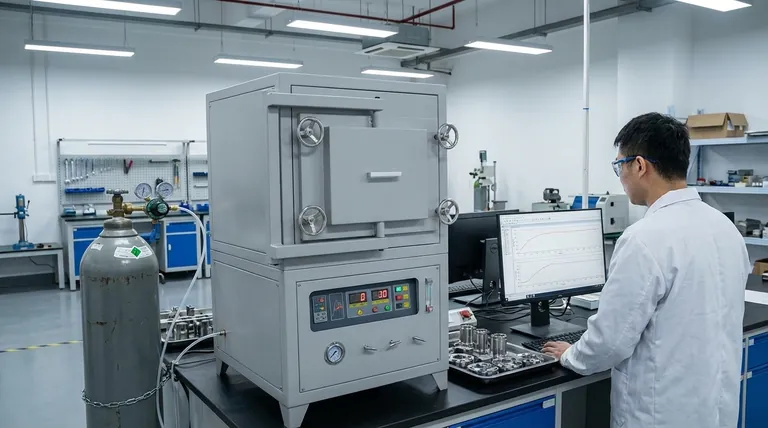
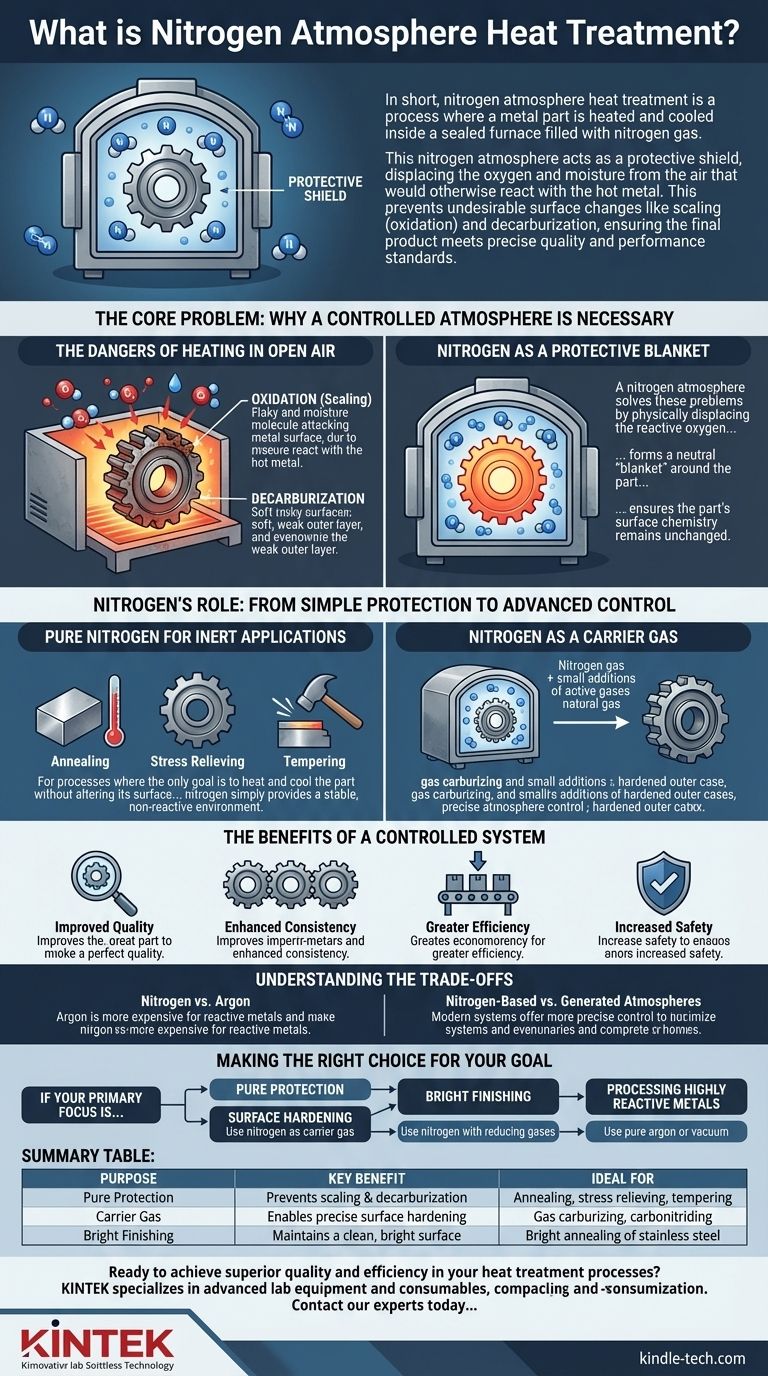
In short, nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment is a process where a metal part is heated and cooled inside a sealed furnace filled with nitrogen gas. This nitrogen atmosphere acts as a protective shield, displacing the oxygen and moisture from the air that would otherwise react with the hot metal. This prevents undesirable surface changes like scaling (oxidation) and decarburization, ensuring the final product meets precise quality and performance standards.
The core purpose of using a nitrogen atmosphere is to move from "uncontrolled" heating in air to "controlled" heating in a predictable environment. This control is the key to achieving consistent, high-quality results, reducing defects, and improving the efficiency of the entire manufacturing process.

