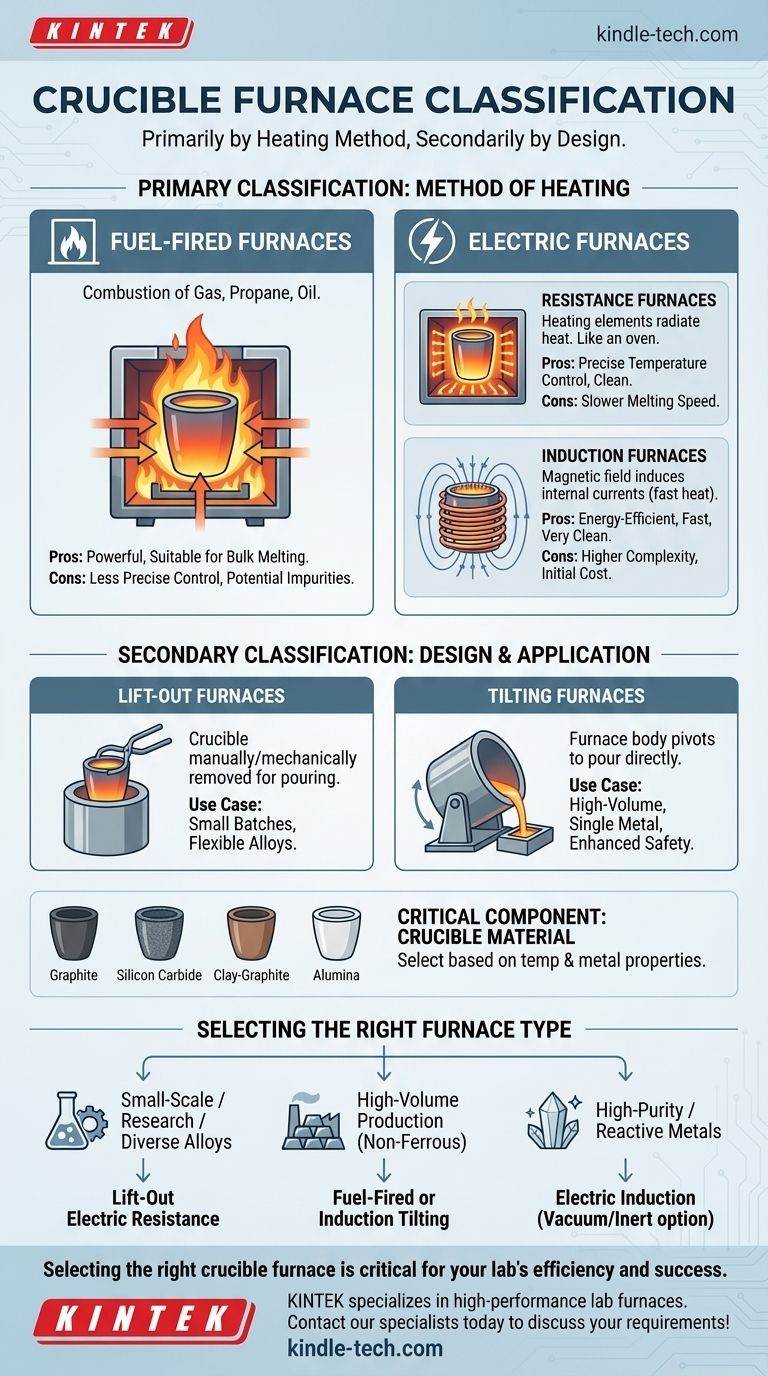
In essence, crucible furnaces are primarily classified by their method of heating. While other factors like furnace design and crucible material are critical for operation, the fundamental distinction between furnace types comes down to the energy source used to generate heat, which is typically either fuel combustion or electricity.
The classification of a crucible furnace is not a single label but a combination of its heating technology and its mechanical design. Understanding these two aspects—how it generates heat and how you access the molten material—is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific application.

The Primary Classification: Method of Heating
The most fundamental way to categorize crucible furnaces is by how they generate the immense heat required for melting materials. This choice impacts efficiency, cost, temperature control, and the types of materials that can be processed.
Fuel-Fired Furnaces
These furnaces use the combustion of fossil fuels to generate heat. Common fuels include natural gas, propane, or oil.
