In powder metallurgy, sintering is the critical heat treatment that transforms a fragile, compressed powder shape into a strong, unified, and functional component. After metal powder is pressed into a desired form, it is heated to a temperature just below its melting point. This process causes the individual metal particles to fuse, or weld, together, creating the final part's structural integrity and mechanical strength.
Sintering is the essential bridge between a loosely-held powder compact and a finished metal part. It provides the final mechanical strength and desired physical properties by bonding the material's particles together at a microscopic level, all without fully melting the metal.

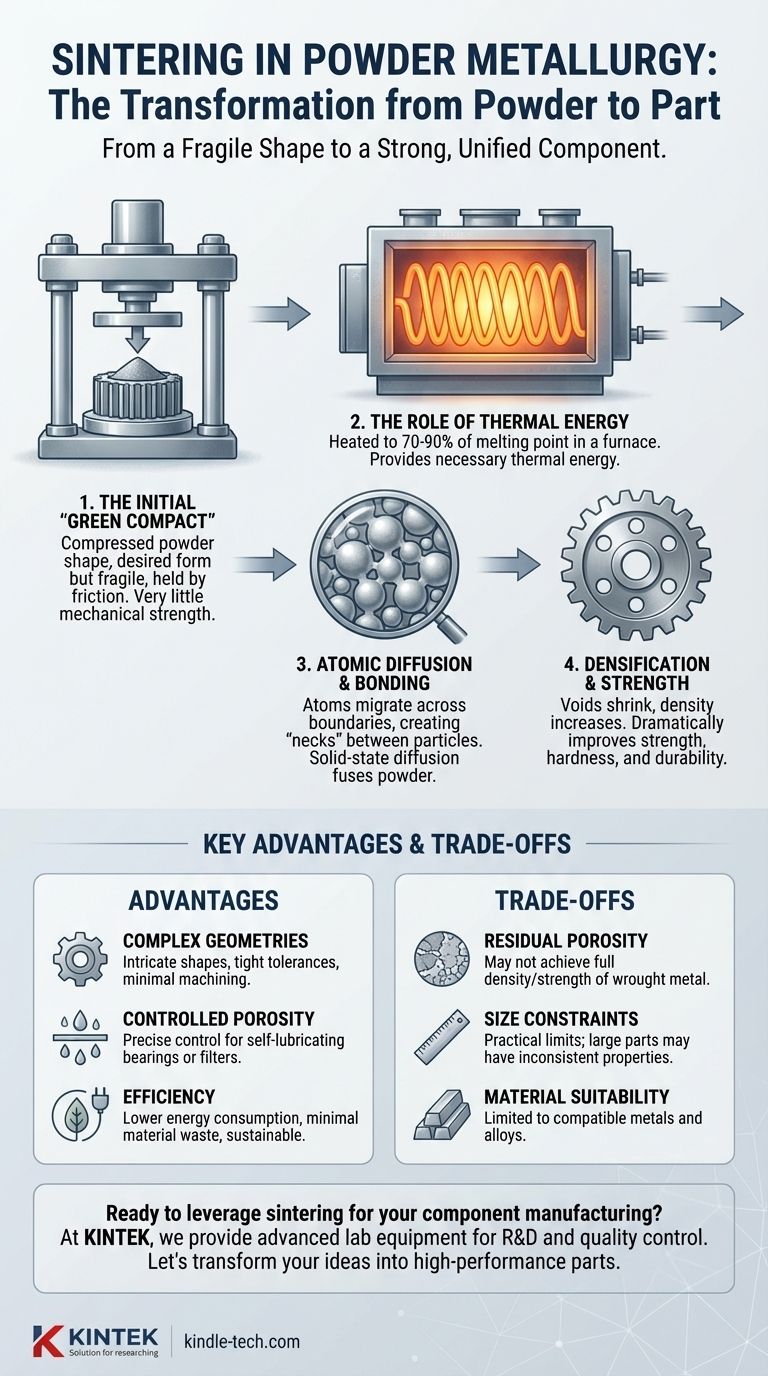
The Fundamental Process: From Powder to Part
To understand the application of sintering, you must first understand the state of the component before it begins. The process is a fundamental transformation of material properties.
