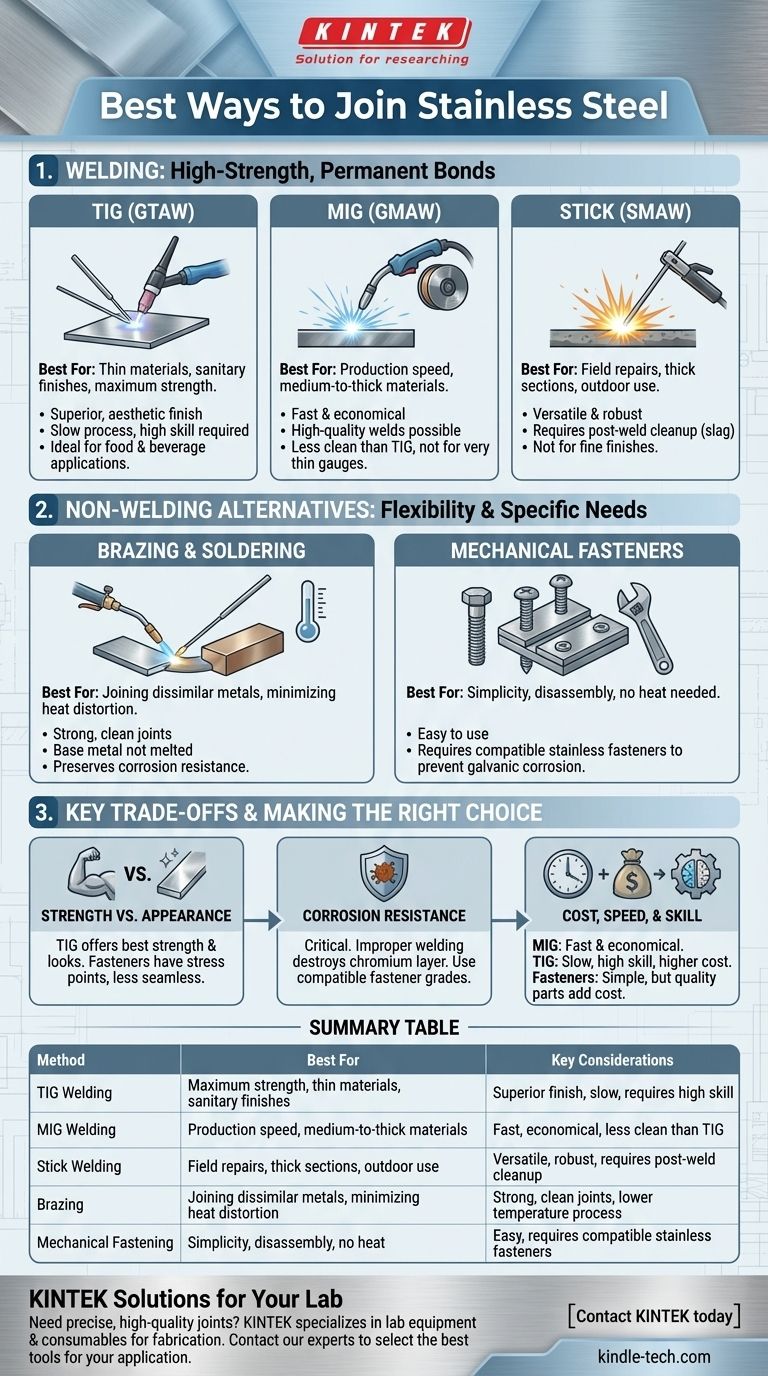
The best method for joining stainless steel depends entirely on your specific application, as there is no single answer. The most common and effective methods fall into three main categories: welding (TIG, MIG, and Stick), brazing, and mechanical fastening. Each technique offers a different balance of strength, corrosion resistance, appearance, and cost.
The optimal joining method is not a single process, but a choice you make by weighing the performance requirements of the joint—such as strength and corrosion resistance—against the practical constraints of your project, like budget, available skill, and equipment.

Understanding Welding Processes for Stainless Steel
Welding is the most common method for achieving a permanent, high-strength bond. It involves melting the base metal and a filler material to fuse the pieces into a single, continuous part.
TIG (GTAW) Welding
TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) is the gold standard for high-quality stainless steel work. It uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create a precise, clean arc.
This process offers a superior, aesthetically pleasing finish with excellent strength. It is the preferred method for thin materials, sanitary applications (like food and beverage), and when appearance is critical.
