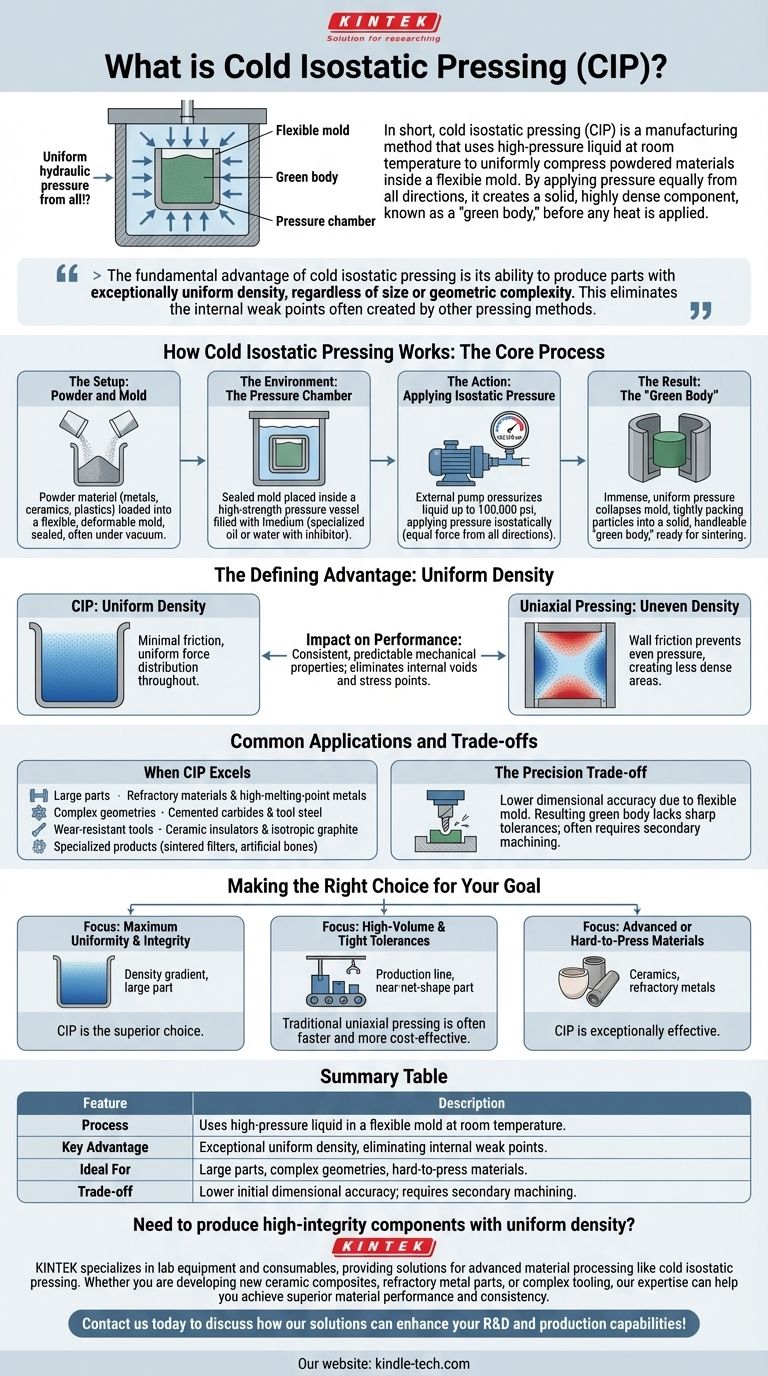
In short, cold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a manufacturing method that uses high-pressure liquid at room temperature to uniformly compress powdered materials inside a flexible mold. By applying pressure equally from all directions, it creates a solid, highly dense component, known as a "green body," before any heat is applied.
The fundamental advantage of cold isostatic pressing is its ability to produce parts with exceptionally uniform density, regardless of size or geometric complexity. This eliminates the internal weak points often created by other pressing methods.
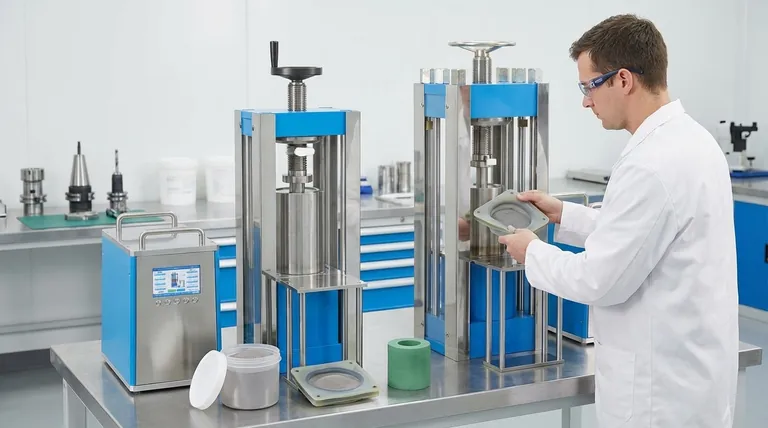

How Cold Isostatic Pressing Works: The Core Process
CIP is a relatively straightforward process valued for its consistency and the quality of the resulting component. It can be broken down into a few key stages.
