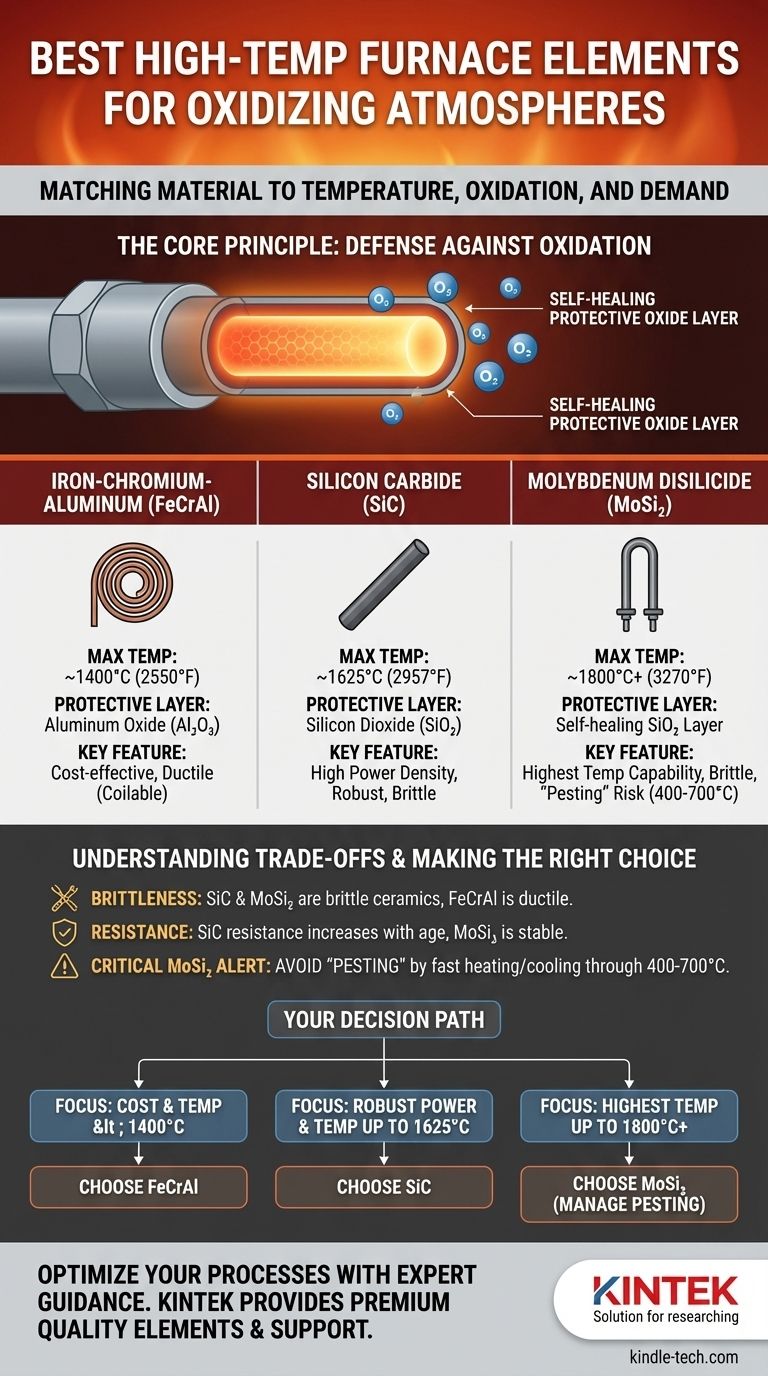
For high-temperature furnaces operating in oxidizing atmospheres, the best heating element is determined by your maximum required temperature. For temperatures up to 1800°C (3270°F), **Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) ** is the industry standard due to its superior performance and lifespan. For mid-range applications up to 1625°C (2957°F), Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a robust and common choice, while Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys are the most cost-effective solution for temperatures below 1400°C (2550°F).
Selecting a heating element is not about finding one universally "best" material. It is about matching a material's ability to form a stable, protective oxide layer against the specific temperature, budget, and operational demands of your furnace.
The Core Principle: A Self-Healing Protective Shield
To understand why certain materials excel, you must first understand the primary challenge: oxidation.
