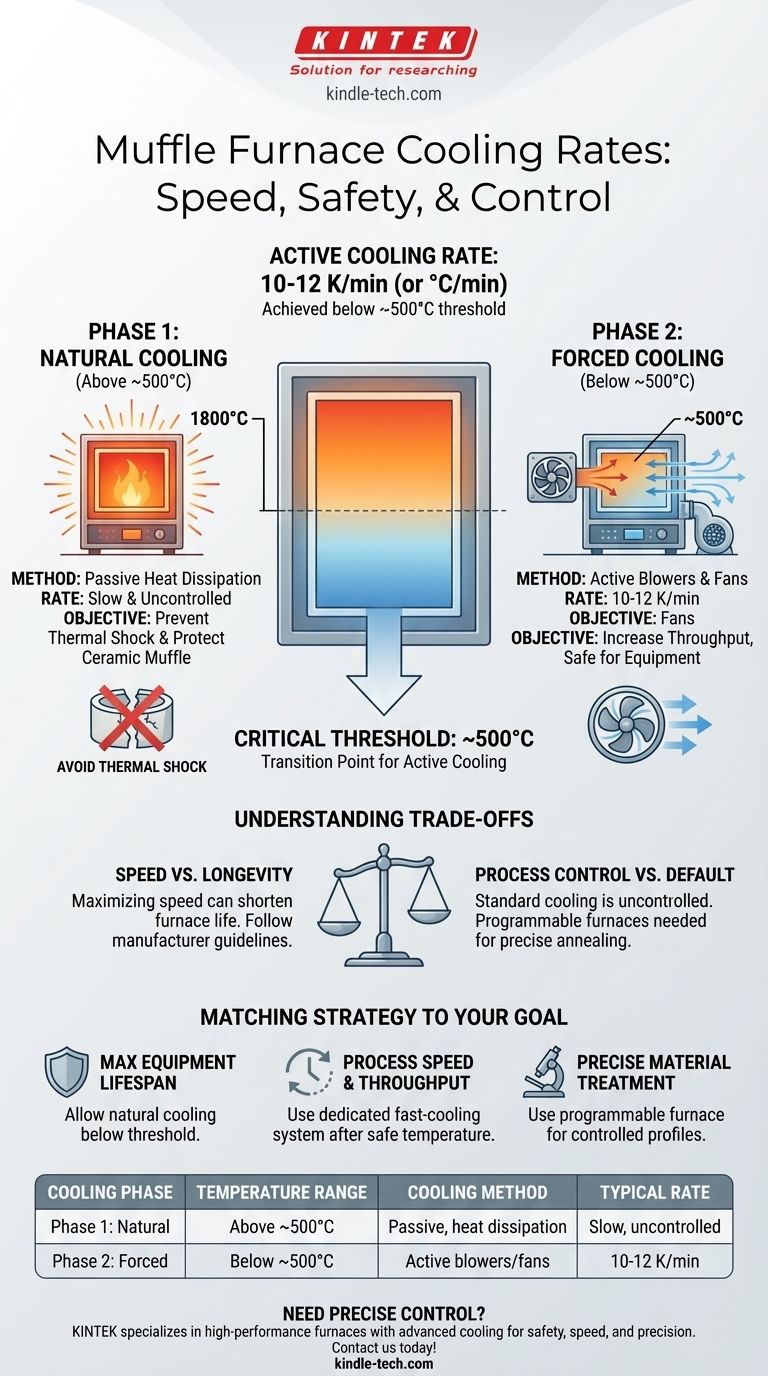
With an active cooling system, the typical cooling rate for a muffle furnace is between 10 to 12 K/min (or °C/min). However, this rate is only achievable once the furnace is below a critical temperature threshold, typically around 500°C, to prevent damaging the internal components from thermal shock.
The cooling rate of a muffle furnace is not a single, constant value. It is a two-stage process: a slow, natural cooling phase at very high temperatures to protect the equipment, followed by a faster, actively-cooled phase at lower temperatures to increase throughput.
