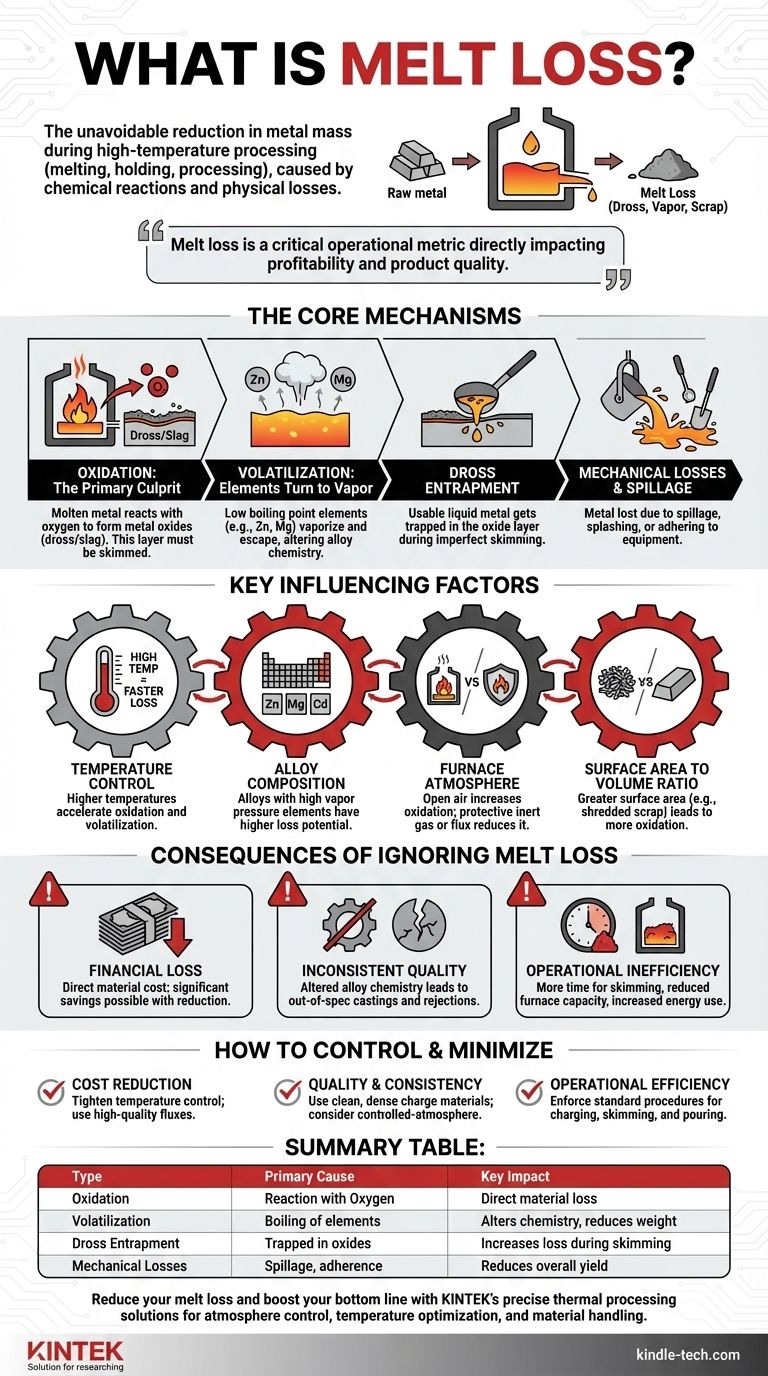
In any high-temperature process involving metals, melt loss is the unavoidable reduction in the mass of a material as it is melted, held in a liquid state, and processed. This loss is the difference between the initial weight of the solid metal charged into the furnace and the final weight of the usable liquid metal tapped out, primarily caused by chemical reactions like oxidation and physical losses.
Melt loss is not just a simple loss of material; it's a critical operational metric that directly impacts profitability and product quality. Understanding its root causes—oxidation, volatilization, and physical handling—is the first step toward controlling it.

The Core Mechanisms of Melt Loss
To effectively manage melt loss, you must first understand the distinct physical and chemical processes that cause it. Each mechanism presents a different challenge and requires a different mitigation strategy.
Oxidation: The Primary Culprit
When molten metal is exposed to the atmosphere, it reacts aggressively with oxygen. This chemical reaction forms metal oxides, which are collectively known as dross (for non-ferrous metals like aluminum) or slag (for ferrous metals like iron and steel).
This oxide layer floats on the surface of the melt. While it offers some protection from further oxidation, it must be skimmed off before casting, representing a direct loss of metallic content.