The fuel is mixed with air and ignited in a combustion chamber surrounding the crucible. The resulting hot gases transfer heat to the crucible walls, which in turn melts the charge inside. They are often favored for large-scale foundry operations.
Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces use electrical energy to generate heat, offering cleaner operation and more precise temperature control compared to fuel-fired models. They are further divided by their specific heating mechanism.
Resistance Furnaces
This is the most straightforward type of electric furnace. It works much like a common electric oven, using heating elements made from a high-resistance material.
When current passes through these elements, they become extremely hot, radiating heat to the crucible. This method offers excellent temperature stability and is common in laboratory settings and small-scale casting.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces are more technologically advanced. They use a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil that surrounds the crucible.
This generates a strong magnetic field that induces electrical currents directly within the conductive charge material or a graphite crucible. This internal resistance generates rapid, efficient, and clean heat from within the material itself.
Secondary Classification: Design and Application
Beyond the heat source, the physical design of the furnace dictates how it is used. This is less a formal classification and more a practical distinction based on workflow.
Lift-Out vs. Tilting Furnaces
This describes how the molten metal is removed from the furnace.
In a lift-out furnace, the crucible is manually or mechanically lifted out of the furnace body. The molten metal is then carried in the crucible to the mold for pouring. This design is simple and ideal for smaller batches or when melting multiple different alloys.
In a tilting furnace, the entire furnace body pivots on a mechanical axis to pour the molten metal directly into a ladle or mold. This design enhances safety and efficiency for large volumes of a single metal, as it avoids the need to transport a heavy, white-hot crucible.
The Role of the Crucible
While not a method of furnace classification, the crucible material is a critical component that defines the furnace's capability. The crucible must be selected based on the furnace's maximum temperature and the chemical properties of the metal being melted.
Common materials include graphite, silicon carbide, clay-graphite, and high-purity ceramics like alumina. Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to catastrophic failure or contamination of the melt.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every furnace type represents a set of compromises between cost, performance, and operational complexity.
Fuel-Fired: Cost vs. Control
Fuel-fired furnaces often have a lower capital cost and can be very powerful, making them suitable for bulk melting. However, they offer less precise temperature control and can introduce impurities from the combustion process into the melt.
Electric Resistance: Simplicity vs. Speed
Resistance furnaces are simple, reliable, and provide clean heat with precise control. Their main limitation is a slower melting speed compared to induction or large fuel-fired units, making them less ideal for high-throughput production.
Electric Induction: Efficiency vs. Complexity
Induction heating is the most energy-efficient and fastest method, providing very clean melts. This performance comes at the cost of higher initial investment and greater equipment complexity.
How to Select the Right Furnace Type
Your choice should be driven by your primary goal, scale of operation, and the materials you work with.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting, hobby work, or research with diverse alloys: A lift-out electric resistance furnace offers the best combination of control, cleanliness, and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A fuel-fired or electric induction tilting furnace will provide the necessary throughput and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity or reactive metals: An electric induction furnace, potentially with vacuum or inert atmosphere capabilities, is the superior choice for its speed and contamination-free heating.
Ultimately, classifying a furnace is the first step toward aligning the right technology with your specific operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Categories | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Fuel-Fired (Gas/Propane), Electric Resistance, Electric Induction | Foundry work, lab melting, high-purity applications |
| Design & Access | Lift-Out Crucible, Tilting Furnace | Small batch flexibility, high-volume production |
| Crucible Material | Graphite, Silicon Carbide, Clay-Graphite, Alumina | Compatible with specific metals and temperatures |
Selecting the right crucible furnace is critical for your lab's efficiency and success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-performance furnaces tailored to your specific melting needs—whether for research, small-scale casting, or high-purity applications. Contact our specialists today to discuss your requirements and discover the ideal furnace solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used for in a lab? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- Will brazing stick to cast iron? A Low-Heat Joining Solution for Crack-Free Repairs
- Does ceramic break with heat? The Real Culprit is Thermal Shock
- What temperature does steel liquify? Understanding the Melting Range for Your Applications
- Why refractory materials are used in furnaces? Ensure Safety, Efficiency, and Process Purity



