The Initial "Green Compact"
After being pressed in a die, the component is known as a green compact. This part has the desired shape but possesses very little mechanical strength. It is held together primarily by the friction between the interlocked powder particles and is often brittle enough to be broken by hand.
The Role of Thermal Energy
The green compact is placed in a furnace and heated to a specific temperature, typically between 70% and 90% of the primary metal's melting point. This high temperature provides the thermal energy necessary for the atoms in the metal particles to become mobile.
Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
At the sintering temperature, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries where individual particles touch. This process, known as solid-state diffusion, creates small "necks" or welds between the particles. As the process continues, these necks grow, effectively fusing the powder into a solid, cohesive mass.
Densification and Strength
As the particles bond, the small voids or pores between them shrink and become more rounded. This increases the density of the component, dramatically improving its strength, hardness, and overall durability. The result is a finished part that is ready for use.
Key Advantages Enabled by Sintering
Sintering is not just a strengthening step; it is what enables the primary advantages of the powder metallurgy manufacturing method.
Creating Complex Geometries
Powder metallurgy excels at producing parts with complex external and internal shapes to very tight tolerances. Sintering finalizes these intricate designs, locking them into a strong final form with an excellent surface finish, minimizing the need for secondary machining.
Achieving Controlled Porosity
One of the most unique applications of sintering is the ability to precisely control the final porosity of a part. By adjusting the process, manufacturers can create components with interconnected pores, ideal for self-lubricating bearings (which hold oil) or filters.
Ensuring Material and Energy Efficiency
Sintering is a highly efficient process. Because the metal is never fully melted, energy consumption is significantly lower than in casting operations. Furthermore, since the part is formed to its final shape from the start, there is minimal material waste, making it a sustainable or "green" technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be considered for any application. An objective analysis requires acknowledging these limitations.
Inherent Residual Porosity
Unless secondary operations are performed, most sintered parts will have some degree of residual porosity. While this can be an advantage, it also means the part may not achieve the same maximum strength or density as a component made from fully dense wrought or cast metal.
Size and Complexity Constraints
There are practical limits to the size of parts that can be effectively sintered. Very large components can suffer from non-uniform heating and densification, leading to inconsistent properties throughout the part.
Material Suitability
The powder metallurgy and sintering process is ideal for many materials, such as iron, steel, bronze, and stainless steel. However, not all metals or alloys are suitable for the process, which can limit material selection for certain high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering as part of your manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Sintering offers exceptional repeatability and minimal material waste for large series of complex parts.
- If your primary focus is unique material properties: The process allows for controlled porosity, enabling applications like self-lubricating components and filters that are difficult to achieve otherwise.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency: Sintering provides a near-net-shape part with good surface finish and low energy consumption, reducing the need for costly machining and finishing operations.
Ultimately, sintering is the enabling technology that unlocks the full potential of powder metallurgy, transforming precisely shaped powders into robust, functional parts.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | Transforms fragile powder compacts into strong, unified parts. |
| Complex Geometries | Enables production of intricate shapes with minimal machining. |
| Controlled Porosity | Creates parts for self-lubricating bearings or filters. |
| Material & Energy Efficiency | Near-net-shape process with low waste and energy consumption. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your component manufacturing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for powder metallurgy R&D and quality control. Whether you are developing new sintered materials or optimizing your production process, our solutions help you achieve precise temperature control and consistent results.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your laboratory's specific needs in powder metallurgy. Let's transform your ideas into high-performance parts.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What technical functions does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Optimize CoCrFeNi Alloy Coatings
- What critical processing conditions are provided by a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 98%+ Density.
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















