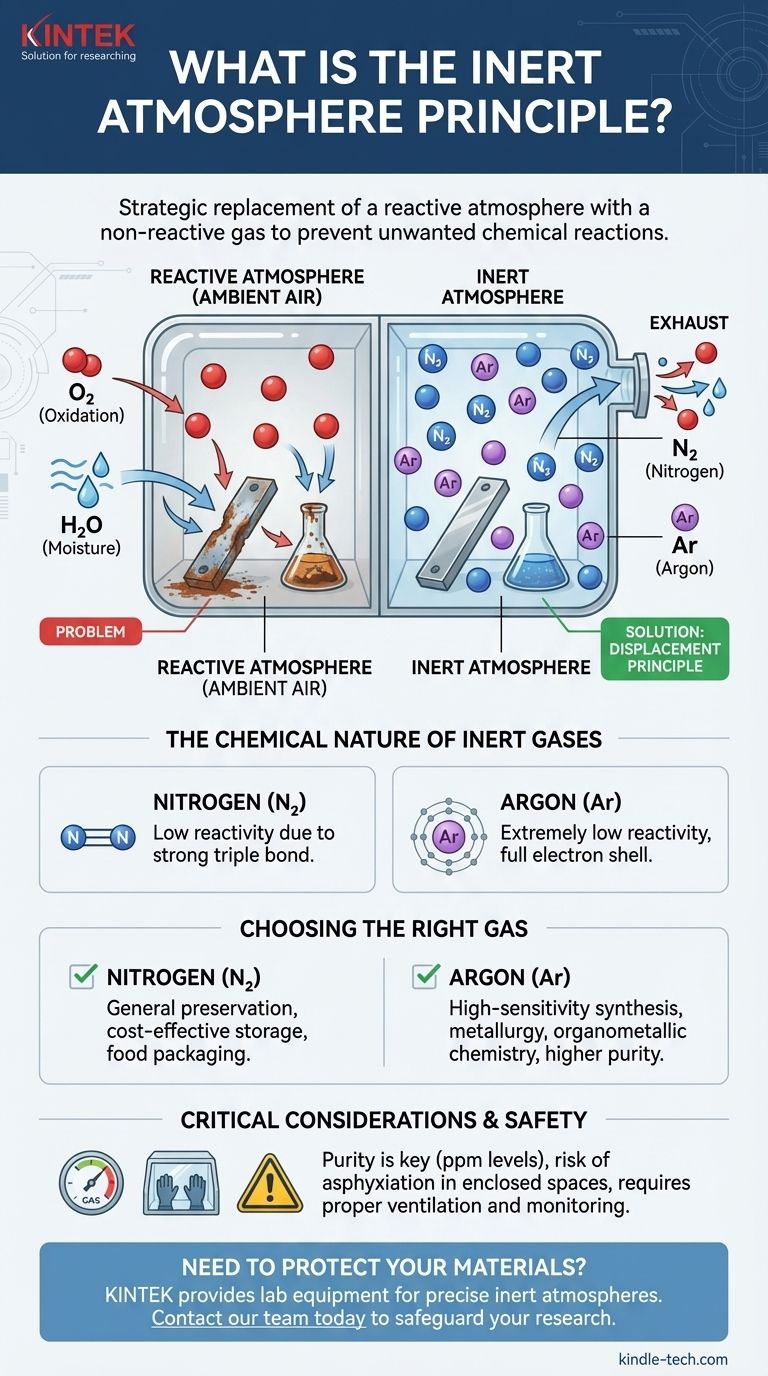
The inert atmosphere principle is the strategic replacement of a reactive atmosphere, like ambient air, with a non-reactive (inert) gas. This is done to create a controlled environment that prevents unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation and moisture-driven degradation. The most common inert gases used for this purpose are nitrogen and argon, which displace oxygen and water vapor from a system.
The goal of an inert atmosphere is not about adding a special ingredient, but about removing problematic ones. By systematically displacing reactive gases like oxygen and water, you create a stable environment that protects sensitive materials and ensures chemical processes proceed without interference.

The Problem: Uncontrolled Atmospheric Reactivity
Normal air, the environment we exist in, is a surprisingly reactive chemical mixture. For many scientific and industrial processes, this reactivity is a significant problem.
Why Normal Air Is a Challenge
Our atmosphere is composed of approximately 21% oxygen and variable amounts of water vapor. Both of these components are highly reactive and eager to participate in chemical reactions.
