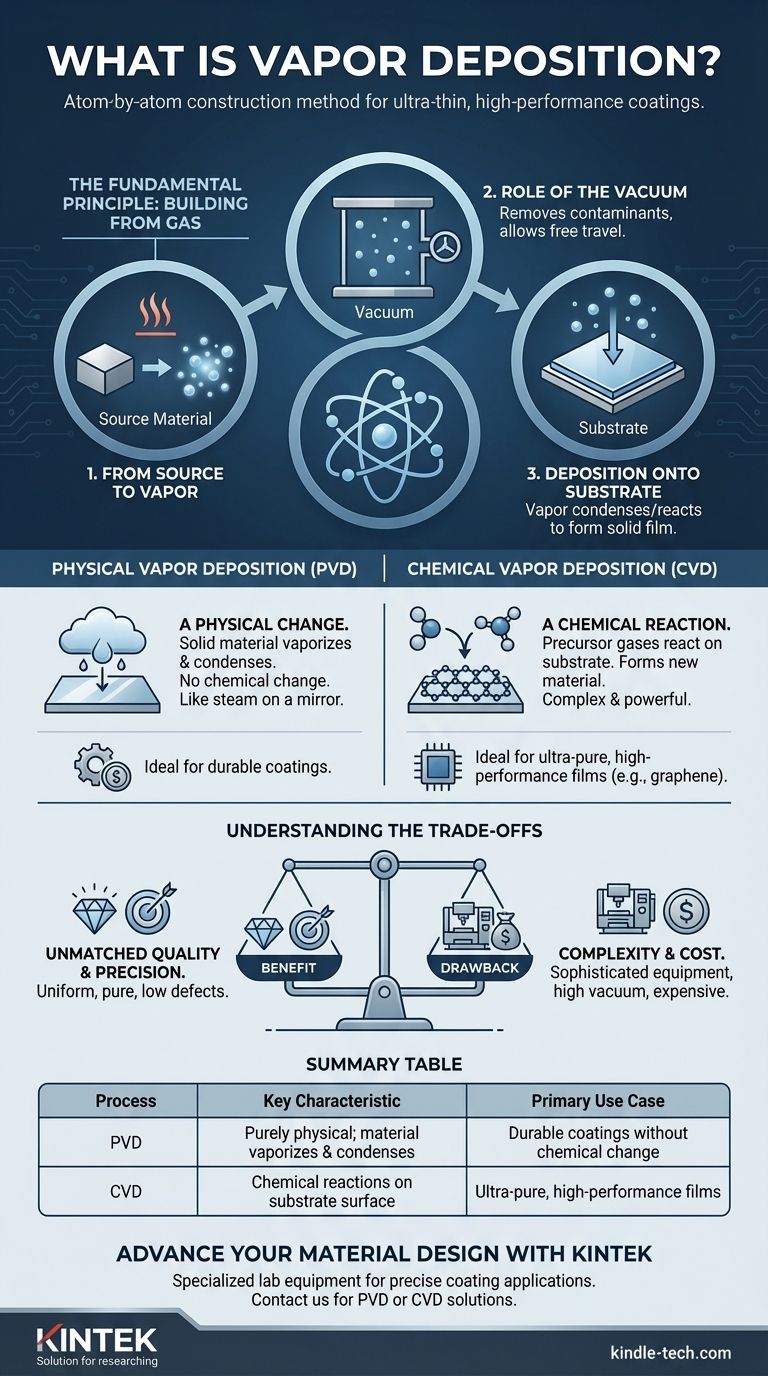
At its core, vapor deposition is a family of manufacturing processes used to apply an extremely thin, high-performance coating of material onto a surface. It works by converting a solid or liquid source material into a gas (a vapor) inside a vacuum chamber, which then condenses or reacts on a target object—known as a substrate—to form a solid film, one layer of atoms at a time.
