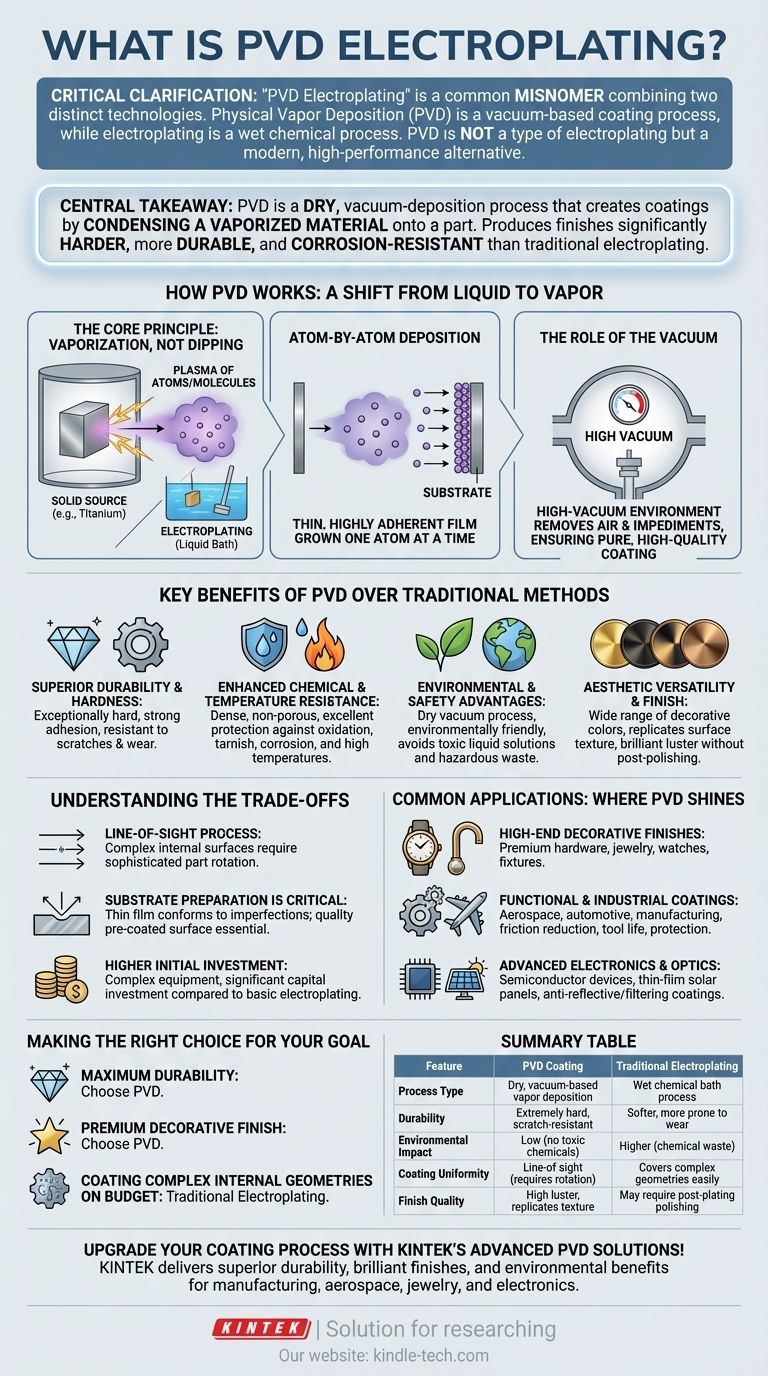
First, a critical clarification: The term "PVD electroplating" is a common misnomer that combines two distinct technologies. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech, vacuum-based coating process, whereas electroplating is a wet chemical process. While both can apply a metallic finish, PVD is not a type of electroplating but is often considered a modern, high-performance alternative.
The central takeaway is that PVD is a dry, vacuum-deposition process that creates coatings by condensing a vaporized material onto a part. This method produces finishes that are significantly harder, more durable, and more corrosion-resistant than those achieved through traditional chemical electroplating.

