In short, a microwave furnace is a high-temperature oven that uses microwave energy instead of conventional heating elements to heat materials. Unlike a kitchen microwave that simply warms food, these industrial and laboratory furnaces are designed for precise, high-temperature processes like sintering, synthesis, and ashing, often reaching temperatures well over 1000°C.
The critical difference is how the heat is generated. A conventional furnace heats from the outside-in, while a microwave furnace heats the material directly and volumetrically, leading to faster, more uniform heating and often resulting in superior material properties.

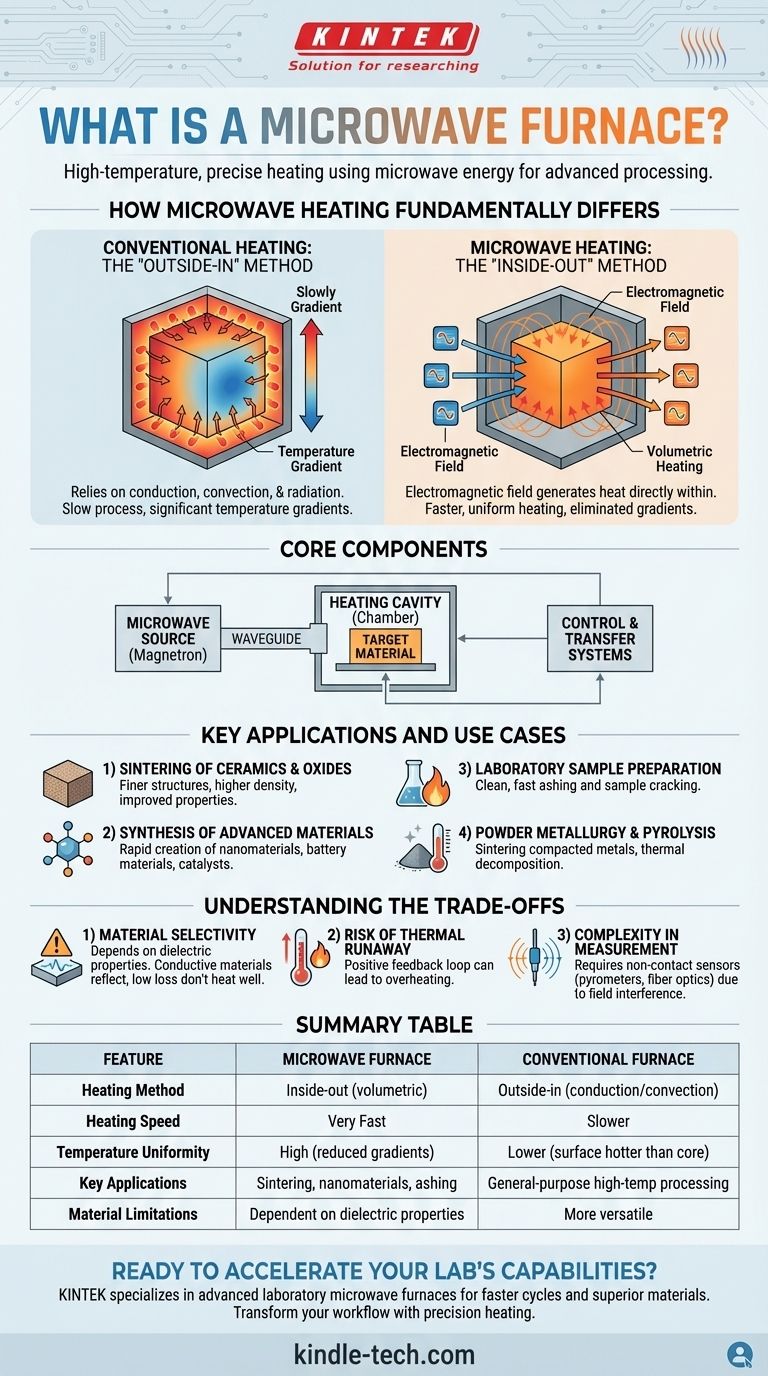
How Microwave Heating Fundamentally Differs
Understanding the distinction between microwave and conventional heating is key to grasping the value of this technology. The two methods are fundamentally different in their approach to transferring thermal energy.
Conventional Heating: The "Outside-In" Method
Traditional furnaces rely on conduction, convection, and radiation. Heating elements warm the furnace chamber, and that heat slowly transfers from the surface of the material inward.