Vapor deposition is not merely a coating technique; it is a precise, atom-by-atom construction method. Its fundamental purpose is to build materials from the ground up, enabling the creation of advanced films with properties (like purity and uniformity) that are impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
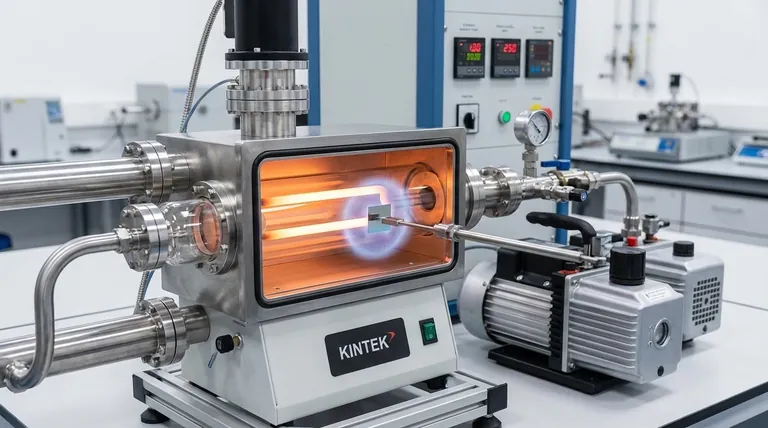

The Fundamental Principle: Building from Gas
To understand vapor deposition, it's best to break it down into its core steps. The process is a highly controlled sequence that transitions a material through different states of matter.
From Source to Vapor
First, a source material is placed inside a reaction chamber. This material is then converted into a gaseous state, or vapor. This can be achieved through various methods, such as heating it until it evaporates or bombarding it with ions.
The Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a vacuum. This is critical for two reasons: it removes any air or other particles that could contaminate the final film, and it allows the vaporized material to travel freely toward the target surface without obstruction.
Deposition onto the Substrate
Finally, this vapor comes into contact with the substrate—the part being coated. The vaporized atoms or molecules then settle on this cooler surface, transforming back into a solid state and forming a thin, uniform film.
The Two Main Pathways: PVD vs. CVD
While the basic principle is the same, there are two major categories of vapor deposition that differ in how the solid film is formed on the substrate.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Physical Change
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the process is purely physical. A solid material is vaporized and then simply condenses on the substrate, much like steam condensing on a cold mirror. There is no chemical change; the deposited film is the same material that was vaporized.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Chemical Reaction
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a more complex and powerful technique. Instead of vaporizing the final coating material itself, one or more precursor gases (called "particulate chemicals" in some contexts) are introduced into the vacuum chamber.
These gases are not the final material. Instead, they are engineered to undergo a chemical reaction directly on the hot surface of the substrate.
This reaction breaks the precursor gases apart and reassembles them into a completely new, solid material that forms the coating. The vacuum helps pull these reactive gases to the workpiece, ensuring the reaction happens precisely where it's needed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method requires understanding the clear benefits and inherent drawbacks. This decision directly impacts the quality, performance, and cost of the final product.
The Benefit: Unmatched Quality and Precision
The primary advantage of vapor deposition, especially CVD, is the exceptional quality of the films it produces. Because the material is built atom by atom, the resulting layer is incredibly uniform, pure, and has a very low defect count.
This is why CVD is a leading approach for manufacturing high-performance materials like graphene, which is essential for next-generation electronics and sensors that demand flawless atomic structures.
The Drawback: Complexity and Cost
The precision of vapor deposition comes at a cost. These systems require sophisticated equipment to manage high temperatures, create strong vacuums, and handle precursor gases. This makes the process significantly more complex and expensive than traditional coating methods like painting or electroplating.
How This Applies to Material Design
The choice between deposition methods depends entirely on the engineering goal for the final product.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure, high-performance films: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the superior method because its surface chemical reactions produce exceptionally uniform and low-defect materials.
- If your primary focus is applying a durable coating without altering its base chemistry: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is often a more direct and cost-effective approach for depositing metals or simple ceramics.
- If your primary focus is developing cutting-edge electronics or semiconductors: Understanding vapor deposition is non-negotiable, as it is the foundational process for building the flawless, nanometer-scale structures that power modern technology.
Ultimately, vapor deposition provides engineers with a powerful toolkit for designing and building materials from the atomic level upwards.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | Purely physical process; material vaporizes and condenses | Applying durable coatings without chemical change |
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Involves chemical reactions on the substrate surface | Creating ultra-pure, high-performance films like graphene |
| General Vapor Deposition | Takes place in a vacuum chamber for purity and precision | Building materials from the atomic level upwards |
Ready to apply vapor deposition technology in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for precise coating applications. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics or need durable PVD coatings, our solutions ensure unmatched purity and uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how our vapor deposition expertise can advance your material design projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