How PVD Works: A Shift From Liquid to Vapor
Physical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally different from the chemical baths of electroplating. The process is entirely "dry" and occurs under a high vacuum.
The Core Principle: Vaporization, Not Dipping
In PVD, a solid source material (like titanium or zirconium) is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules inside a vacuum chamber. This vapor is then precisely controlled and directed toward the parts being coated.
This contrasts sharply with electroplating, which involves submerging parts in a chemical solution and using an electric current to cause dissolved metal ions to plate onto the surface.
Atom-by-Atom Deposition
The vaporized material travels across the vacuum chamber and condenses on the substrate, building a thin, highly adherent film. This coating is grown one atom at a time, resulting in an extremely dense, uniform, and strong layer.
The Role of the Vacuum
The process must occur in a high-vacuum environment. This removes air and other gas particles that could otherwise react with or impede the vapor, ensuring a pure and high-quality coating.
Key Benefits of PVD Over Traditional Methods
PVD was developed to provide functional characteristics that older methods could not. Its adoption in decorative finishing is a testament to its superior performance.
Superior Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and have a high level of adhesion to the substrate. This makes them incredibly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and wear.
Enhanced Chemical and Temperature Resistance
The dense, non-porous nature of PVD coatings provides excellent protection against oxidation, tarnish, and corrosion. They can also be engineered to withstand very high temperatures.
Environmental and Safety Advantages
As a dry vacuum process, PVD is significantly more environmentally friendly than chemical-based plating. It avoids the use of toxic liquid solutions and the associated hazardous waste disposal.
Aesthetic Versatility and Finish
PVD can produce a wide range of colors for decorative finishes, from brass and gold tones to black, bronze, and iridescent looks. The process perfectly replicates the underlying surface texture, providing a brilliant luster on polished parts without requiring any post-coating polishing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This means that complex internal surfaces or deeply recessed areas may not receive a uniform coating without sophisticated part rotation.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
PVD is a thin-film process that conforms precisely to the existing surface. It will not hide scratches, dents, or other imperfections. The quality of the final finish is directly dependent on the quality of the pre-coated surface.
Higher Initial Investment
PVD equipment is complex and requires a significant capital investment compared to a basic electroplating setup. This can make it less economical for very small-scale or low-cost applications.
Common Applications: Where PVD Shines
PVD's unique properties make it the preferred choice for a vast range of demanding applications.
High-End Decorative Finishes
PVD is widely used for premium hardware, jewelry, watches, and fixtures. It provides a finish that looks pristine for years, resisting the wear and tear of daily use.
Functional and Industrial Coatings
In the aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, PVD coatings are used to reduce friction on moving parts, increase the lifespan of cutting tools, and protect components from extreme environments.
Advanced Electronics and Optics
The precision of PVD is essential for manufacturing semiconductor devices, thin-film solar panels, and specialized glass coatings that provide anti-reflective or filtering properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating technology depends entirely on your project's specific performance and aesthetic requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: PVD is the superior choice due to its hardness and strong atomic bond to the substrate.
- If your primary focus is a premium decorative finish: PVD offers a wider range of colors and a more consistent, long-lasting finish that is highly resistant to tarnish and scratches.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries on a tight budget: Traditional electroplating may be more suitable as it does not have the line-of-sight limitations of PVD.
By understanding the fundamental differences between these processes, you can choose the technology that truly meets your product's performance and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Traditional Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Dry, vacuum-based vapor deposition | Wet chemical bath process |
| Durability | Extremely hard, scratch-resistant | Softer, more prone to wear |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no toxic chemicals) | Higher (chemical waste) |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (requires rotation) | Covers complex geometries easily |
| Finish Quality | High luster, replicates surface texture | May require post-plating polishing |
Upgrade your coating process with KINTEK's advanced PVD solutions!
As a leading supplier of laboratory and industrial equipment, KINTEK specializes in PVD coating systems that deliver superior durability, brilliant finishes, and environmental benefits. Whether you're in manufacturing, aerospace, jewelry, or electronics, our PVD technology can enhance your product performance and lifespan.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD coating can transform your products and give you a competitive edge!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films



















