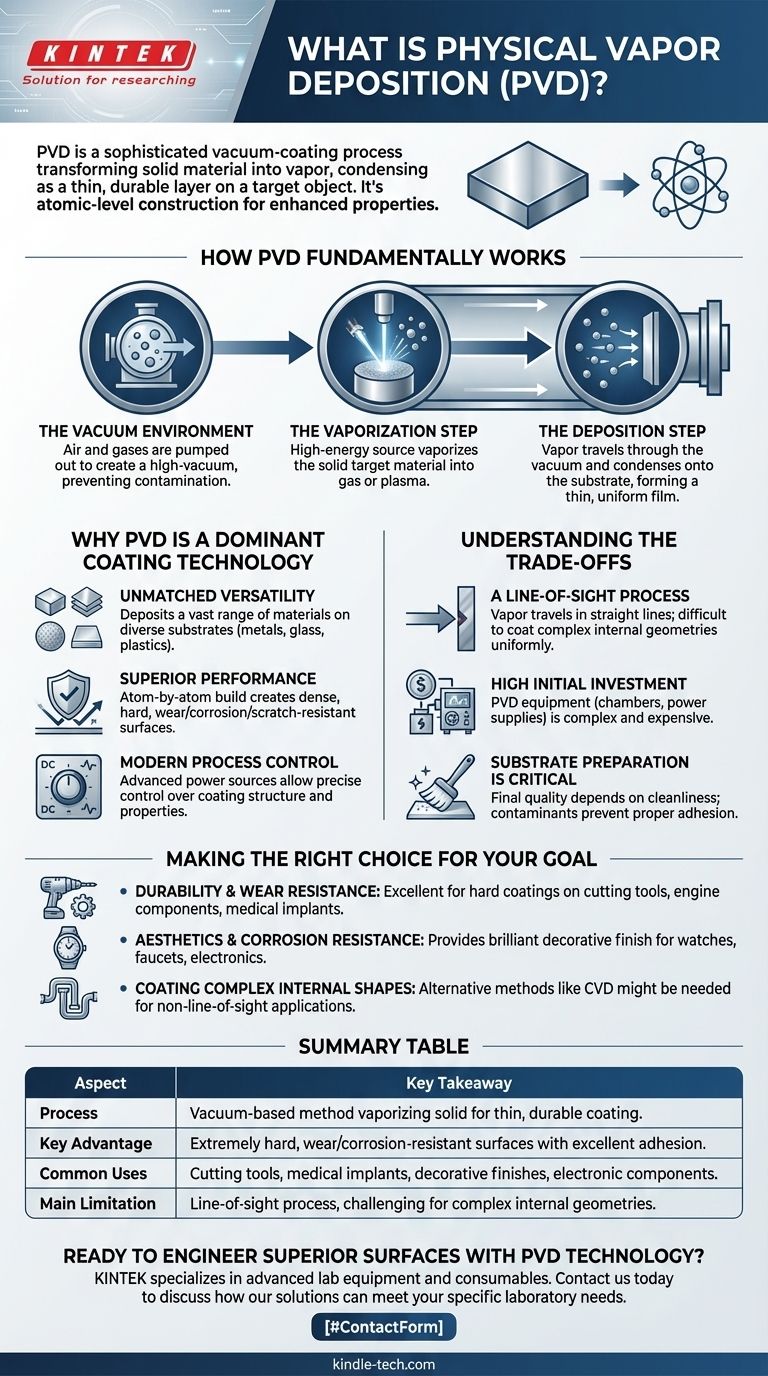
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated vacuum-coating process. It transforms a solid material into a vapor, which then travels through a vacuum and condenses onto a target object, forming an extremely thin yet highly durable layer. This technique allows for the creation of high-performance coatings on an atomic scale.
The crucial insight is that PVD is not merely applying a layer of paint; it is an atom-by-atom construction process that enhances a material's surface properties—like hardness, wear resistance, and color—in ways that are often impossible with traditional methods.

How PVD Fundamentally Works
The PVD process can be broken down into three essential stages, all of which occur inside a high-vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is critical to the quality of the final coating.
The Vacuum Environment
First, all the air and other gases are pumped out of the deposition chamber to create a vacuum. This step is non-negotiable because it prevents any unwanted atoms from contaminating the coating or interfering with the vapor's path.
The Vaporization Step
Next, a high-energy source, such as an electric arc or an electron beam, is aimed at the solid coating material (known as the "target"). This intense energy vaporizes the target, releasing its atoms and turning the solid directly into a gas or plasma.
The Deposition Step
The vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum chamber and condense onto the substrate (the object being coated), which is often given an electrical charge to attract the vapor. This results in a thin, highly-adherent, and uniform film bonding to the surface.
Why PVD is a Dominant Coating Technology
The use of PVD has grown rapidly because its unique characteristics offer significant advantages over older coating methods like electroplating or painting.
Unmatched Versatility
PVD can deposit a vast range of materials, including metals, alloys, and ceramics. This allows it to be used on an equally wide variety of substrates, from metals and glass to plastics.
Superior Performance
Because the coating is built atom by atom, PVD films are incredibly dense, hard, and strongly bonded to the substrate. This creates surfaces that are highly resistant to wear, corrosion, and scratches.
Modern Process Control
Over the last few decades, plasma-assisted PVD (PAPVD) has evolved with advanced power sources like DC, radio-frequency (RF), and pulsed plasma. These technologies give engineers precise control over the coating's structure and properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively and avoiding costly mistakes.
A Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This makes it very difficult to uniformly coat complex internal geometries or the backsides of objects without rotating them extensively.
High Initial Investment
PVD equipment—including vacuum chambers, high-voltage power supplies, and control systems—is complex and expensive. This makes the initial capital cost a significant consideration.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The final quality of a PVD coating is heavily dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate's surface. Any contaminants, oils, or oxides will prevent proper adhesion and can lead to coating failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if PVD is the correct approach, consider the primary objective of your surface treatment.
- If your primary focus is durability and wear resistance: PVD is an excellent choice for applying hard coatings to cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and corrosion resistance: PVD provides a thin, durable, and brilliant decorative finish for products like watches, faucets, and electronic devices.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal shapes: You may need to investigate alternative methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which does not have the same line-of-sight limitation.
By controlling materials at the atomic level, PVD empowers you to engineer surfaces for optimal performance and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | A vacuum-based method that vaporizes a solid material to create a thin, durable coating on a substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Creates extremely hard, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant surfaces with excellent adhesion. |
| Common Uses | Cutting tools, medical implants, decorative finishes (watches, faucets), and electronic components. |
| Main Limitation | A line-of-sight process, making it challenging to coat complex internal geometries uniformly. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surfaces with PVD Technology?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science and surface engineering. Whether you are developing next-generation coatings or need reliable solutions for your R&D, our expertise can help you achieve precise and durable results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