Why Oxidation is the Enemy
At high temperatures, an oxidizing atmosphere (any environment with free oxygen, including air) is extremely aggressive. Most metals will rapidly combine with oxygen and essentially burn up, leading to catastrophic element failure.
The Role of the Oxide Layer
The solution is not to find a material that is inert to oxygen, but one that uses oxygen to its advantage. The best materials react with oxygen to form a thin, stable, and non-reactive protective oxide layer on their surface. This ceramic-like "skin" acts as a gas-tight barrier, preventing further oxidation of the underlying element material and allowing it to operate for thousands of hours.
Comparing the Primary Material Candidates
Your choice of material is a direct trade-off between operating temperature and cost. Each material relies on forming a different protective layer.
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl / "Kanthal")
This is the workhorse for lower-temperature applications, often seen in lab furnaces and kilns.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to ~1400°C (2550°F)
- Protective Layer: Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃)
- Key Feature: These alloys are ductile and can be easily formed into coiled wires, making them inexpensive and simple to work with.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
SiC elements are common in industrial processes like glass manufacturing and metal heat treating. They are typically available as rigid rods or tubes.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to ~1625°C (2957°F)
- Protective Layer: Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
- Key Feature: Offers high power density (can get very hot, very fast) and is mechanically robust at operating temperature.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂)
This is the premier material for the most demanding high-temperature air furnaces, used in dental, ceramic, and advanced materials research.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to ~1800°C (3270°F), with some grades exceeding this.
- Protective Layer: A glassy, self-healing Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) layer.
- Key Feature: Unmatched high-temperature capability in air. When hot, the glassy oxide layer can even "heal" small surface cracks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
No material is perfect. Understanding their limitations is critical for reliable operation.
Brittleness vs. Ductility
FeCrAl is ductile and forgiving. SiC and MoSi₂ are both hard ceramics and are extremely brittle at room temperature. They must be handled with care during installation to prevent fracture from mechanical shock.
Resistance Stability and Power Control
The electrical resistance of SiC elements increases over their lifespan as the material ages. This requires a more sophisticated power controller (typically an SCR or a tapped transformer) that can supply increasing voltage to maintain power output. In contrast, MoSi₂ has a very stable resistance over its life, simplifying power supply requirements.
The Risk of MoSi₂ "Pesting"
MoSi₂ has a unique and critical vulnerability. In the temperature range of 400-700°C (750-1300°F), it can undergo a catastrophic form of low-temperature oxidation called "pesting," where the element rapidly disintegrates into powder. To avoid this, a furnace using MoSi₂ elements must be programmed to heat and cool through this temperature zone as quickly as possible.
Cost Considerations
The cost of the materials directly correlates with their temperature capability. The general hierarchy from least to most expensive is: FeCrAl < SiC < MoSi₂. The higher initial cost of MoSi₂ is often justified by its longer life and higher process temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Furnace
Your decision should be a direct function of your operational requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for temperatures below 1400°C: FeCrAl alloys are the clear and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is robust performance and high power density up to 1625°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements provide an excellent balance of cost and capability.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (up to 1800°C+) with long-term stability: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is the definitive solution, provided you can manage its installation and avoid the "pesting" zone.
By understanding how these materials defend themselves against oxidation, you can confidently select an element that ensures the performance and longevity of your high-temperature system.

Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Protective Oxide Layer | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) | Up to 1400°C | Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) | Cost-effective, ductile |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1625°C | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | High power density, robust |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C+ | Self-healing SiO₂ layer | Highest temperature capability |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Processes with KINTEK
Selecting the right heating element is critical for the performance, efficiency, and longevity of your laboratory furnace. Whether your application requires the cost-effectiveness of FeCrAl, the robust power of SiC, or the extreme temperature capability of MoSi₂, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs.
Why choose KINTEK for your lab equipment?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you select the perfect element material based on your specific temperature requirements, budget, and operational demands.
- Premium Quality: We supply reliable, high-performance heating elements and consumables designed for durability and precise control.
- Comprehensive Support: From selection to installation and maintenance, we ensure your furnace operates at peak performance.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can power your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