The Core Problem: Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Necessary
To understand the value of a nitrogen atmosphere, you first have to understand the problems that occur when heating steel in open air. Metal, especially steel, is highly reactive at elevated temperatures.
The Dangers of Heating in Open Air
When you heat steel in a normal furnace that uses the surrounding air, two destructive chemical reactions occur on its surface.
First is oxidation. The oxygen in the air reacts with the iron, forming a brittle, flaky layer of iron oxide known as scale. This scale must be cleaned off later, which adds cost and can damage the part's surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Second is decarburization. The carbon within the steel—a critical element for its hardness and strength—can react with oxygen and be drawn out of the surface. This leaves a soft, weak outer layer that severely compromises the performance of components like gears, bearings, and tools.
Nitrogen as a Protective Blanket
A nitrogen atmosphere solves these problems by physically displacing the reactive oxygen. Because nitrogen is largely inert and does not readily react with steel at typical heat-treating temperatures, it forms a neutral "blanket" around the part.
By operating in a sealed furnace flushed with at least 99% pure nitrogen, you effectively remove the oxygen and moisture from the equation. This ensures the part's surface chemistry remains unchanged during processes like annealing, normalizing, or stress relieving.
Nitrogen's Role: From Simple Protection to Advanced Control
While pure nitrogen is excellent for simple protection, its most powerful application in modern manufacturing is as a base or "carrier" gas for more complex, chemically active atmospheres.
Pure Nitrogen for Inert Applications
For processes where the only goal is to heat and cool the part without altering its surface, a pure nitrogen atmosphere is ideal. This includes:
- Annealing: Softening a metal to make it easier to machine.
- Stress Relieving: Reducing internal stresses created during manufacturing or welding.
- Tempering: Improving the toughness of a previously hardened part.
In these cases, nitrogen simply provides a stable, non-reactive environment.
Nitrogen as a Carrier Gas
For processes designed to intentionally change the surface of the steel, such as surface hardening, nitrogen serves as the carrier gas. Other "active" gases are precisely metered into the nitrogen stream to create a specific, reactive atmosphere.
A prime example is gas carburizing. Here, a small, controlled amount of a carbon-rich gas (like natural gas or propane) is added to the nitrogen atmosphere. The nitrogen transports this active gas to the steel's surface, where the carbon diffuses into the part to create a hard, wear-resistant outer case. This is common for producing high-performance gears and bearings.
The Benefits of a Controlled System
Using a nitrogen-based system provides significant advantages:
- Improved Quality: Eliminates surface defects like scale and decarburization, leading to higher qualification rates.
- Enhanced Consistency: Automated gas control ensures every part in every batch is treated identically, delivering repeatable results.
- Greater Efficiency: Reduces or eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming post-treatment cleaning steps.
- Increased Safety: Nitrogen is used to purge furnaces of flammable gases before and after processing cycles, improving operational safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While nitrogen atmospheres offer superior control, it's important to understand the context and alternatives.
Nitrogen vs. Argon
Argon is another inert gas that can be used for protective atmospheres. However, argon is significantly more expensive than nitrogen. Its use is typically reserved for highly reactive metals like titanium or certain specialty stainless steels, which can form nitrides (a reaction with nitrogen) at high temperatures. For the vast majority of steel applications, nitrogen is the far more economical choice.
Nitrogen-Based vs. Generated Atmospheres
Traditionally, furnaces used "generators" to produce a protective atmosphere by partially combusting natural gas to create a mix of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen.
- Endothermic atmospheres are rich in reducing gases and used for carburizing.
- Exothermic atmospheres are leaner and used for bright annealing.
Modern systems increasingly favor a pure nitrogen supply combined with synthetic additions of other gases. This "nitrogen-methanol" or "nitrogen-natural gas" approach offers far more precise and repeatable control over the atmosphere's chemical potential than a traditional generator can provide.
The Cost of Control
The primary trade-off is upfront investment. A sealed furnace capable of holding a controlled atmosphere and the associated gas supply and control systems are more complex and costly than a simple open-air furnace. However, this investment is often quickly recovered through reduced scrap rates, eliminated secondary operations, and higher-value product output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct atmosphere depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome of the heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is simple stress relief or annealing of carbon steels: A pure nitrogen atmosphere provides excellent, cost-effective protection against oxidation.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening like carburizing or carbonitriding: Use nitrogen as a carrier gas with precise additions of active hydrocarbon and ammonia gases for superior control over case depth and hardness.
- If your primary focus is achieving a "bright" finish on steel: A nitrogen-based atmosphere with small, controlled additions of reducing gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide is necessary to prevent any surface dulling.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium: A pure argon atmosphere or a high vacuum is required to prevent any reaction with the protective gas itself.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is fundamental to achieving precision and repeatability in modern metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Protection | Prevents scaling & decarburization | Annealing, stress relieving, tempering |
| Carrier Gas | Enables precise surface hardening | Gas carburizing, carbonitriding |
| Bright Finishing | Maintains a clean, bright surface | Bright annealing of stainless steel |
Ready to achieve superior quality and efficiency in your heat treatment processes?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise furnace systems and expertise needed to implement nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment. Whether you are processing carbon steel, stainless steel, or other alloys, our solutions help you eliminate defects, improve consistency, and boost your manufacturing output.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions



