Oxygen is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it readily accepts electrons from other substances. This is the root cause of common processes like rusting and combustion.
The Impact of Oxidation and Degradation
When sensitive materials are exposed to air, they can degrade quickly. For example, oxygen can ruin a delicate electrochemical experiment by reacting at the electrode surface, obscuring the results you are trying to measure.
Similarly, many advanced chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and reagents will decompose or lose their potency when exposed to oxygen or moisture. This principle is also why food manufacturers package products like potato chips in nitrogen-filled bags to prevent the oils from going rancid.
How an Inert Atmosphere Solves the Problem
An inert atmosphere directly counteracts the threat of atmospheric reactivity by physically changing the environment at a gaseous level.
The Principle of Displacement
The core technique involves purging a container, reaction vessel, or chamber with an inert gas. As the inert gas flows in, it physically pushes out, or displaces, the ambient air containing oxygen and water vapor.
This is often achieved by bubbling the inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) through a liquid solution or by continuously flushing a sealed enclosure, such as a glovebox.
The Chemical Nature of Inert Gases
Gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are chosen because they are extremely non-reactive.
Argon is a noble gas, meaning its outermost electron shell is full. It has no chemical incentive to react with other elements.
Nitrogen gas is a diatomic molecule (N₂) held together by an exceptionally strong triple bond. A significant amount of energy is required to break this bond, making nitrogen gas very stable and unlikely to participate in most reactions under normal conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the principle is straightforward, its practical application involves important choices and potential challenges.
Choosing the Right Gas: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inert atmospheres. It is far less expensive than argon and is sufficiently inert for the vast majority of applications, from food packaging to general chemical storage.
Argon is used for highly sensitive applications where even the slightest reactivity cannot be tolerated. It is chemically more inert than nitrogen and, being denser than air, can form a more stable protective "blanket" over a process. This makes it ideal for high-temperature metallurgy and sensitive organometallic synthesis.
The Challenge of Purity
Simply purging a system once may not be enough. Even trace amounts of oxygen or water vapor (measured in parts per million) can be enough to disrupt highly sensitive experiments or degrade ultra-pure materials.
Achieving and maintaining a high level of purity often requires continuous purging, meticulous sealing of the system, and sometimes the use of oxygen scrubbers to remove the final residual traces.
Critical Safety Considerations
Inert gases are simple asphyxiants. They are not toxic, but they displace the oxygen necessary for breathing. Working in an enclosed space where an inert gas is in use can be extremely dangerous and requires proper ventilation and continuous oxygen monitoring to prevent suffocation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right approach depends entirely on your objective, budget, and sensitivity requirements.
- If your primary focus is general preservation or bulk storage: Nitrogen is almost always the most cost-effective and practical choice for preventing oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity synthesis or electrochemistry: Argon is the superior choice for its near-total lack of reactivity, justifying its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metal processing: Argon is essential, as nitrogen can react with some metals at high temperatures to form unwanted nitrides.
Ultimately, mastering the inert atmosphere principle is about controlling the chemical environment to achieve predictable and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Nitrogen (N₂) | Argon (Ar) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General preservation, cost-effective storage | High-sensitivity synthesis, high-temperature processes |
| Reactivity | Low (strong triple bond) | Extremely low (noble gas) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal For | Food packaging, bulk chemical storage | Metallurgy, organometallic chemistry, sensitive electrochemistry |
Need to protect your materials or processes from oxidation?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to create and maintain precise inert atmospheres for your specific application. Whether you require a cost-effective nitrogen solution or an ultra-pure argon environment for sensitive work, our experts can help you select the optimal system.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can safeguard your research and production with reliable inert atmosphere solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is atmosphere controlled furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Enable Advanced Material Processing
- Why is an atmosphere-controlled reduction experimental device required? Precision in Ore Pellet Swelling Analysis
- How does a lab atmosphere furnace help synthesize PdCuAu alloys? Optimize Your Material Research Results
- What is brazing? A Guide to Strong, Precise Metal Joining for High-Performance Applications
- Why argon is used in annealing? To Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity in Heat Treatment
- What is the necessity of maintaining a continuous nitrogen gas flow? Protect Silver/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Integrity
- Why is controlling the sintering atmosphere essential? Achieve Optimal Material Properties
- How does a high-vacuum or atmosphere carbonization furnace facilitate the preparation of activated carbon? Expert Guide



