This process can be slow and often results in a temperature gradient, where the outside of the material is significantly hotter than the core.
Microwave Heating: The "Inside-Out" Method
A microwave furnace uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the material itself. The microwaves couple with the molecules or microstructure, causing them to vibrate and generate heat throughout the entire volume simultaneously.
This is known as volumetric heating, which virtually eliminates temperature gradients and dramatically reduces processing time.
The Core Components
A typical microwave furnace consists of three primary systems:
- A Microwave Source: Usually a magnetron, which generates the microwave energy.
- A Heating Cavity: A precisely engineered chamber or waveguide that directs the microwaves onto the target material.
- Control and Transfer Systems: Sophisticated controls for managing power and temperature, along with mechanisms for loading and unloading the material.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique heating mechanism of microwave furnaces makes them exceptionally well-suited for a range of advanced scientific and industrial applications.
Sintering of Ceramics and Oxides
This is a primary application. By heating uniformly, microwave sintering can produce ceramics with finer grain structures, higher density, and improved mechanical properties compared to those from conventional methods.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
Researchers use microwave furnaces for the rapid synthesis of nanomaterials, battery materials, phosphors, and catalysts. The speed and precision of the heating process allow for the creation of materials with unique characteristics.
Laboratory Sample Preparation
Microwave ashing is used to remove organic matter from a sample cleanly and quickly, preparing it for chemical analysis. It is also used for sample cracking and other pretreatment steps in medical and materials labs.
Powder Metallurgy and Pyrolysis
In powder metallurgy, microwaves can rapidly sinter compacted metal powders. They are also used for pyrolysis, the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an inert atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, microwave furnaces are a specialized tool with specific limitations that must be considered.
Material Selectivity
The effectiveness of microwave heating depends entirely on a material's dielectric properties—its ability to absorb microwave energy. Materials with low dielectric loss (like certain polymers or pure alumina at room temp) do not heat well, while conductive materials like metals can reflect microwaves and cause arcing.
Risk of Thermal Runaway
For some materials, the ability to absorb microwave energy increases as their temperature rises. Without precise control, this can create a positive feedback loop, leading to thermal runaway and potential damage to the material or furnace.
Complexity in Measurement
Accurately measuring the temperature inside a strong electromagnetic field is challenging. It requires specialized, non-contact probes (like pyrometers) or fiber optic sensors, as traditional metal thermocouples would interfere with the field and produce false readings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between a microwave and a conventional furnace depends entirely on your material, your desired outcome, and your processing priorities.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing and high throughput: A microwave furnace is an excellent choice due to its dramatically faster heating cycles.
- If you are developing advanced ceramics or nanomaterials: The unique volumetric heating can produce superior microstructures and properties that are unattainable with conventional methods.
- If your goal is clean, efficient sample preparation for analysis: Microwave ashing offers unparalleled speed and control for laboratory work.
- If you are working with a wide range of unknown or metallic materials: A conventional furnace provides greater versatility and is less sensitive to the material's specific electromagnetic properties.
Ultimately, adopting microwave furnace technology is about leveraging a unique heating mechanism to achieve results that were previously impossible or impractical.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Furnace | Conventional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Inside-out (volumetric) | Outside-in (conduction/convection) |
| Heating Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Temperature Uniformity | High (reduced gradients) | Lower (surface hotter than core) |
| Key Applications | Sintering, nanomaterials synthesis, ashing | General-purpose high-temperature processing |
| Material Limitations | Dependent on dielectric properties | More versatile for various materials |
Ready to Accelerate Your Lab's Capabilities with Precision Heating?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including microwave furnaces designed for sintering, synthesis, and sample preparation. Our solutions deliver faster cycle times, superior material properties, and enhanced process control for researchers and engineers working with ceramics, nanomaterials, and more.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a microwave furnace can transform your materials processing workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What apparatus is used for heating in a lab? A Guide to Choosing the Right Tool
- What are the requisites of refractories? The Four Pillars for High-Temperature Success
- How is metal purity measured? Understand Karats, Fineness & Percentage for Gold & Silver
- What is the primary characteristic of a muffle furnace? Unlock Pure, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the maintenance of laboratory equipment? Ensure Data Integrity and Extend Equipment Lifespan



















