In the field of heat treatment, nitriding is a thermochemical case-hardening process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a hardened outer layer. This process is used to significantly increase surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance without altering the core properties of the component.
At its core, nitriding solves a fundamental engineering challenge: how to make a component's surface exceptionally durable without making the entire part brittle. It achieves this by chemically modifying only the surface at relatively low temperatures, resulting in minimal distortion and superior performance.
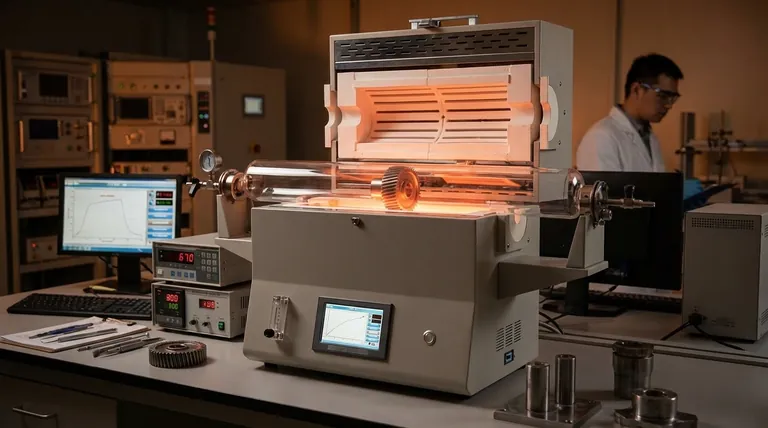

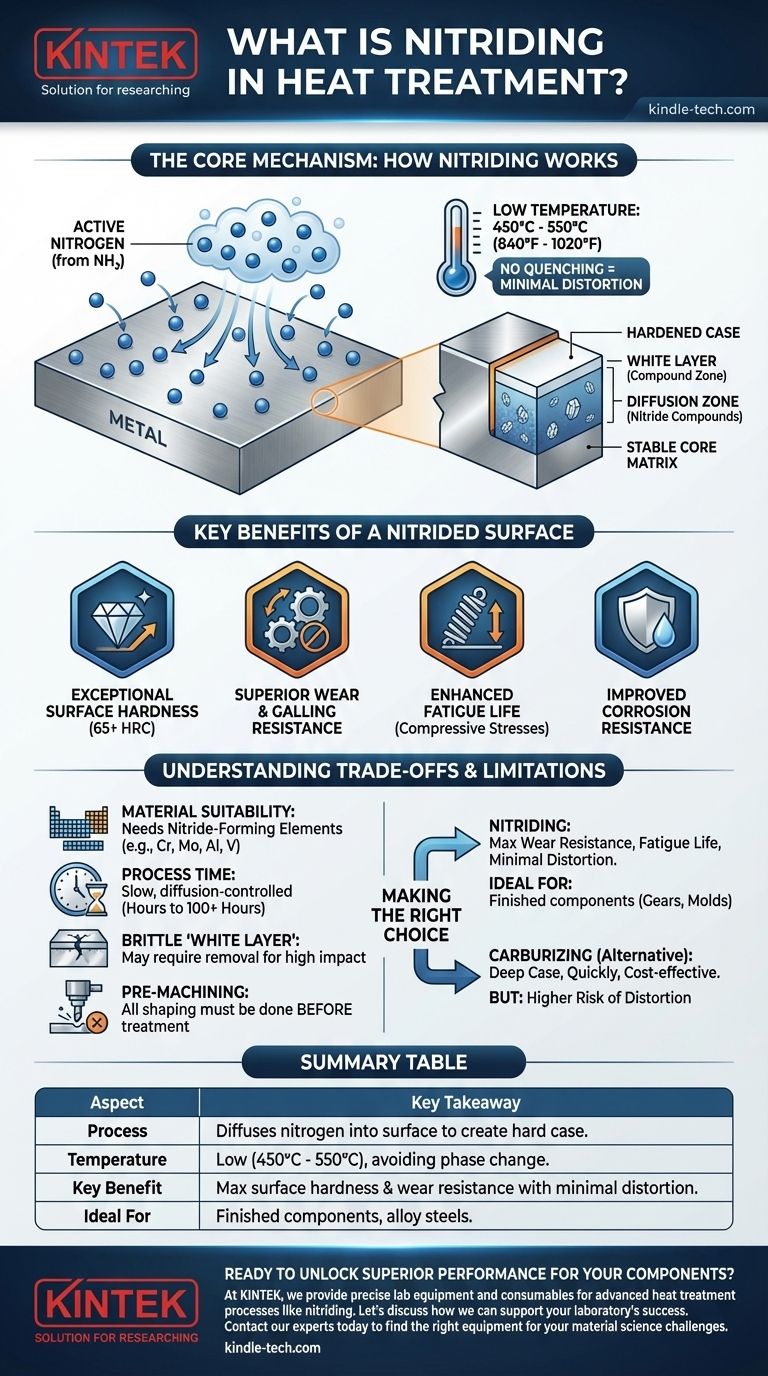
The Core Mechanism: How Nitriding Works
Nitriding is a surface diffusion process, not a bulk material change. It relies on the introduction of active nitrogen atoms at the surface of a steel or alloy component, which then diffuse into the material.