The Setup: Powder and Mold
First, the powdered material—which can range from metals and ceramics to plastics—is loaded into a flexible, deformable mold, typically made of an elastomer like rubber. This mold is then sealed, often under a vacuum to remove trapped air.
The Environment: The Pressure Chamber
The sealed mold is placed inside a high-strength pressure vessel. This chamber is then filled with a liquid medium, usually a specialized oil or water mixed with a corrosion inhibitor.
The Action: Applying Isostatic Pressure
An external pump pressurizes the liquid within the chamber, with pressures that can reach as high as 100,000 psi. Because the pressure is transmitted through a fluid, it is applied to the mold isostatically—meaning with equal force from all directions.
The Result: The "Green Body"
The immense, uniform pressure collapses the flexible mold around the powder. This forces the individual particles to pack tightly together, mechanically locking to form a solid, handleable object known as a green body. This part is dense but has not yet undergone sintering (heating) to create final metallurgical bonds.
The Defining Advantage: Uniform Density
The primary reason to choose CIP over other powder compaction methods, like traditional uniaxial pressing, comes down to one critical factor: density.
Overcoming Wall Friction
In a conventional press, pressure is applied from one or two directions. Friction between the powder and the rigid die walls prevents pressure from being transmitted evenly, creating less dense areas within the part.
CIP avoids this entirely. Because the "walls" are a flexible mold pushed by liquid, there is minimal friction, allowing the compaction force to be distributed uniformly throughout the powder mass.
The Impact on Performance
This uniform density ensures that the final product will have consistent, predictable mechanical properties after sintering. It eliminates the internal voids and stress points that can lead to premature failure in components made with other methods.
Common Applications and Trade-offs
CIP is not a universal solution. Its unique characteristics make it ideal for some applications but less suitable for others.
When CIP Excels
This method is commonly chosen for parts that are too large to fit in conventional presses or have complex geometries. It is widely used for producing wear-resistant tools, metal forming dies, and components from high-performance materials like:
- Refractory materials and high-melting-point metals
- Cemented carbides and tool steel
- Ceramic insulators and isotropic graphite
- Specialized products like sintered filters and artificial bones
The Precision Trade-off
The key limitation of CIP is dimensional accuracy. Because the mold is flexible, the resulting green body does not have the sharp, precise tolerances of a part made in a rigid die. Consequently, components made via CIP often require secondary machining to achieve their final, precise dimensions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on the priorities of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum material uniformity and integrity: CIP is the superior choice for eliminating density gradients, especially in large parts or those with complex shapes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with tight initial tolerances: Traditional uniaxial pressing is often faster and more cost-effective, as it produces near-net-shape parts that require less finishing.
- If you are working with advanced or hard-to-press materials: CIP is an exceptionally effective method for compacting materials like ceramics and refractory metals that do not respond well to other methods.
Ultimately, cold isostatic pressing is a powerful tool for creating high-performance components where internal structural integrity is more critical than initial dimensional precision.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses high-pressure liquid in a flexible mold at room temperature. |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional uniform density, eliminating internal weak points. |
| Ideal For | Large parts, complex geometries, hard-to-press materials like ceramics and refractory metals. |
| Trade-off | Lower initial dimensional accuracy; parts often require secondary machining. |
Need to produce high-integrity components with uniform density?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for advanced material processing like cold isostatic pressing. Whether you are developing new ceramic composites, refractory metal parts, or complex tooling, our expertise can help you achieve superior material performance and consistency.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your R&D and production capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between wet bag and dry bag isostatic pressing? Flexibility vs. High-Volume Production
- What is the difference between isostatic pressing and uniaxial pressing? Choosing the Right Powder Compaction Method
- What role does an industrial-grade high-pressure manual screw pump play in an HHIP system? Achieve Precise Densification
- What is the meaning of isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Parts
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Preferred for Sulfide Solid Electrolytes? Maximize Your Ionic Conductivity
- What is cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- What is the cold isostatic press process? Create Uniform, High-Integrity Parts
- What is the purpose of stainless steel cans in the HIP treatment? Achieve Full Densification of AlFeTiCrZnCu Alloys



















