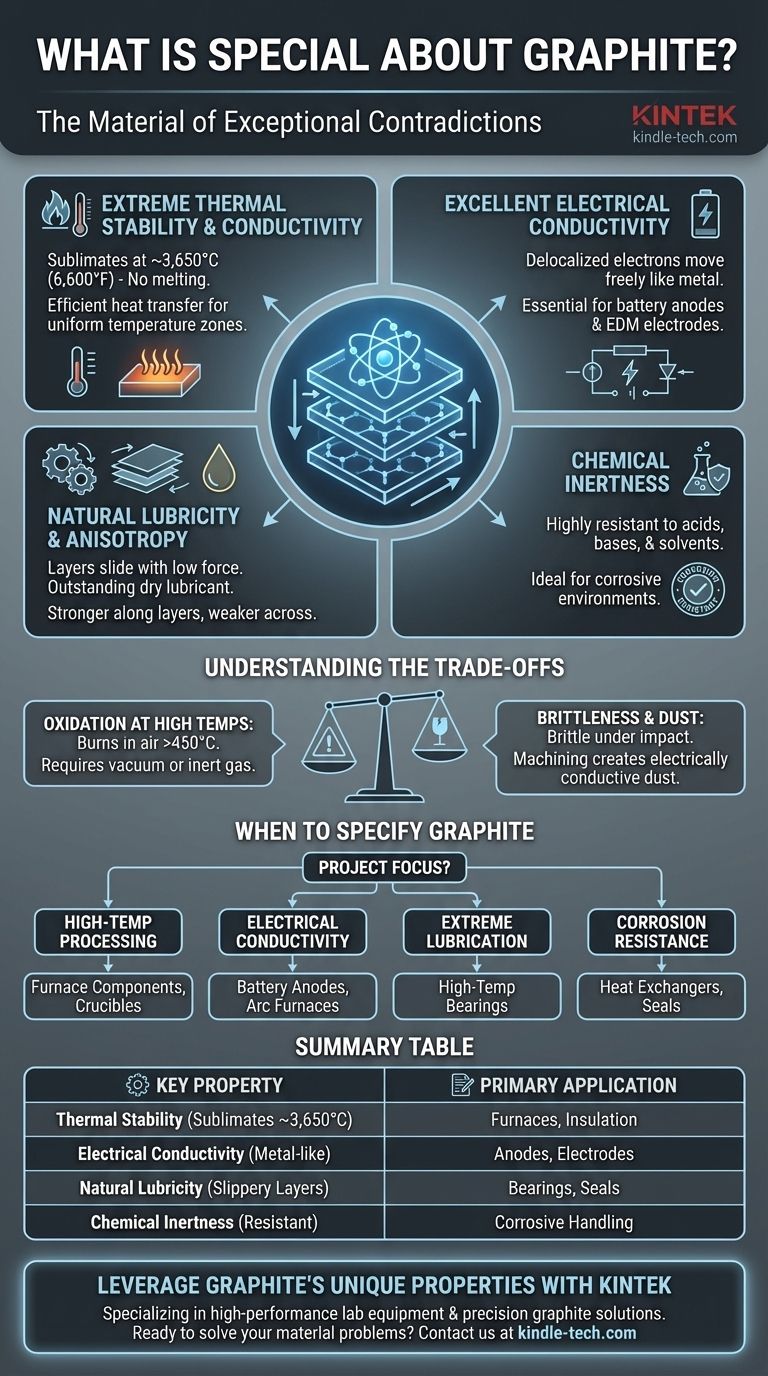
What makes graphite exceptional is its unique combination of seemingly contradictory properties. It is one of the few non-metals that is an excellent electrical and thermal conductor, yet it also possesses the high-temperature stability and chemical resistance typically associated with ceramics. This duality makes it an indispensable material in a vast range of demanding applications.
Graphite's true value lies not in a single trait, but in its synergistic combination of properties. Its ability to simultaneously manage extreme heat, conduct electricity, resist chemical attack, and act as a lubricant is unmatched by most other materials.

The Core Properties Defining Graphite
To understand why graphite is specified for applications from furnace insulation to batteries, we must examine its fundamental characteristics. These properties originate from its unique atomic structure: layers of strongly-bonded carbon atoms that are weakly bonded to each other.
