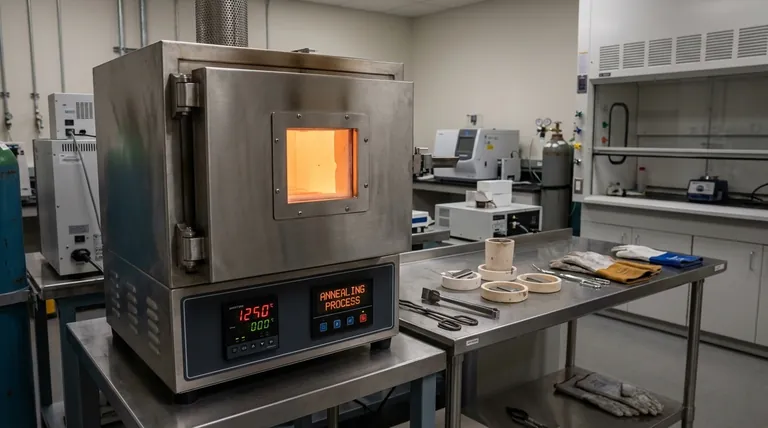
In an industrial context, annealing is a critical heat treatment process used to alter the microstructure of a material, primarily metals. By heating the material to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it, annealing makes the material softer, more ductile, and easier to work with. It effectively reverses the negative effects of manufacturing processes like cold forming or welding.
The core purpose of annealing is not just to heat and cool a material, but to strategically reset its internal structure. This removes accumulated stress and brittleness, making the material predictable and fit for further manufacturing or its final application.

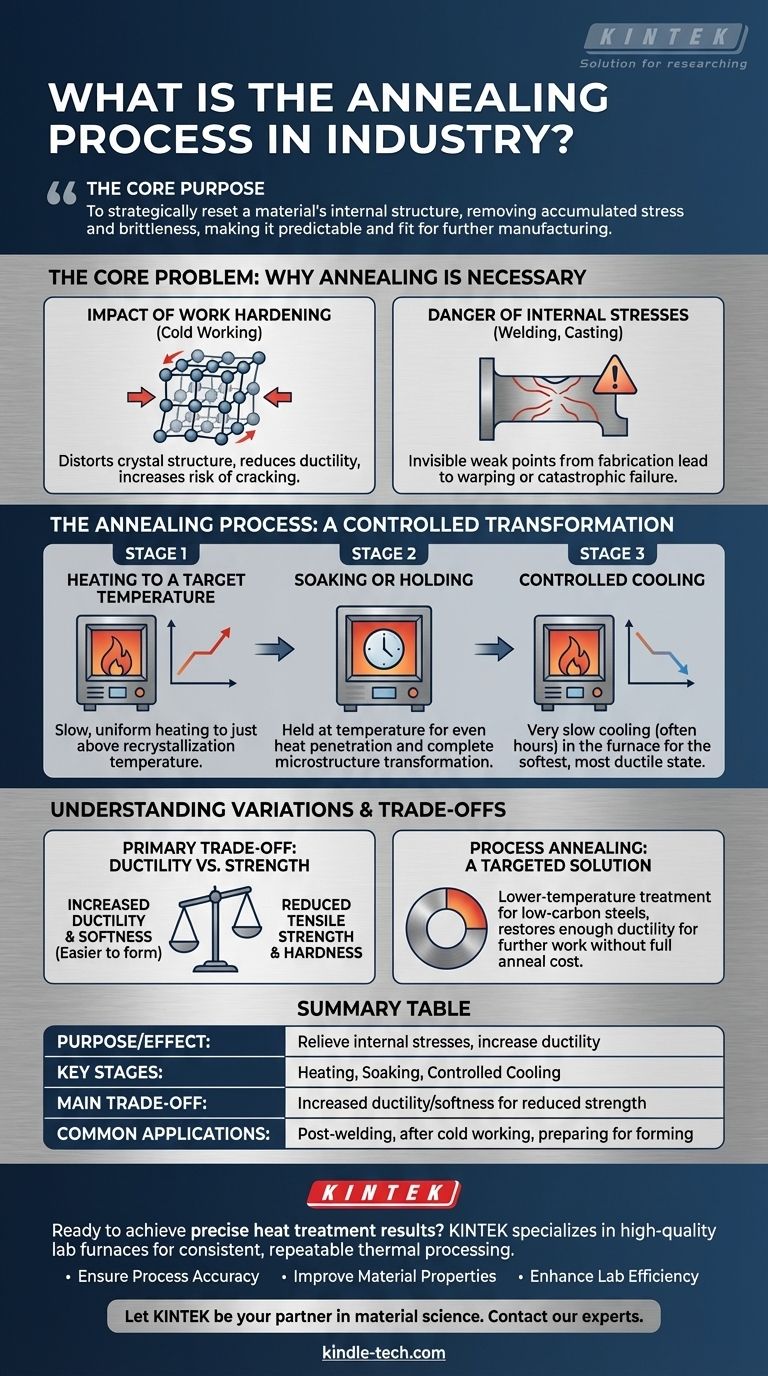
The Core Problem: Why Annealing is Necessary
Before understanding the process, it's essential to understand the problems it solves. Annealing is a corrective measure for issues introduced during fabrication.
