Ultimately, the capacity of a sieve shaker is defined by the number and size of the sieves it can hold in a single stack. A common electromagnetic sieve shaker can accommodate a stack of up to 10 standard test sieves, plus a bottom collecting pan and a lid, with sieve diameters ranging from 8 to 12 inches (200 mm to 315 mm).
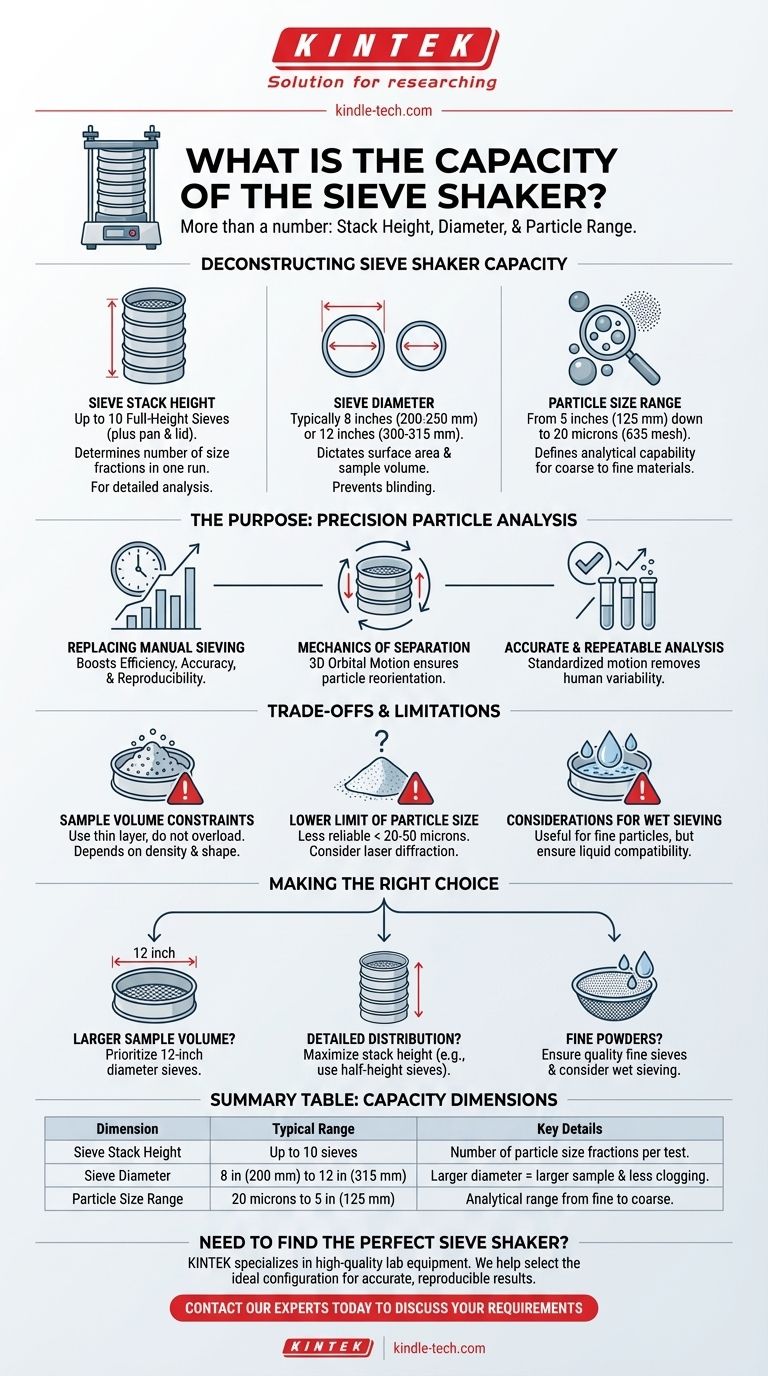
The concept of "capacity" for a sieve shaker goes beyond a simple number. It's a combination of the physical stack height, the diameter of the sieves, and the particle size range the equipment is designed to analyze.
Deconstructing Sieve Shaker Capacity
To properly evaluate if a sieve shaker meets your needs, you must consider capacity across three dimensions: stack height, sieve diameter, and the range of particle sizes it can effectively separate.