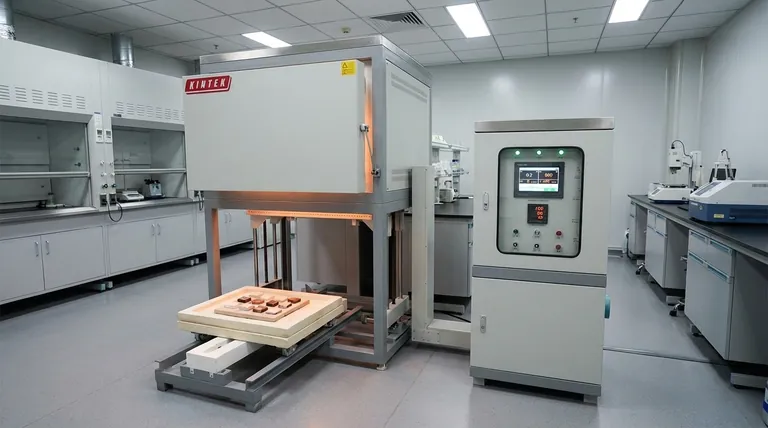

The Two Phases of Muffle Furnace Cooling
A muffle furnace's cooling process is intentionally designed to balance speed with the physical limitations of its materials. Attempting to cool a furnace from 1800°C too quickly would cause catastrophic failure.
Phase 1: Natural Cooling at High Temperatures
Above approximately 500°C, a muffle furnace is left to cool naturally. During this phase, the cooling rate is slow and dictated purely by the dissipation of heat into the surrounding environment.
There is no active cooling (e.g., blowers or fans) during this stage. This slow, passive process is essential to prevent thermal shock.
Phase 2: Forced Cooling at Lower Temperatures
Once the furnace's internal temperature drops to a safe level (e.g., 500°C), a fast-cooling system can be engaged.
This system typically uses blowers to introduce ambient air, which dramatically increases the rate of heat removal. It is in this phase that cooling rates of 10-12 K/min are achieved. This rate gradually decreases as the furnace approaches room temperature.
Why the 500°C Threshold is Critical
The inner chamber of a muffle furnace is made of refractory ceramic materials that are excellent at handling extreme heat but are brittle and susceptible to cracking if their temperature changes too rapidly.
Forcing cool air into a chamber at 1000°C or higher would create an extreme temperature gradient, causing the material to crack and destroying the furnace muffle. The 500°C threshold is a standard engineering compromise to protect the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The cooling strategy you use involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to effective and safe operation.
Speed vs. Equipment Longevity
The primary trade-off is between sample throughput and the lifespan of your furnace. While it may be tempting to find ways to cool the furnace faster from its peak temperature, doing so will inevitably shorten the life of the ceramic muffle and heating elements.
Following the manufacturer's recommended procedure for engaging active cooling is the single best way to protect your investment.
Process Control vs. Default Cooling
The natural, two-stage cooling curve of a standard furnace may not be suitable for all applications.
Processes like annealing metals or growing certain crystals require a slow, precisely controlled cooling rate. A standard furnace's cooling is uncontrolled; a programmable furnace is required to manage a specific downward temperature ramp.
Matching Cooling Strategy to Your Goal
Your application determines the right approach to cooling.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Always allow the furnace to cool naturally below the manufacturer's specified threshold (typically 500-600°C) before engaging any active cooling systems.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Invest in a furnace with a dedicated fast-cooling system and use it as intended—only after the furnace has reached its safe cooling temperature.
- If your primary focus is precise material treatment (e.g., annealing): A standard cooling rate is irrelevant; you need a furnace with a programmable controller that can execute a specific, controlled cooling profile.
Understanding that muffle furnace cooling is a deliberate, two-stage process is key to ensuring both equipment longevity and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Phase | Temperature Range | Cooling Method | Typical Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Natural Cooling | Above ~500°C | Passive, heat dissipation | Slow, uncontrolled |
| Phase 2: Forced Cooling | Below ~500°C | Active blowers/fans | 10-12 K/min |
Need precise control over your lab's heating and cooling cycles? KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces with advanced cooling systems designed to protect your equipment while maximizing throughput. Whether you require fast cooling for efficiency or programmable profiles for annealing, our solutions are tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the theory of calcination? Master Precise Thermal Decomposition for Your Materials
- What affects the melting point of a substance? Uncover the Key Factors & Forces
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What temperature should a muffle furnace be for ash content? Achieve Accurate Results with the Right Heat
- How do you perform calcination? Master Precise Thermal Treatment for Your Materials



















