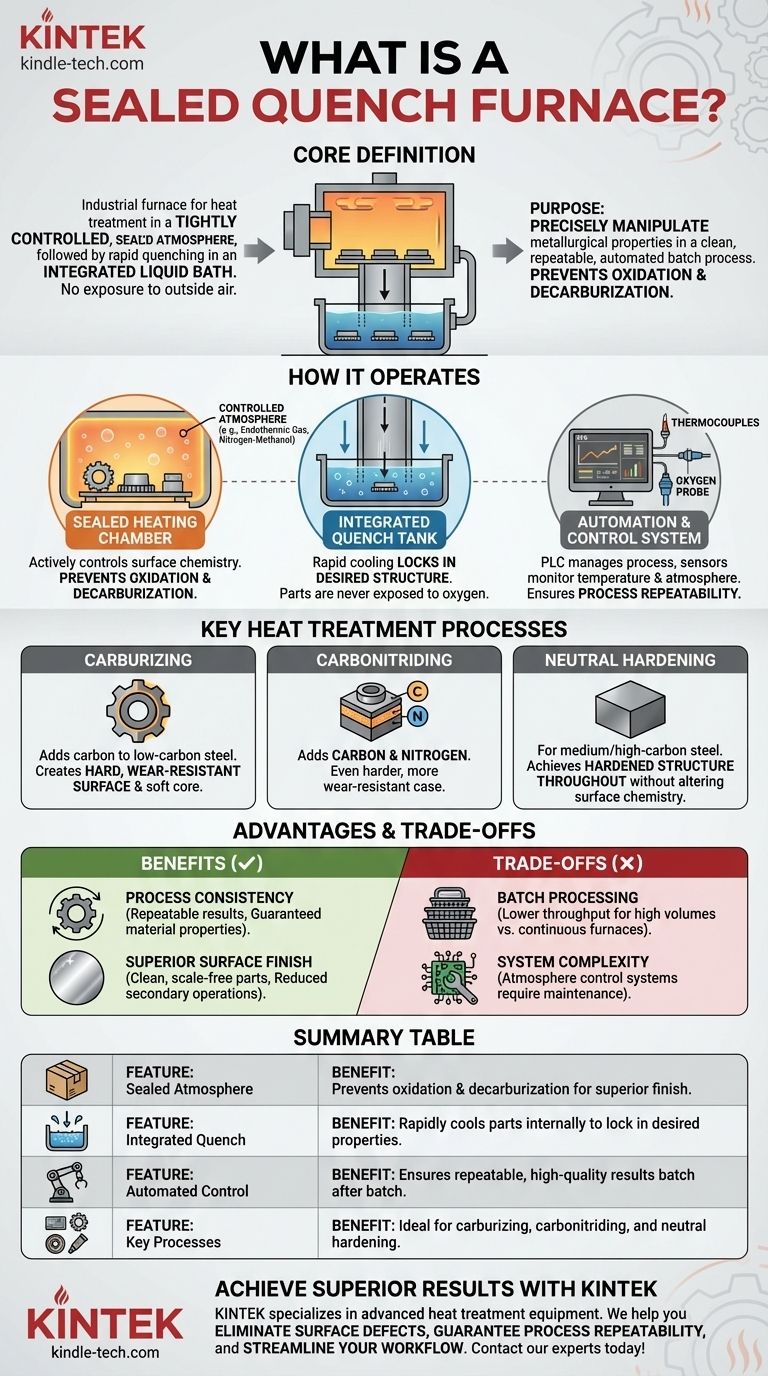
At its core, a sealed quench furnace is an industrial furnace that performs heat treatment processes within a tightly controlled, sealed atmosphere before rapidly cooling—or "quenching"—the parts in an integrated liquid bath. This entire sequence, from heating to quenching, occurs without the metal ever being exposed to outside air, which is the key to its function and high-quality results.
A sealed quench furnace is designed for one primary purpose: to precisely manipulate the metallurgical properties of steel parts in a clean, repeatable, and automated batch process. It prevents surface defects like oxidation and decarburization, which are common in open-air heat treatments.

How a Sealed Quench Furnace Operates
The furnace's design integrates several critical zones into a single, automated system. A typical operational cycle involves loading parts into a vestibule, transferring them into the heating chamber, and then dropping them into the quench tank below.
