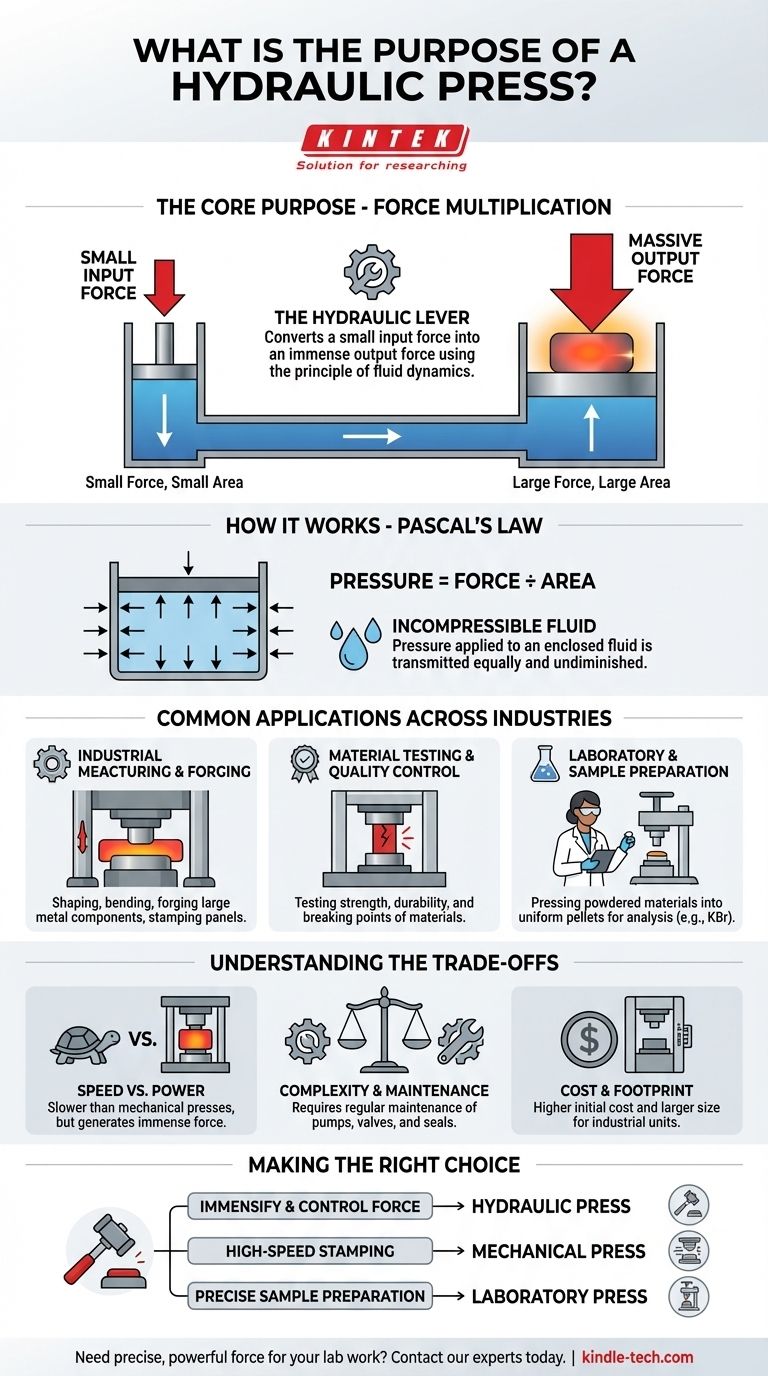
At its core, a hydraulic press is a machine designed for one primary purpose: to multiply force. Using the principle of fluid dynamics, it transforms a small, manageable input force into an immense compressive output force, allowing it to shape, crush, or compress materials that would otherwise be unworkable.
The true purpose of a hydraulic press is not just to press things, but to act as a "hydraulic lever." It leverages the incompressibility of a liquid to convert a small force applied over a small area into a massive force exerted over a large area.
The Core Principle: How Force Is Multiplied
The effectiveness of a hydraulic press hinges on a fundamental law of physics discovered in the 17th century. Understanding this principle is key to understanding the machine itself.
Pascal's Law in Action
A hydraulic press operates on Pascal's Law. This principle states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally and undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
In simple terms, Pressure = Force ÷ Area.
The "Hydraulic Lever" Effect
Imagine two pistons connected by a cylinder filled with hydraulic oil. One piston is small (the input) and the other is large (the output).
When you apply a small force to the small piston, you create pressure in the fluid. According to Pascal's Law, this exact same pressure is applied to the large piston.
Because the large piston has a much bigger surface area, that same pressure results in a proportionally larger output force. This is force multiplication in its purest form.
Why Liquid Is the Key
This entire process works because the hydraulic fluid (typically oil) is incompressible. Unlike a gas, it does not shrink in volume under pressure, allowing it to transmit force with near-perfect efficiency from one point to another.
Common Applications Across Industries
The ability to generate controlled, massive force makes the hydraulic press incredibly versatile. Its applications span from massive industrial operations to precise laboratory work.
Industrial Manufacturing and Forging
In heavy industry, hydraulic presses are used to shape, bend, and form large metal components. This includes everything from forging steel ingots and stamping car body panels to crushing entire vehicles for recycling.
Operators have precise control over the ram speed and pressure, making it ideal for creating complex or unique geometries.
Material Testing and Quality Control
Engineers use hydraulic presses to test the strength and durability of materials. By applying a measured compressive force, they can determine a material's breaking point and overall resilience, ensuring it meets safety and quality standards.
Laboratory and Sample Preparation
On a smaller scale, laboratory presses are essential for sample preparation. Scientists use them to press powdered materials into dense, uniform pellets or thin films, which are then analyzed using techniques like spectroscopy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the hydraulic press is not the solution for every problem. Its design comes with specific trade-offs that are important to recognize.
Speed vs. Power
The primary trade-off is speed. Hydraulic presses are capable of generating enormous force, but they are typically much slower than their mechanical counterparts. The movement of fluid simply takes more time.
Complexity and Maintenance
Hydraulic systems involve pumps, valves, seals, and high-pressure hoses. These components require regular maintenance to prevent fluid leaks, contamination, and loss of performance.
Cost and Footprint
Industrial hydraulic presses are often large, heavy, and represent a significant capital investment. Their power and control come at a higher initial cost compared to simpler mechanical presses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of press depends entirely on the specific task you need to accomplish.
- If your primary focus is generating immense, controllable force: The hydraulic press is unmatched for heavy forging, deep drawing, or compression testing.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is often a better, faster choice for operations like blanking or coining sheet metal.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable sample preparation: A dedicated laboratory hydraulic press is the standard tool for creating consistent pellets for scientific analysis.
Ultimately, understanding the hydraulic press means understanding its role as a powerful tool for force multiplication.

Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Pascal's Law: Pressure in an incompressible fluid is transmitted equally, enabling force multiplication. |
| Primary Function | Acts as a 'hydraulic lever' to transform a small input force into a massive compressive output force. |
| Common Applications | Industrial forging, metal forming, material testing, and laboratory sample preparation (e.g., KBr pellets). |
| Main Trade-offs | High force capability but slower speed than mechanical presses; requires more complex maintenance. |
Need precise, powerful force for your lab work?
Whether you're preparing uniform samples for analysis or require reliable compression testing, the right hydraulic press is critical for accuracy and repeatability.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our range of hydraulic presses is designed to deliver the controlled force and durability your research demands.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to find the perfect hydraulic press solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?



















