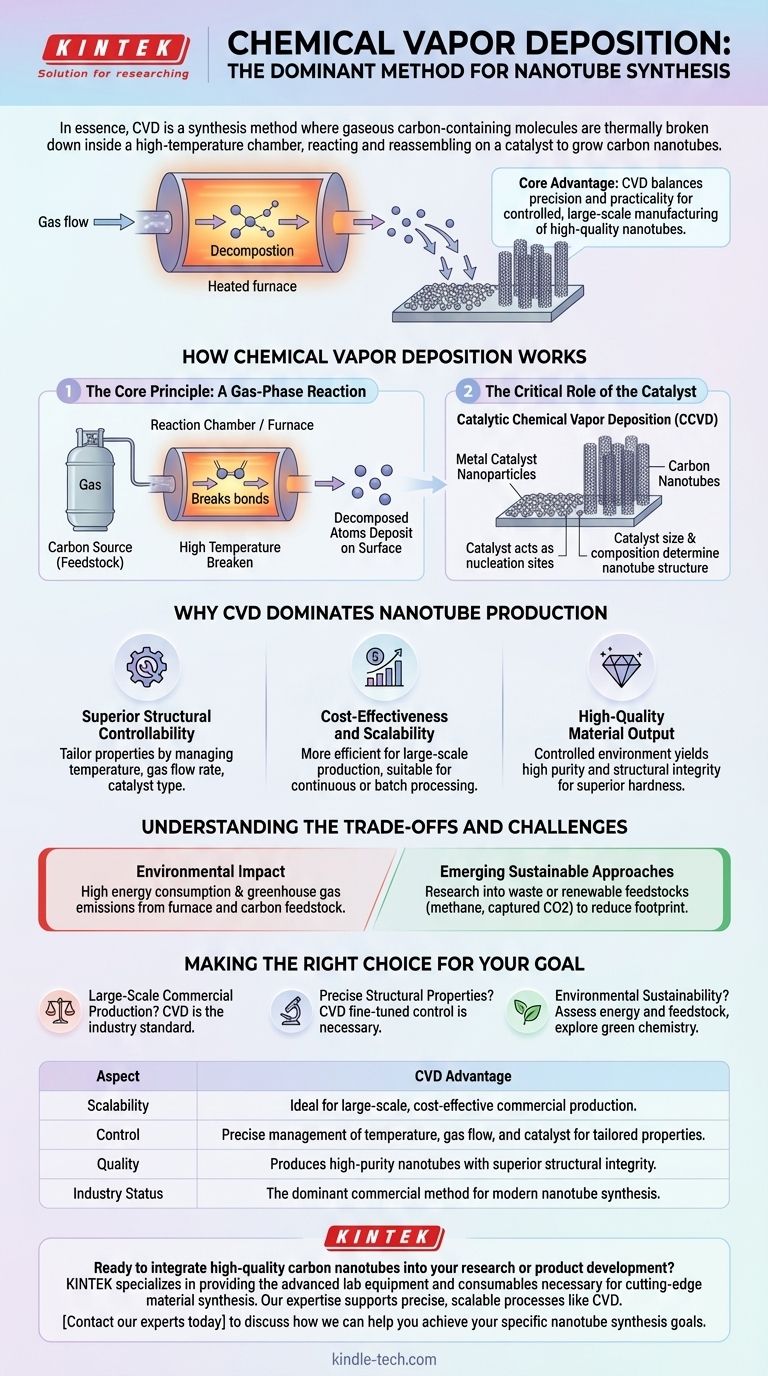
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a synthesis method where gaseous carbon-containing molecules are thermally broken down inside a high-temperature chamber, reacting and reassembling on a catalyst to grow carbon nanotubes. This process is the dominant commercial method for producing nanotubes because it offers unparalleled control over the final structure while being more cost-effective and scalable than older techniques like laser ablation or arc discharge.
The core advantage of CVD is its balance of precision and practicality. It allows for the controlled, large-scale manufacturing of high-quality nanotubes, making it the backbone of the modern carbon nanomaterials industry.

How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works
The CVD process can be understood as a highly controlled gas-to-solid conversion. It involves three fundamental components: a carbon source, energy, and a catalyst.
The Core Principle: A Gas-Phase Reaction
The process begins by introducing a carbon-containing gas, known as a feedstock, into a reaction chamber or furnace.
This chamber is heated to a high temperature, providing the thermal energy needed to break the chemical bonds within the gas molecules.
These decomposed atoms then deposit onto a prepared surface, forming the solid structure of the carbon nanotubes.
The Critical Role of the Catalyst
For nanotube synthesis, the process is more accurately called Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD).
A substrate within the chamber is coated with nanoparticles of a metal catalyst. These catalyst particles act as nucleation sites, or "seeds," from which the nanotubes begin to grow.
The size and composition of the catalyst are critical variables that directly influence the diameter and structure of the resulting nanotubes.
Why CVD Dominates Nanotube Production
While other methods exist, CVD became the industry standard for clear, practical reasons related to control, cost, and quality.
Superior Structural Controllability
CVD offers a level of precision that other methods lack. By carefully managing variables like temperature, gas flow rate, and catalyst type, operators can tailor the nanotubes' specific properties.
This control is essential for creating materials suited for specific applications in electronics, composites, and medicine.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Compared to the extremely high energy requirements of laser ablation or arc-discharge methods, CVD is more efficient for large-scale production.
Its adaptability for continuous or batch processing makes it the most economically viable option for commercial and industrial output.
High-Quality Material Output
The controlled environment of a CVD reactor results in nanotubes with high purity and structural integrity.
This produces materials with superior hardness and resistance to damage, which is a key requirement for advanced material applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite its advantages, the CVD process is not without significant considerations, particularly regarding its environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact
The synthesis process is the primary source of potential ecotoxicity in the nanotube life cycle.
This is driven by high energy consumption to maintain furnace temperatures and the emission of greenhouse gases depending on the carbon feedstock used.
Emerging Sustainable Approaches
To address these challenges, research is focused on greener alternatives.
This includes using waste or renewable feedstocks, such as methane from pyrolysis or even carbon dioxide captured from industrial processes, to reduce the overall environmental impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting or evaluating a synthesis method depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial production: CVD is the established industry standard due to its unmatched scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is precise structural properties: The fine-tuned control offered by CVD is necessary for creating custom nanotubes for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: You must carefully assess the energy consumption and feedstock of any CVD process and explore emerging green chemistry alternatives.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is the foundational technology for nanotube synthesis, but its responsible application requires a clear understanding of its operational trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Advantage |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Ideal for large-scale, cost-effective commercial production |
| Control | Precise management of temperature, gas flow, and catalyst for tailored properties |
| Quality | Produces high-purity nanotubes with superior structural integrity |
| Industry Status | The dominant commercial method for modern nanotube synthesis |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for cutting-edge material synthesis. Our expertise supports precise, scalable processes like CVD. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your specific nanotube synthesis goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















