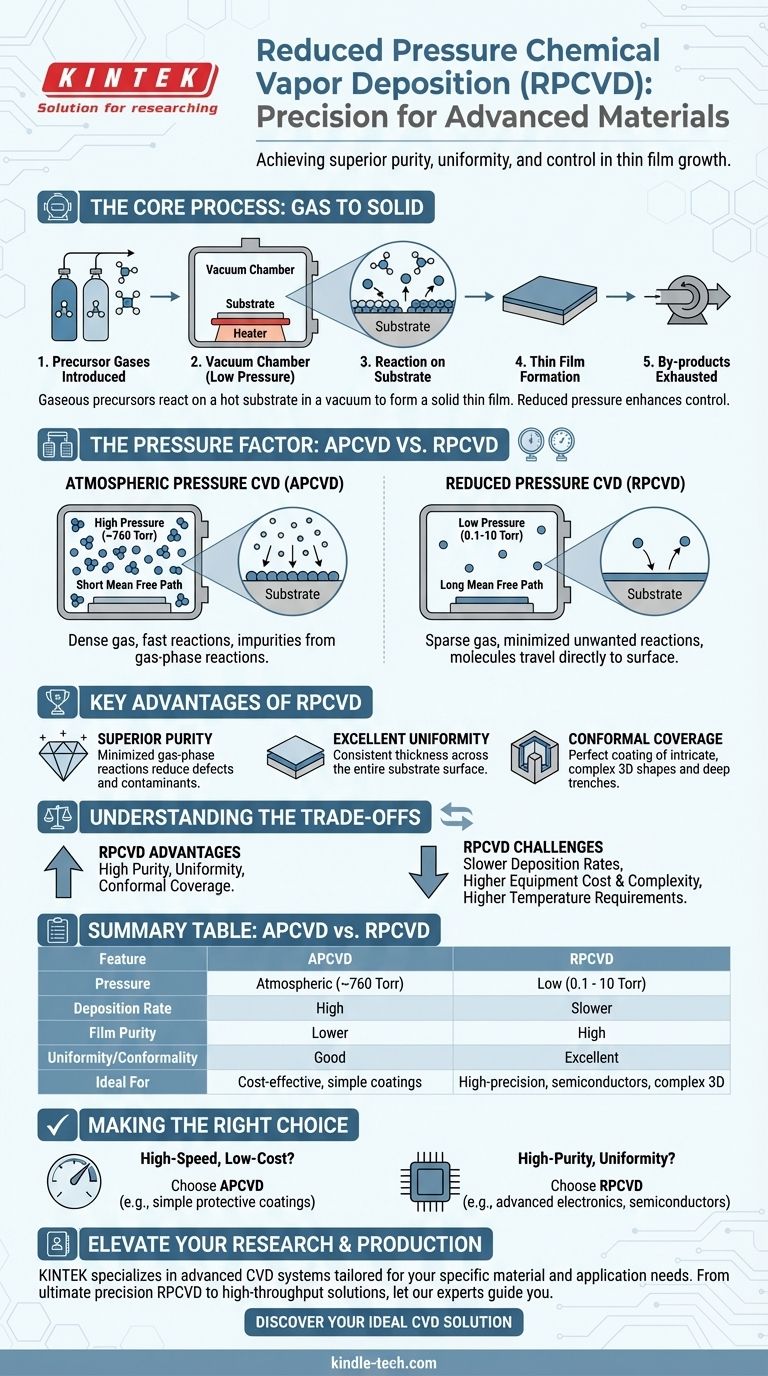
At its core, reduced pressure chemical vapor deposition (RPCVD) is a high-precision manufacturing process where thin films of solid material are grown on a substrate from gaseous precursors inside a vacuum chamber. Unlike processes run at normal atmospheric pressure, RPCVD significantly lowers the chamber pressure to enhance the purity, uniformity, and overall quality of the resulting film. This control is critical for creating the high-performance materials used in modern electronics and advanced coatings.
The central purpose of reducing the pressure in a chemical vapor deposition process is to gain control. By lowering the gas pressure, you increase the "mean free path" of precursor molecules, reducing unwanted reactions in the gas and ensuring the film forms cleanly and uniformly on the target surface.

The Fundamentals of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The Core Process: Gas to Solid
Chemical vapor deposition is a method for creating high-quality solid materials, typically as a thin film. The process involves placing a target object, or substrate, inside a reaction chamber.
