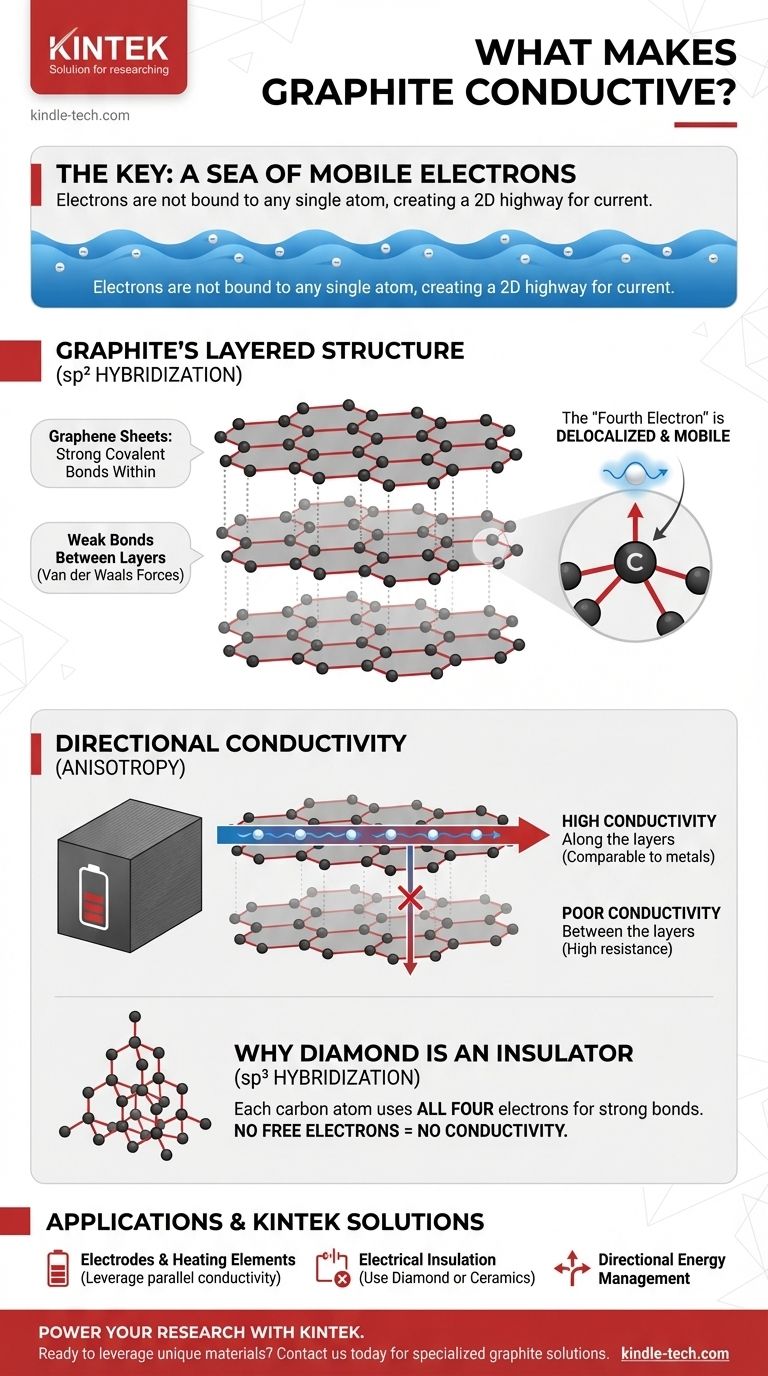
At its core, electrical conductivity in graphite is caused by a sea of mobile electrons that are not bound to any single atom. This unique electron behavior is a direct result of graphite's specific layered atomic structure and the way its carbon atoms bond together.
The crucial insight is that while most non-metals lock their electrons into place, graphite's unique sheet-like structure leaves one electron per atom free to move. This "delocalized" electron creates a 2D electron highway, allowing graphite to conduct electricity much like a metal.

The Foundation: Graphite's Layered Structure
To understand the flow of electricity, we must first visualize the material's physical form. Graphite isn't a random jumble of atoms; it's a highly organized crystal.