The Impact of Work Hardening
When you bend, draw, or form a metal at room temperature (a process known as cold working), its internal crystal structure becomes distorted and strained.
This makes the material harder and stronger, but it also significantly reduces its ductility, or its ability to deform without fracturing. Pushing a work-hardened material too far will cause it to crack.
The Danger of Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, or even aggressive machining introduce internal stresses into a material.
These stresses are invisible but create weak points within the part. Over time, or under load, these stresses can lead to unexpected warping, cracking, or catastrophic failure.
The Annealing Process: A Controlled Transformation
Annealing is a precise, three-stage process designed to relieve these stresses and restore ductility by allowing the material's internal grain structure to reform.
Stage 1: Heating to a Target Temperature
The material is heated slowly and uniformly in a furnace to a specific temperature. This temperature is critical and is typically just above the material's recrystallization temperature, where new, strain-free grains begin to form.
Stage 2: Soaking or Holding
Once at the target temperature, the material is "soaked" or held there for a set period. This allows the heat to penetrate the entire part evenly, ensuring the complete transformation of the internal microstructure into a new, unstressed state.
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling
This is the most defining step. The material is cooled very slowly, often by simply turning the furnace off and letting it cool down over many hours. This slow cooling rate is crucial for producing the softest, most ductile, and stress-free final state.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
While full annealing is powerful, it is not always the only or best option. The choice involves balancing desired properties with cost and time.
The Cost of Time and Energy
A full anneal cycle, especially the slow cooling phase, can take many hours or even days for very large parts. This consumes significant furnace time and energy, adding cost to the final product.
The Primary Trade-off: Ductility vs. Strength
The primary outcome of annealing is increased ductility and softness. The unavoidable trade-off is a reduction in tensile strength and hardness. The material becomes easier to form but less resistant to force.
Process Annealing: A Targeted Solution
For some applications, a full anneal is unnecessary. Process annealing is a specific, lower-temperature treatment used on work-hardened, low-carbon steels.
It doesn't achieve the full softness of a true anneal but restores enough ductility to allow for further cold working without the risk of fracture, making it a more efficient intermediate step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying annealing effectively requires matching the process to the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is preparing for extensive forming: A full anneal is necessary to restore maximum ductility after an initial cold-working operation.
- If your primary focus is ensuring long-term structural stability: Use annealing to remove dangerous internal stresses from critical components, especially after welding or casting.
- If your primary focus is continuing a multi-stage manufacturing process: Use a more efficient method like process annealing to soften a part just enough for the next step without the time and cost of a full anneal.
Ultimately, annealing empowers engineers to control a material's properties, turning the limitations of one process into the starting point for the next.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Purpose/Effect |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Relieve internal stresses and increase ductility. |
| Key Process Stages | Heating, Soaking, Controlled Cooling. |
| Main Trade-off | Increased ductility and softness for reduced strength/hardness. |
| Common Applications | Post-welding, after cold working, preparing for further forming. |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable heat treatment results in your lab?
The annealing process requires uniform heating and exact temperature control to be effective. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for consistent, repeatable thermal processing.
Our solutions help you:
- Ensure Process Accuracy: Achieve the specific temperatures and soak times critical for successful annealing.
- Improve Material Properties: Reliably produce softer, more ductile, and stress-free materials.
- Enhance Lab Efficiency: Benefit from durable equipment built for industrial-grade applications.
Let KINTEK be your partner in material science. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your annealing and heat treatment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More



