The Role of Active Nitrogen
The process requires a source of nascent, or atomic, nitrogen, which is highly reactive. This is typically generated by the dissociation of nitrogen-rich gas, most commonly ammonia (NH₃), at the treatment temperature.
A Low-Temperature Process
A critical advantage of nitriding is its relatively low process temperature, typically between 450°C and 550°C (840°F and 1020°F). This is below the critical transformation temperature of steels, meaning the core microstructure and dimensions of the part remain stable.
Because it avoids this phase change, no quenching is required, which dramatically minimizes the risk of distortion and cracking common with other hardening methods like carburizing.
Formation of the Hardened Case
As nitrogen atoms diffuse into the steel's surface, they react with the base metal and specific alloying elements (such as aluminum, chromium, and molybdenum). This reaction forms extremely hard metallic nitride compounds.
These microscopic, hard particles precipitate within the steel's matrix, creating an exceptionally hard and wear-resistant surface layer known as the case. This case is composed of two main zones: a thin, outermost "white layer" (compound zone) and a deeper "diffusion zone" beneath it.
Key Benefits of a Nitrided Surface
The unique case structure created by nitriding imparts several significant performance advantages to a component.
Exceptional Surface Hardness
Nitriding can produce some of the highest surface hardness levels achievable in steel, often exceeding 65 HRC (Rockwell C scale). This makes it ideal for components subjected to high contact stress and abrasive wear.
Superior Wear and Galling Resistance
The hard nitride compounds provide outstanding resistance to sliding wear, abrasion, and galling (a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces).
Enhanced Fatigue Life
The nitrided case introduces high compressive stresses at the component's surface. These stresses counteract the tensile stresses that cause fatigue cracks to initiate and grow, significantly extending the fatigue life of parts like crankshafts and gears.
Improved Corrosion Resistance
The outermost compound layer (the "white layer") is a dense, nitrogen-rich structure that is significantly more resistant to corrosion than the underlying steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, nitriding is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material Suitability is Critical
Nitriding is most effective on alloy steels that contain nitride-forming elements like chromium, molybdenum, aluminum, and vanadium. Plain carbon steels show a very limited hardening response and are generally not suitable for this process.
Process Time and Case Depth
Nitriding is a relatively slow, diffusion-controlled process. Achieving a deep case can take anywhere from a few hours to over 100 hours. This makes it less economical for applications requiring very deep hardening compared to a process like carburizing.
The Brittle "White Layer"
While it provides corrosion resistance, the compound "white layer" can be very brittle. For applications involving high impact or specific contact stresses, this layer may be considered undesirable and require removal through a post-process grinding or lapping operation.
Final Machining Must Precede Treatment
Due to the extreme hardness of the nitrided surface, all machining, drilling, and shaping must be completed before the part undergoes nitriding. Post-treatment modifications are generally not feasible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your hardening process based on your specific performance requirements, material, and budget.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum wear resistance and fatigue life with minimal distortion: Nitriding is an excellent choice for finished, high-value components like gears, crankshafts, molds, and extrusion dies.
- If your primary focus is achieving a deep hardened case quickly and cost-effectively: A process like carburizing and quenching may be a more suitable option, provided you can manage the higher risk of distortion.
- If your primary focus is improving surface hardness and corrosion resistance on an appropriate alloy steel: Nitriding provides a unique combination of benefits that few other single treatments can match.
By understanding nitriding as a precise surface engineering tool, you can strategically apply it to create components with exceptional durability and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Diffuses nitrogen into the metal surface to create a hard case. |
| Temperature | Low (450°C - 550°C / 840°F - 1020°F), avoiding phase change. |
| Key Benefit | Maximum surface hardness and wear resistance with minimal part distortion. |
| Ideal For | Finished components like gears, molds, and shafts made from alloy steels. |
Ready to unlock superior performance for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced heat treatment processes like nitriding. Whether you are in R&D or quality control, our solutions help you achieve the exceptional surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life detailed in this article.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's success.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your material science challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is protective atmosphere in heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation & Decarburization for Superior Parts
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance
- What is the primary function of an atmosphere protection furnace during the brazing process of martensitic stainless steel?
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing atmospheres? Key Insights for Your Applications
- How does a high-temperature annealing furnace facilitate carbon activation? Unlock Superior Surface Area with KOH
- What is nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment? A Guide to Controlled, High-Quality Metal Processing
- Why is atmosphere-protected heating equipment necessary for Pyr-IHF? Achieve Precision in Material Synthesis
- What dangers should you be aware of when working with inert gases? Silent Asphyxiation and Oxygen Displacement Risks



