A Stack of Graphene Sheets
Graphite is composed of countless layers of carbon atoms. Each individual layer, known as a graphene sheet, is a flat, two-dimensional plane.
Strong Bonds Within, Weak Bonds Between
Within each sheet, carbon atoms are arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb pattern, connected by extremely strong covalent bonds. However, the bonds holding the separate sheets together are very weak (van der Waals forces).
The Electron's Role: Unlocking Conductivity
The specific nature of the bonds within the graphene sheets is the true source of graphite's conductivity.
The sp² Hybridization Bond
Each carbon atom has four outer-shell electrons available for bonding. In graphite, each atom uses three of these electrons to form strong, flat bonds with its three neighbors in the hexagonal sheet.
The "Fourth Electron" Creates a Sea of Mobility
This leaves one electron per carbon atom that is not involved in the primary bonding framework. This electron occupies a different type of orbital (p orbital) and is no longer tied to its original atom.
Instead, these "fourth electrons" from all the atoms in a sheet merge to form a delocalized sea of electrons. These electrons are free to move anywhere across the entire two-dimensional surface of their graphene sheet.
How Mobile Electrons Enable Current
Electrical current is simply the flow of charge. When a voltage is applied across a piece of graphite, this vast pool of mobile electrons is easily pushed along the graphene sheets, creating a powerful electrical current.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Directional Conductivity
Graphite's conductivity is not uniform in all directions. This property, known as anisotropy, is a critical consideration in any practical application.
High Conductivity Along the Layers
Electricity flows exceptionally well parallel to the graphene sheets. The delocalized electron sea provides a nearly unobstructed path for current, making graphite's conductivity in this direction comparable to many metals.
Poor Conductivity Between the Layers
In contrast, it is very difficult for electrons to jump from one sheet to the next. The large gap and weak forces between layers create high resistance, making graphite a poor conductor perpendicular to its layers.
Why Isn't Diamond Conductive? A Key Comparison
To fully appreciate graphite's uniqueness, it helps to compare it to diamond, another form of pure carbon.
The sp³ Bonding in Diamond
In diamond, each carbon atom uses all four of its outer electrons to form strong covalent bonds with four neighboring atoms in a rigid, three-dimensional lattice.
No Free Electrons, No Conductivity
Because every electron is locked into a fixed, localized bond, there are no mobile electrons available to carry a current. This is why diamond is one of the best known electrical insulators.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The unique properties of graphite's conductivity dictate its use in various applications.
- If your primary focus is creating an electrode or heating element: Leverage graphite's excellent conductivity along its planes, orienting the material so the current flows parallel to the graphene sheets.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Graphite is the wrong choice; a material like diamond or a ceramic is required, as they have no free electrons.
- If your primary focus is managing heat or electricity directionally: Graphite's anisotropic nature is an advantage, allowing you to channel energy along one axis while insulating along another.
Ultimately, graphite serves as a perfect example of how a material's atomic structure directly dictates its most fundamental properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Conductivity |
|---|---|
| sp² Hybridization | Creates a 2D hexagonal lattice, leaving one electron per atom delocalized. |
| Delocalized Electrons | Forms a "sea" of mobile charge carriers that can move freely within a graphene sheet. |
| Layered Structure | Enables high conductivity along the sheets but poor conductivity between them (anisotropy). |
| Comparison to Diamond (sp³) | Diamond has no free electrons (all electrons are bonded), making it an insulator. |
Ready to leverage graphite's unique conductive properties in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Whether you need graphite for electrodes, heating elements, or specialized applications, our materials are engineered to provide superior performance and directional conductivity.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can power your research and innovation. Let our experts help you select the perfect materials for your specific laboratory needs.
Get in touch with our team now →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of isostatic graphite manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Material Uniformity and Performance
- What is the function of the graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat for Analysis & Materials Processing
- What are the benefits of a graphite furnace? Achieve Rapid, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What is the application of graphite furnace? Essential for High-Temp Material Processing & Synthesis
- What are the interferences of graphite furnace? Overcome Matrix & Spectral Issues for Accurate GFAAS
- What is a carbonization furnace? Transform Waste Biomass into Valuable Charcoal Efficiently



