Volatilization: When Elements Turn to Vapor
Certain elements within an alloy have relatively low boiling points. When the melt temperature approaches these points, these elements can literally boil off and escape as a vapor or fume.
This is a significant issue in alloys containing zinc (like brass) or magnesium (in many aluminum alloys). This loss not only reduces the total weight but also critically alters the final chemical composition of the alloy.
Slag and Dross Entrapment
The process of removing the slag or dross layer is imperfect. A significant amount of good, usable liquid metal can become physically trapped or entrained within the oxide layer.
When this layer is skimmed off, the trapped metal is removed along with it, contributing to the overall melt loss figure. Poor skimming techniques can drastically increase this form of loss.
Spillage and Mechanical Losses
This is the most straightforward form of melt loss. It includes any metal lost due to spillage during transfer, splashing during charging, or material that solidifies and adheres to furnace walls, ladles, and tools.
While seemingly minor, these mechanical losses can add up over many production cycles and indicate a need for process and handling improvements.
Key Factors That Influence Melt Loss Rates
Melt loss is not a fixed constant. It is a variable rate heavily influenced by your specific process parameters and material choices.
Temperature Control
Higher melt temperatures dramatically accelerate the rates of both oxidation and volatilization. Operating at the lowest possible temperature that still ensures metal fluidity and quality is a fundamental principle of melt loss control.
Alloy Composition
The specific elements in your alloy are a primary determinant of melt loss. As mentioned, alloys rich in high-vapor-pressure elements like zinc, magnesium, or cadmium will inherently have higher loss potential.
Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere directly above the molten metal has a profound impact. An open-air induction furnace will have higher oxidation rates than a furnace using a protective cover of inert gas (like argon) or a specific flux that creates a liquid barrier against oxygen.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Oxidation is a surface phenomenon. Therefore, a larger surface area exposed to the atmosphere results in greater loss.
Using finely shredded scrap or turnings, which have a very high surface area-to-volume ratio, will produce significantly more dross than melting solid ingots or large scrap pieces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Consequences
Ignoring melt loss has direct and indirect consequences that extend far beyond the simple loss of material.
The Obvious Cost: Lost Material
Every kilogram of metal lost to dross or vapor is a direct financial loss. A 1% reduction in melt loss for a high-volume foundry can translate into hundreds of thousands of dollars in savings on raw material purchases annually.
The Hidden Cost: Inconsistent Quality
Melt loss is not uniform across all elements in an alloy. The preferential loss of a key alloying element like magnesium or zinc will alter the final chemistry of your product.
This can lead to castings that fail to meet mechanical or chemical specifications, resulting in internal scrap, customer rejections, and damage to your reputation.
The Operational Cost: Reduced Efficiency
High dross or slag formation requires more time and labor for skimming. It can also lead to the buildup of oxides on furnace walls (corundum in aluminum furnaces), which reduces furnace capacity and thermal efficiency, increasing energy consumption per kilogram of metal produced.
How to Control and Minimize Melt Loss
Controlling melt loss is about implementing a disciplined approach to every stage of the melting process.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: Tightly control furnace temperatures to avoid overheating and use appropriate, high-quality fluxes to shield the melt from atmospheric oxygen.
- If your primary focus is alloy quality and consistency: Prioritize using clean, dry, and dense charge materials to minimize surface area and impurities, and consider investing in controlled-atmosphere melting where practical.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Implement and enforce standard operating procedures for charging, melt treatment, skimming, and pouring to minimize mechanical losses and ensure repeatable results.
Ultimately, managing melt loss is a fundamental discipline that directly enhances a facility's material efficiency, product quality, and financial performance.
Summary Table:
| Type of Melt Loss | Primary Cause | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation | Reaction with oxygen forming dross/slag | Direct loss of metallic content |
| Volatilization | Boiling off of low-boiling-point elements (e.g., Zn, Mg) | Alters alloy chemistry, reduces weight |
| Dross Entrapment | Trapping of good metal in oxide layer during skimming | Increases material loss during processing |
| Mechanical Losses | Spillage, splashing, adherence to equipment | Reduces overall yield and efficiency |
Reduce your melt loss and boost your bottom line. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Our solutions help you control furnace atmospheres, optimize temperature, and improve material handling—directly addressing the root causes of melt loss. Let our experts help you enhance your metal melting efficiency and product quality. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is the melting point different for different substances? The Key Role of Bond Strength
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the effect of temperature on calcination? Master Precise Heat Control for Material Properties
- Can a muffle furnace be used for calcination? Achieve Pure, Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What temperature causes melting? Debinding vs. Melting in Metal Fabrication



