However, TIG welding is significantly slower than other methods and requires a high level of operator skill.
MIG (GMAW) Welding
MIG (Gas Metal Arc Welding) is a faster and more economical welding process. It uses a continuously fed wire electrode that also acts as the filler metal.
MIG is ideal for thicker materials and production environments where speed is a key factor. Modern MIG equipment can produce very high-quality welds.
While faster, it can be more challenging to produce welds as clean as TIG, and it is less suited for very thin gauges of stainless steel.
Stick (SMAW) Welding
Stick welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) is a versatile and robust process that uses a consumable electrode coated in flux to protect the weld pool.
This method is excellent for field repairs and welding on thicker sections of stainless steel, especially in outdoor or windy conditions where a shielding gas might be blown away.
Stick welding produces the least "clean" weld, requiring significant post-weld cleanup to remove slag, and is generally not suitable for thin materials or applications requiring a fine finish.
Exploring Non-Welding Alternatives
In some cases, welding is not the ideal or even a possible solution. Heat distortion, metallurgical concerns, or the need for disassembly may lead you to other methods.
Brazing and Soldering
Brazing is a process that joins metals using a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the stainless steel itself. The base metal is heated, but not melted.
This method is highly effective for joining stainless steel to dissimilar metals (like copper or brass) and for applications where minimizing heat input and distortion is critical. The resulting joints are clean and strong, though not as strong as a full-penetration weld.
Mechanical Fasteners
Using bolts, screws, and rivets is the simplest joining method. It requires no specialized thermal equipment and allows for easy disassembly and reassembly.
This is the obvious choice for components that need to be serviced or replaced. The primary consideration is to use stainless steel fasteners of a compatible grade to prevent galvanic corrosion, which can rapidly destroy the joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires you to balance competing priorities. What you gain in one area, you often sacrifice in another.
Strength vs. Appearance
A properly executed TIG weld provides the highest-strength, most visually appealing joint. Mechanical fasteners, while strong, introduce stress concentrations around the holes and do not create a seamless part.
Corrosion Resistance
This is the most critical trade-off. Improper welding—using the wrong filler rod or applying too much heat—can destroy the chromium oxide layer that gives stainless steel its "stainless" properties, leading to "weld decay" and rust.
Using fasteners of a different metal (like zinc-plated steel) will create a galvanic cell and cause the joint to corrode quickly. Brazing, done correctly, generally preserves corrosion resistance well.
Cost, Speed, and Skill
MIG welding is built for speed and efficiency, making it cost-effective in production. TIG welding is a slow, meticulous craft that commands a higher cost due to labor time and skill requirements. Mechanical fastening is fast and requires minimal specialized skill, but the cost of high-quality stainless fasteners can add up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Analyze your project's non-negotiable requirements to find your answer.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and a flawless, sanitary finish: TIG welding is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is production speed on medium-to-thick materials: MIG welding offers the best balance of speed and quality.
- If your primary focus is avoiding heat distortion or joining stainless to another metal: Brazing provides a strong, reliable bond at lower temperatures.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and the ability to disassemble: Using stainless steel mechanical fasteners is the most direct approach.
Ultimately, understanding the specific demands of your project is the key to selecting the truly best joining method.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| TIG Welding | Maximum strength, thin materials, sanitary finishes | Superior finish, slow, requires high skill |
| MIG Welding | Production speed, medium-to-thick materials | Fast, economical, less clean than TIG |
| Stick Welding | Field repairs, thick sections, outdoor use | Versatile, robust, requires post-weld cleanup |
| Brazing | Joining dissimilar metals, minimizing heat distortion | Strong, clean joints, lower temperature process |
| Mechanical Fastening | Simplicity, disassembly, no heat | Easy, requires compatible stainless fasteners |
Need precise, high-quality joints for your lab equipment? The right joining method is critical for the performance and longevity of your stainless steel components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables that support these precise fabrication processes. Whether your project requires the clean finish of TIG welding or the assembly simplicity of fasteners, we have the solutions to meet your lab's specific needs.
Let our experts help you select the best tools and materials for your application. Contact KINTEL today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's fabrication and maintenance requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- 12 Inch 24 Inch High Precision Automatic Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
- High Precision Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What are the three 3 differences between compression molding and injection molding? Choose the Right Process for Your Project
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing



