The Sealed Heating Chamber
The heart of the system is the heating chamber, which is filled with a controlled atmosphere. This is not simply air; it is a precisely mixed gas, such as endothermic gas or a blend of nitrogen and methanol.
The purpose of this atmosphere is to actively control the surface chemistry of the steel. It prevents oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface), ensuring a clean, bright finish and preserving the material's integrity. For processes like carburizing, this atmosphere is enriched to intentionally add carbon to the steel's surface.
The Integrated Quench Tank
Directly beneath the heating chamber is a quench tank filled with a specific medium, most commonly oil, but sometimes water, polymer, or molten salt.
Once the heating cycle is complete, an internal elevator mechanism quickly lowers the hot parts from the heating chamber into the quench tank. This rapid cooling locks in the desired metallurgical structure, such as martensite for hardness. Because this transfer happens internally, the parts are never exposed to oxygen while at high temperatures.
The Automation and Control System
Modern sealed quench furnaces are highly automated. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) manages the entire process, including temperatures, cycle times, and atmosphere composition.
Sensors like thermocouples monitor temperature, while an oxygen probe measures the carbon potential of the atmosphere. This precise control ensures that every batch is processed under identical conditions, leading to exceptional process repeatability.
Key Heat Treatment Processes Performed
The versatility of the sealed quench furnace allows it to perform several critical case hardening and through-hardening processes.
Carburizing
Carburizing is a process that adds carbon to the surface of low-carbon steel parts. The controlled atmosphere is enriched with carbon, which diffuses into the hot steel. Subsequent quenching creates a part with a hard, wear-resistant surface (case) and a softer, ductile core.
Carbonitriding
Carbonitriding is similar to carburizing, but ammonia is also added to the furnace atmosphere. This introduces both carbon and nitrogen into the steel's surface, resulting in an even harder and more wear-resistant case than carburizing alone.
Neutral Hardening
This process is used for medium and high-carbon steels that already have sufficient carbon for hardening. The furnace atmosphere is maintained to be "neutral" to the steel, meaning it neither adds nor removes carbon. The parts are heated to the proper temperature and quenched to achieve a hardened structure throughout the entire part.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
While powerful, a sealed quench furnace is not the solution for every application. Understanding its benefits and limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Primary Advantage: Process Consistency
The precise digital control over temperature, time, and atmosphere chemistry delivers highly repeatable results from batch to batch. This is critical for manufacturing high-performance components used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery where material properties must be guaranteed.
The Primary Advantage: Superior Surface Finish
By preventing oxidation and decarburization, parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, scale-free surface. This dramatically reduces or eliminates the need for costly secondary operations like sandblasting or grinding.
The Trade-off: Batch Processing
Sealed quench furnaces are inherently batch furnaces. While they can be automated to run continuously (one batch after another), their throughput may be lower than a continuous mesh-belt furnace for very high volumes of small parts. They are ideal for medium to large parts or baskets of smaller parts processed in distinct loads.
The Trade-off: System Complexity
The systems required to generate, monitor, and control the furnace atmosphere add complexity and maintenance requirements. Proper maintenance of gas generators, control probes, and safety systems is essential for reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on the material you are using and the final properties your component requires.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant surface on a tough, low-carbon steel component: A sealed quench furnace is the industry standard for carburizing or carbonitriding.
- If your primary focus is hardening a medium-to-high carbon steel part without altering its surface chemistry: Neutral hardening in a sealed quench furnace provides unmatched control and a clean finish.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum repeatability for critical components: The tightly controlled and automated nature of a sealed quench furnace makes it the superior choice over older, less-controlled methods.
Understanding the principles of a sealed quench furnace empowers you to engineer steel components with precise, predictable, and reliable performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation & decarburization for a superior surface finish. |
| Integrated Quench | Rapidly cools parts internally to lock in desired metallurgical properties. |
| Automated Control | Ensures repeatable, high-quality results batch after batch. |
| Key Processes | Ideal for carburizing, carbonitriding, and neutral hardening of steel parts. |
Ready to achieve superior metallurgical results with precision and consistency?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and industrial heat treatment equipment. Our expertise in sealed quench furnace technology can help you:
- Eliminate surface defects like scaling and decarburization.
- Guarantee process repeatability for critical components in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
- Streamline your workflow with automated, reliable systems.
Let's discuss how our solutions can meet your specific lab or production needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