Sieve Stack Height
The vertical capacity determines how many different particle size fractions you can separate in a single test run.
Most standard shakers are designed to hold up to 10 full-height sieves. This allows for a detailed analysis with multiple data points across your particle size distribution.
Sieve Diameter
The diameter of the sieves dictates the surface area available for separation and, consequently, the volume of sample material you can process efficiently.
Common diameters include 8 inches (200-250 mm) and 12 inches (300-315 mm). A larger diameter provides more mesh area, which is crucial for preventing screen "blinding" (clogging) and for processing larger initial sample weights.
Particle Size Range
A shaker's true analytical capacity is defined by the range of particle sizes it can separate. This is a function of the woven-wire mesh test sieves themselves.
The operational range spans from coarse materials as large as 5 inches (125 mm) down to very fine powders as small as 20 microns (equivalent to a 635 mesh screen).
The Purpose of a Sieve Shaker
Understanding the intended function of a sieve shaker provides context for its capacity. It is not a bulk processing tool, but a precision instrument for particle analysis.
Replacing Manual Sieving
The primary advantage of a sieve shaker is its ability to automate the laborious process of hand sieving. This delivers a dramatic increase in efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility.
The Mechanics of Separation
Effective sieve shakers impart a three-dimensional, orbital motion on the sieve stack. This combined circular and vertical movement ensures particles are constantly reoriented, maximizing their opportunities to pass through the mesh openings.
Ensuring Accurate and Repeatable Analysis
By standardizing the shaking motion and time, the instrument removes human variability. This leads to highly accurate and reproducible particle sizing results, which is essential for quality control and research environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a sieve shaker is not the right tool for every task. Its capacity has inherent limitations that are critical to understand.
Sample Volume Constraints
The primary limitation is sample volume. The goal is to form a thin layer of material on each sieve, not to fill it. Overloading a sieve prevents particles from reaching the mesh, leading to inaccurate results. The appropriate sample weight depends entirely on the material's density and particle shape.
The Lower Limit of Particle Size
Sieve analysis becomes less reliable for extremely fine particles. While it can be effective down to around 20-50 microns, particles smaller than this are often better analyzed using other methods like laser diffraction or light scattering.
Considerations for Wet Sieving
A sieve shaker can be used for wet analysis, which helps separate fine particles that might otherwise agglomerate. However, you must ensure the liquid used (typically water) does not dissolve or otherwise damage the sample material itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your sieve shaker configuration based on the specific requirements of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is processing a larger sample volume: Prioritize a shaker that accepts larger, 12-inch diameter sieves.
- If your primary focus is a highly detailed size distribution: Maximize the number of sieves in your stack, potentially using half-height sieves to fit more gradations.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders: Ensure your finest sieve (e.g., 20 microns) is of high quality and consider wet sieving to improve separation accuracy.
Choosing the right sieve shaker configuration is about matching the instrument's capacity to your specific analytical needs.

Summary Table:
| Capacity Dimension | Typical Range | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Sieve Stack Height | Up to 10 sieves | Determines the number of particle size fractions you can separate in a single test. |
| Sieve Diameter | 8 inches (200 mm) to 12 inches (315 mm) | Larger diameters allow for processing larger sample weights and prevent screen clogging. |
| Particle Size Range | 20 microns to 5 inches (125 mm) | Defines the analytical range, from fine powders to coarse materials. |
Need to find the perfect sieve shaker for your lab's particle analysis?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including sieve shakers and test sieves. We can help you select the ideal configuration—whether you need a larger diameter for bigger samples or a taller stack for detailed analysis—to ensure accurate and reproducible results for your quality control and research.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your laboratory's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- Why use a laboratory crushing and sieving system for rice husks? Optimize Hydrolysis for 1mm Particle Size
- How do air classifiers or sieving machines contribute to methane pyrolysis? Refine Carbon Black for Market Success
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What are the parts of a sieve shaker? The Key Components for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why are crushing and sieving systems necessary for biomass pyrolysis? Ensure Feedstock Quality and High Yields
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- Why are industrial-grade crushing and sieving systems essential for adsorbents? Maximize Your Filtration Efficiency
- How does a constant temperature air shaker provide process assurance during enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob residues?



