One or more volatile chemical gases, known as precursors, are then introduced into the chamber. These precursors decompose or react on the hot substrate's surface, leaving behind a solid layer of the desired material. Any leftover gaseous by-products are exhausted from the chamber.
Key Applications
CVD is a foundational technology in many advanced industries. It is used to deposit the delicate semiconducting films in microchips, apply ultra-hard protective coatings on cutting tools to prevent wear, and grow materials like carbon nanotubes or GaN nanowires.
The Advantage Over Line-of-Sight Methods
A key strength of CVD is its ability to deposit a uniform coating on complex, three-dimensional shapes. Unlike physical deposition methods (PVD) that often require a direct line-of-sight from the source to the substrate, the gaseous precursors in CVD can flow around and into intricate features, ensuring complete and even coverage.
Why Pressure is the Critical Control Knob
The pressure inside the reaction chamber is one of the most important parameters in any CVD process. It directly dictates the behavior of the precursor gases and, consequently, the quality of the final film.
Atmospheric Pressure (APCVD): The Baseline
When CVD is performed at standard atmospheric pressure, the chamber is dense with gas molecules. This allows for very fast deposition rates, making it an economical choice.
However, the high concentration of molecules increases the likelihood of unwanted chemical reactions occurring in the gas phase, away from the substrate. These reactions can form tiny particles that rain down on the film, creating impurities and defects.
Reduced Pressure (RPCVD): The Solution for Quality
RPCVD, often used interchangeably with low-pressure CVD (LPCVD), operates at pressures hundreds or thousands of times lower than atmospheric pressure. This creates a much larger average distance between gas molecules, a property known as the mean free path.
This increased mean free path is the key to RPCVD's advantages. It ensures that precursor molecules are far more likely to travel directly to the substrate surface before reacting.
The Result: Superior Film Properties
By minimizing gas-phase reactions, RPCVD produces films with significantly higher purity and fewer defects. Furthermore, the unimpeded travel of molecules allows them to better migrate across the surface and into deep trenches or holes, leading to exceptional uniformity and conformal coverage over complex topographies.
Understanding the Trade-offs of RPCVD
Choosing to reduce pressure is a deliberate engineering decision that involves balancing competing factors. It is not universally superior, but rather optimized for specific goals.
Slower Deposition Rates
The most significant trade-off is speed. With fewer precursor molecules available in the chamber at any given moment, the film grows much more slowly than in an atmospheric pressure system. This directly impacts manufacturing throughput.
Increased Equipment Complexity and Cost
Operating under vacuum requires specialized, robust chambers and expensive vacuum pumping systems. The engineering required to maintain a stable, low-pressure environment adds significant cost and complexity to the equipment compared to a simpler atmospheric pressure reactor.
Higher Temperature Requirements
To achieve a sufficient reaction rate on the substrate surface with fewer available precursor molecules, RPCVD processes often need to run at higher temperatures than their atmospheric counterparts. This can limit the types of substrates that can be used, as some materials cannot withstand the heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use RPCVD versus another method depends entirely on the requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, low-cost production: Atmospheric pressure CVD is often sufficient for applications like simple protective coatings where ultimate purity is not the main concern.
- If your primary focus is film purity and uniformity: RPCVD is the standard for demanding applications like semiconductor manufacturing, where even microscopic defects can cause device failure.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D structures: RPCVD is essential, as its ability to provide highly conformal coatings is unmatched by higher-pressure or line-of-sight techniques.
Ultimately, selecting a deposition pressure is about deliberately balancing the demands of speed, cost, and the required perfection of the final material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) | Reduced Pressure CVD (RPCVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Atmospheric (~760 Torr) | Low (typically 0.1 - 10 Torr) |
| Deposition Rate | High | Slower |
| Film Purity | Lower (more gas-phase reactions) | High (minimized gas-phase reactions) |
| Uniformity/Conformality | Good | Excellent |
| Equipment Cost | Lower | Higher (vacuum system required) |
| Ideal For | High-speed, cost-effective coatings | High-precision applications (semiconductors, complex 3D structures) |
Need to deposit high-purity, uniform thin films for your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including chemical vapor deposition systems tailored to your specific material and application requirements. Our experts can help you select the right technology—whether RPCVD for ultimate precision or other methods for high-throughput needs—to ensure your success.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover the ideal CVD solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















