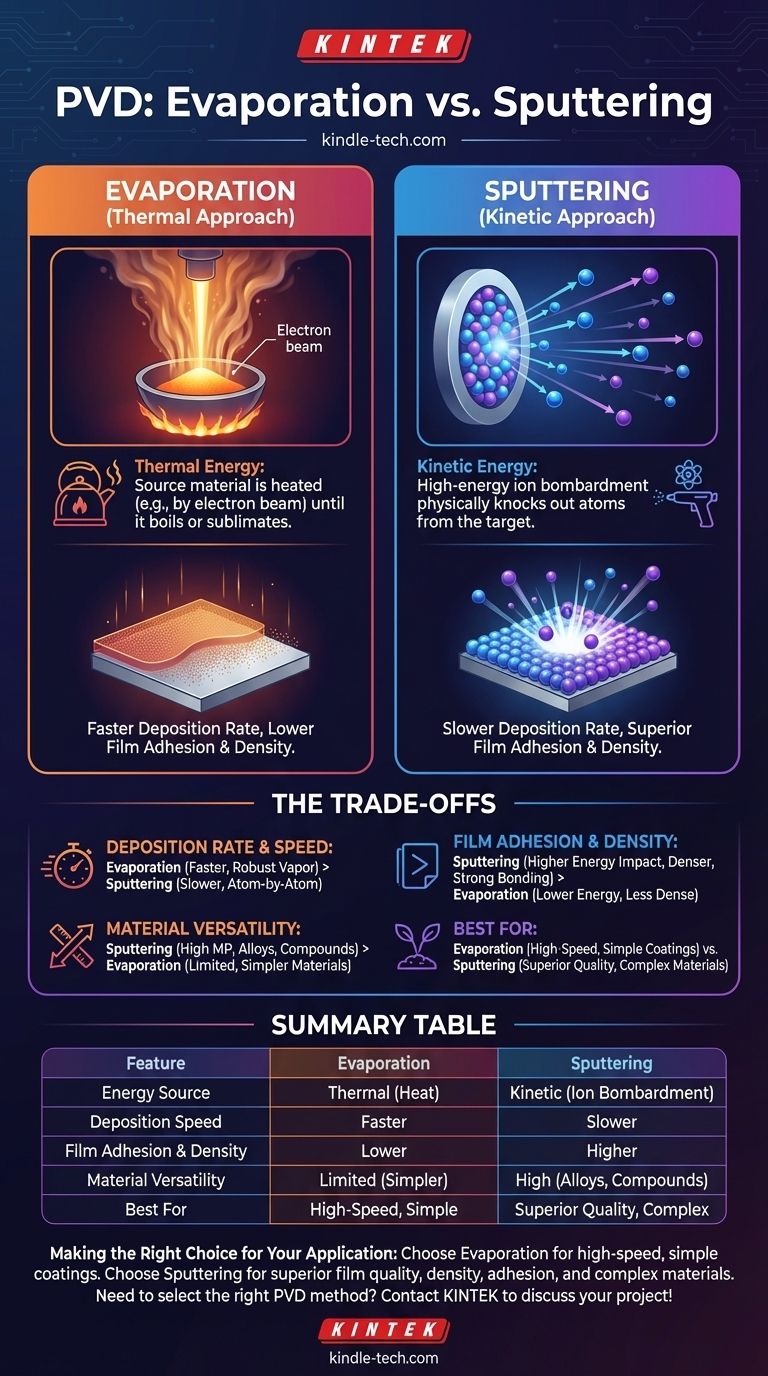
In short, both evaporation and sputtering are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) techniques used to create thin films in a vacuum. The fundamental difference lies in how they turn the solid source material into a vapor. Evaporation uses heat to boil the material off, while sputtering uses high-energy ion bombardment to knock atoms loose.
The core distinction is one of energy transfer. Evaporation is a thermal process, like boiling a kettle, resulting in faster deposition. Sputtering is a kinetic process, like an atomic-scale sandblaster, resulting in higher quality films with better adhesion.
The Mechanism: How Vapor is Created
Both methods operate in a high-vacuum environment to ensure the vaporized atoms can travel from the source to the target substrate with minimal interference from air or other gas molecules. The real difference is the engine driving this vaporization.
Evaporation: The Thermal Approach
Evaporation relies on thermal energy. The source material, or "charge," is heated in a crucible using methods like resistive heating or an electron beam.
As the material heats up, its vapor pressure increases until it begins to sublimate or evaporate, releasing a stream of vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses on the cooler substrate, forming a thin film.
Sputtering: The Kinetic Approach
Sputtering is a purely kinetic process that does not rely on melting or boiling. Instead, it uses momentum transfer.
First, an inert gas like Argon is introduced into the chamber and ionized to create a plasma. A high voltage is then applied to the source material (called the "target"), causing these positive ions to accelerate and bombard its surface.
This high-energy impact physically knocks out, or "sputters," individual atoms from the target. These ejected atoms have significant kinetic energy, and they travel across the chamber to deposit onto the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two methods involves a direct trade-off between deposition speed and final film quality. Neither is universally "better"; they are simply suited for different goals.
Deposition Rate and Speed
Evaporation is generally much faster. The application of intense heat can create a robust and dense vapor stream, allowing for high deposition rates and shorter process times.
Sputtering, by contrast, is a slower, more deliberate process. Because it ejects atoms or small clusters one at a time, the overall material transfer rate is significantly lower.
Film Adhesion and Density
This is where sputtering holds a distinct advantage. Sputtered atoms arrive at the substrate with much higher kinetic energy than evaporated atoms.
This high energy allows them to impact the surface with force, leading to denser, more uniform films with superior adhesion. Evaporated atoms land more gently, which can result in less dense films with weaker bonding to the substrate.
Material and Process Control
Sputtering offers greater versatility. It can be used to deposit materials with very high melting points (refractory metals) or complex alloys and compounds without changing their chemical composition.
Evaporation is more limited. It works best for materials that evaporate cleanly at manageable temperatures. Attempting to evaporate an alloy can be difficult, as the element with the higher vapor pressure will evaporate first, altering the final film's composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on what properties are most critical for your final product.
- If your primary focus is high-speed deposition for simpler coatings: Evaporation is often the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is superior film quality, density, and adhesion: Sputtering is the superior method, despite its slower deposition rate.
- If you are working with complex alloys, compounds, or high-temperature materials: Sputtering provides the process control and versatility that evaporation cannot match.
Understanding this fundamental difference between using thermal versus kinetic energy is the key to selecting the ideal PVD process for your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Evaporation | Sputtering |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal (Heat) | Kinetic (Ion Bombardment) |
| Deposition Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Film Adhesion & Density | Lower | Higher |
| Material Versatility | Limited (simpler materials) | High (alloys, compounds) |
| Best For | High-speed, simpler coatings | Superior quality, complex materials |
Need to select the right PVD method for your lab's thin-film application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Whether you require the speed of evaporation or the superior film quality of sputtering, our experts can help you choose the ideal solution to enhance your research and production outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials



