Extreme Thermal Stability and Conductivity
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates (turns from a solid to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature, around 3,650°C (6,600°F). This makes it a premier material for high-temperature environments like furnaces and crucibles.
Furthermore, it has high thermal conductivity, meaning it transfers heat very efficiently. This is critical for applications like the furnace insulation mentioned in the reference, as it helps create uniform temperature zones by preventing hot spots.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Unlike most non-metals, graphite is an excellent electrical conductor. This is because of its layered atomic structure, where delocalized electrons are free to move along the layers, much like electrons in a metal.
This property is the reason graphite is essential for electrodes in electric arc furnaces and batteries, particularly as the anode material in most lithium-ion batteries today.
Natural Lubricity and Anisotropy
The weak bonds between the layers of carbon atoms allow them to slide over each other with very little force. This is what gives graphite its characteristic slippery feel and makes it an outstanding dry lubricant.
This layered structure also makes graphite anisotropic, meaning its properties differ depending on the direction of measurement. It is far stronger and more conductive along the layers than it is across them.
Chemical Inertness
Graphite is highly resistant to chemical attack. It does not react with most acids, bases, or solvents, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, and vessels that must handle corrosive substances.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging graphite's limitations is key to using it effectively and safely.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
While graphite excels in vacuum or inert atmospheres, its high-temperature stability vanishes in the presence of oxygen. It will begin to oxidize (burn) at temperatures around 450°C (842°F), turning into carbon dioxide gas.
This is the single most important limitation to consider for high-temperature applications. Graphite furnaces require a vacuum or an inert gas environment to prevent the heating elements and insulation from being consumed.
Brittleness and Mechanical Strength
Graphite is not a ductile material like steel. It is relatively brittle and can fracture under sharp impact or high tensile stress.
While it has excellent compressive strength, designs must account for its brittle nature. It is often reinforced with carbon fibers to create composites with superior mechanical properties.
Purity and Machinability
The properties of graphite can vary significantly based on its purity and manufacturing process. High-purity, isotropic graphite required for semiconductor manufacturing is far more expensive than graphite used for basic electrodes.
It is also a soft material that can be easily machined, but the resulting dust is electrically conductive and requires careful management in a workshop to prevent shorting out electrical equipment.
When to Specify Graphite in Your Application
Your choice to use graphite should be driven by the primary demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing: Graphite's thermal stability in non-oxidizing environments makes it ideal for furnace components, insulation, and crucibles.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Its excellent conductivity and resistance to thermal shock make it the go-to material for EDM electrodes and battery anodes.
- If your primary focus is lubrication in extreme conditions: Its self-lubricating properties are perfect for high-temperature bearings or applications where liquid lubricants would fail.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Use graphite for heat exchangers, seals, and pumps that must handle aggressive chemicals without degradation.
Ultimately, understanding graphite's unique profile of strengths and weaknesses allows you to leverage it as a powerful problem-solving material.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It's Special | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal Stability | Sublimates at ~3,650°C; ideal for high-temp environments. | Furnace components, crucibles, insulation |
| Excellent Electrical Conductivity | Conducts electricity like a metal; essential for energy transfer. | Battery anodes, EDM electrodes, arc furnaces |
| Natural Lubricity | Layers slide easily, providing dry lubrication. | High-temperature bearings, seals |
| Chemical Inertness | Highly resistant to acids, bases, and solvents. | Corrosive chemical handling, seals, gaskets |
| Key Limitation | Oxidizes in air above ~450°C; requires inert atmosphere. | Must be used in vacuum or inert gas environments |
Leverage Graphite's Unique Properties in Your Lab
Graphite's unparalleled combination of thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and chemical resistance makes it a cornerstone material for demanding laboratory and industrial processes. Whether you are designing a high-temperature furnace, developing next-generation battery technology, or need components that can withstand corrosive environments, the right graphite solution is critical to your success.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision graphite components tailored to your specific needs. Our expertise ensures you get the material properties required for reliability, efficiency, and breakthrough results.
Ready to solve your most challenging material problems? Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite solutions can enhance your application's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What are the disadvantages of using graphite? Key Limitations in High-Tech Applications
- Why is graphite melting point high? Unlocking the Power of Strong Covalent Bonds
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability
- How well does graphite transfer heat? Unlock Superior Thermal Management for Your Electronics



















